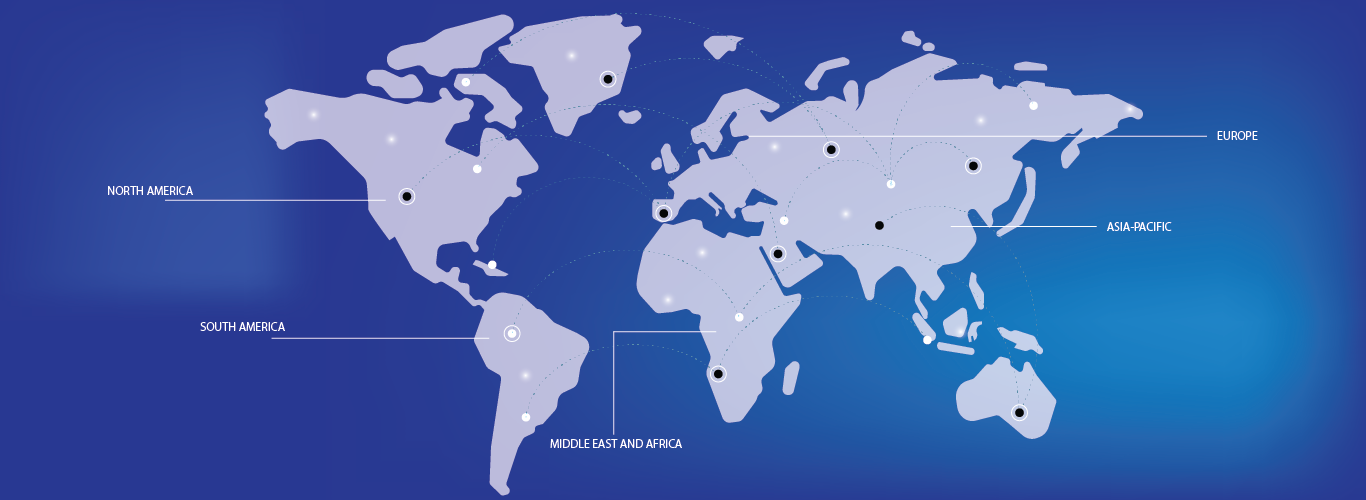
Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to make images of the human body (or parts of it) for a variety of clinical applications, including medical operations and diagnosis, as well as medical science, which includes the study of normal anatomy and function. It is a subset of biological imaging that includes radiography, endoscopy, thermography, medical photography, and microscopy in a broader sense. Measurement and recording techniques such as electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) are examples of medical imaging since they create data that can be represented as maps rather than images.