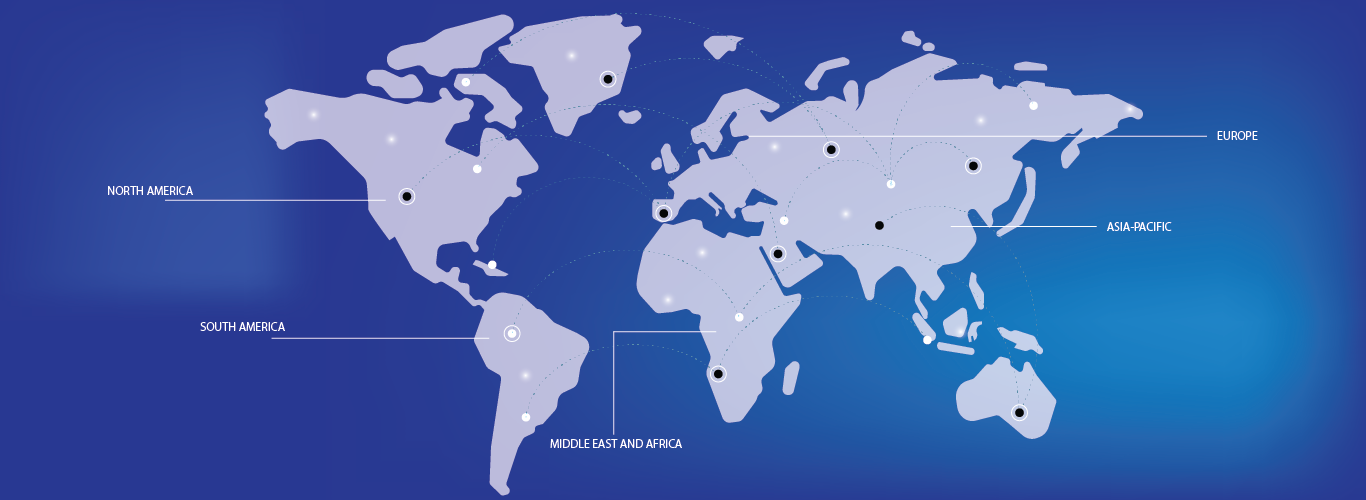
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) analysis involves using laser light to measure distances to the Earth's surface, producing highly accurate 3D models of environments. LiDAR systems emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for them to return after reflecting off objects. This data helps create detailed topographical maps, identify vegetation, model infrastructure, and monitor environmental changes. LiDAR is widely used in applications like forestry, urban planning, archaeology, and disaster management. By processing the reflected signals, LiDAR analysis generates high-resolution point clouds, which can be used for terrain modeling, contour mapping, and vegetation classification.