What is Smart Packaging?

The term "smart packaging," also referred to as "connected packaging," refers to packaging that makes use of distinctive barcodes, QR codes, or other digital identities to interact with customers, confirm product legitimacy, and trace a product's path. With the help of this unmatched technology, a once-simple box is transformed into a digital tool that offers both brand owners and consumers useful insights and data.
Retailers, manufacturers, customers, and digital channels can all be reached through smart packaging, which connects the real and digital worlds. By leveraging modern technology, packages can be more communicative, dynamic, personalized, and actualized rather than just being a simple container.
To know about the smart packaging market study in term of qualitative and quantitative research on present and what impact on future, driving factors driving the market demand in the near future, industry challenges, and market growth potential for smart packaging market kindly visit the below mention website link.
Types Of Smart Packaging Technology
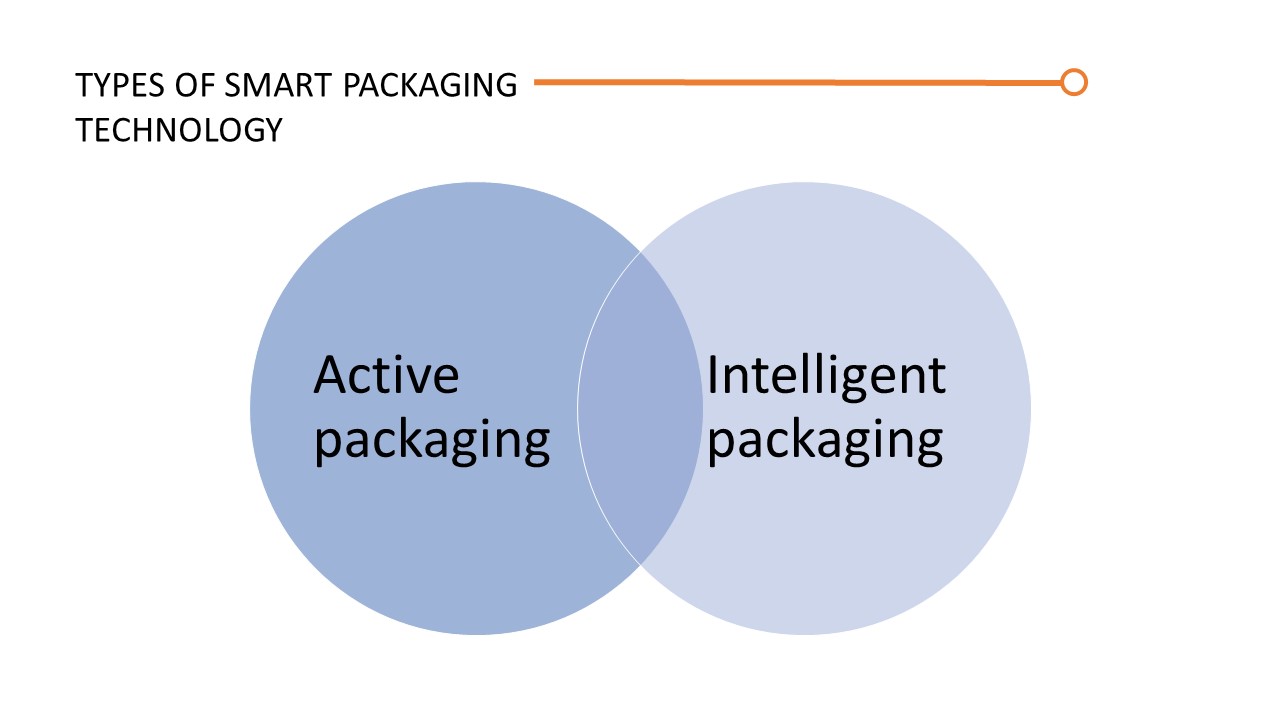
- Active Packaging: Packaging is referred to as active if it serves more purposes than simply containing or safeguarding an object. For instance, active packaging enhances the freshness or shelf life of food products by working in tandem with their contents.
Active packaging in this category uses oxygen absorbers and other filtering materials to keep food and beverage products fresh. Beverages in plastic containers, such as soda or beer, are another common example of oxygen absorbers. To assure quality control and add 3-6 months to the shelf life, the cap works as an oxygen absorber.
Connected packaging that can communicate with the outside world is referred to as intelligent packaging. Instead of concentrating solely on the packaging, intelligent packaging can also have diagnostic and indication capabilities.
Sensors and indicators are used in intelligent packaging to offer information about the contents during storage. As an illustration, color-changing food-related packaging may be used to signal contamination.
Packaging Enterprises Encounter Numerous Hurdles in the Current Dynamic Market Landscape
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: One of the significant challenges faced by packaging businesses is addressing sustainability and environmental concerns. There is an increasing demand for eco-friendly and recyclable packaging materials. Businesses need to find ways to reduce their environmental impact, develop sustainable packaging solutions, and incorporate circular economy principles
- Cost Management: Cost management is a constant challenge for packaging businesses. Fluctuating raw material prices, transportation costs, and labor expenses can impact profitability. Businesses need to find ways to optimize their supply chains, streamline operations, and identify cost-saving opportunities without compromising quality
- Regulatory Compliance: Packaging businesses must comply with various regulations and standards related to packaging materials, labeling, safety, and waste management. Keeping up with changing regulations and ensuring compliance across different regions can be complex and time-consuming. Failure to meet regulatory requirements can result in fines, product recalls, and reputational damage
- Consumer Preferences and Branding: Consumer preferences and market trends are constantly evolving, presenting challenges for packaging businesses. They need to stay updated on consumer demands, such as convenience, personalization, and sustainability, to design packaging that aligns with these preferences. Additionally, packaging plays a crucial role in branding and product differentiation, so businesses need to create visually appealing and engaging packaging designs
- Supply Chain Complexity: Packaging businesses often rely on a global supply chain involving multiple suppliers and partners. Managing this complex network can be challenging, especially considering factors such as lead times, quality control, logistics, and demand forecasting. Disruptions, such as natural disasters, geopolitical issues, or supply chain interruptions (such as the COVID-19 pandemic), can have a significant impact on operations
- Technological Advancements: The packaging industry is being transformed by technological advancements. Adopting and integrating new technologies, such as automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and digital printing, can be a challenge for traditional packaging businesses. They need to invest in technology, train employees, and adapt their processes to leverage the benefits these advancements offer
- E-Commerce Packaging: With the rise of e-commerce, packaging businesses face unique challenges related to online retail. They need to design packaging that ensures product safety during transit, minimizes waste, and provides an optimal unboxing experience. Balancing protection, cost-efficiency, and sustainability in e-commerce packaging can be a complex task
- Innovation and Differentiation: The packaging industry is highly competitive, requiring businesses to constantly innovate and differentiate themselves. Standing out in the market means developing new packaging solutions, incorporating smart packaging technologies, and staying ahead of the competition. However, innovation can be expensive and time-consuming, requiring substantial research and development investments
- Counterfeiting and Product Security: Counterfeiting is a persistent challenge for packaging businesses, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics. Developing secure packaging solutions, integrating anti-counterfeiting measures, and ensuring product authenticity are crucial to protecting brand reputation and consumer safety
- Changing Consumer Behaviors: Understanding and adapting to changing consumer behaviors is vital for packaging businesses. Consumer preferences, shopping habits, and expectations are continually evolving, driven by factors such as convenience, e-commerce, and sustainability. Keeping up with these changes and aligning packaging strategies accordingly can be a challenge.
Packaging businesses need to be proactive, flexible, and responsive to these challenges to thrive in the evolving market landscape.
Involvement of Several Critical Process Steps in the Smart Packaging
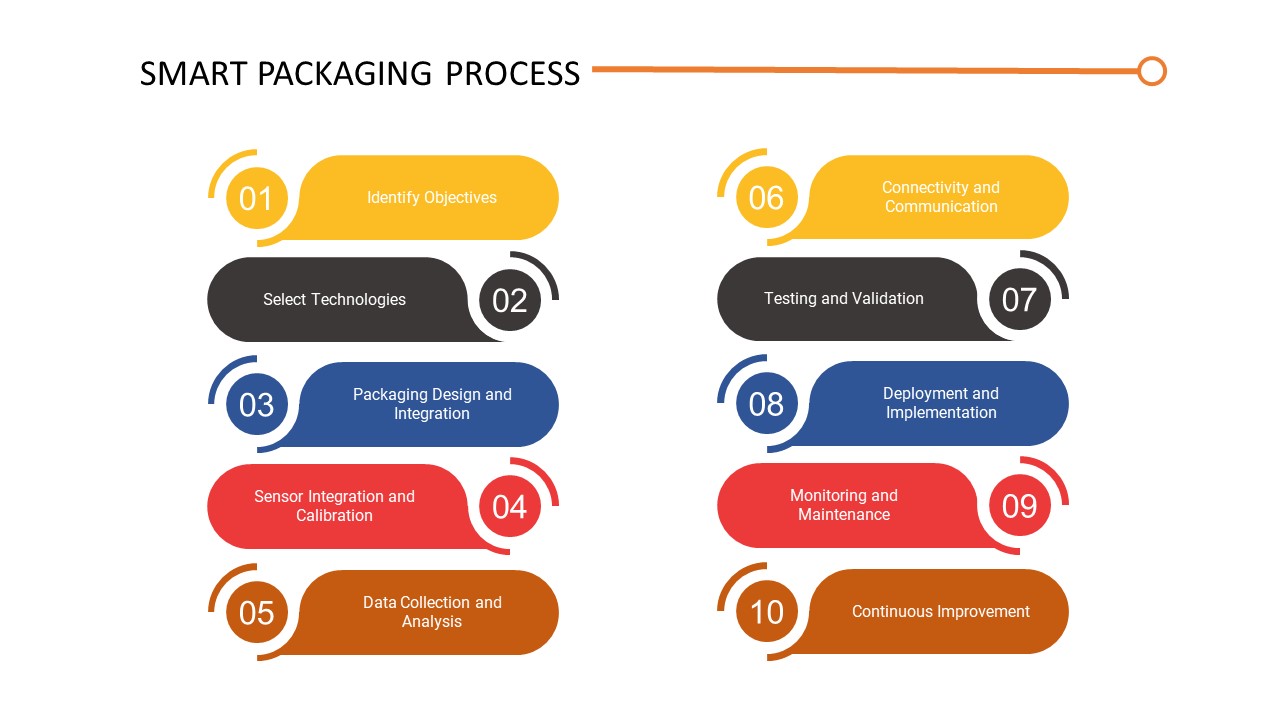
- Identify Objectives: Determine the specific goals and objectives for implementing smart packaging. This could include improving product safety, enhancing customer engagement, optimizing supply chain operations, or promoting sustainability. Clearly defining the objectives helps guide the implementation process
- Select Technologies: Research and select the appropriate smart packaging technologies that align with the identified objectives. This may involve technologies such as RFID, NFC, QR codes, sensors, or augmented reality. Factors that can be considered are cost, compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and the desired functionalities
- Packaging Design and Integration: Incorporate the selected smart packaging technologies into the packaging design. This may involve working with packaging designers, engineers, and technology providers to ensure seamless integration of the technologies into the packaging materials or labels. Consider factors such as durability, aesthetics, and user-friendliness
- Sensor Integration and Calibration: If sensors are part of the smart packaging solution, they need to be integrated and calibrated properly. This involves installing and configuring sensors to accurately measure and monitor relevant parameters such as temperature, humidity, or movement. Calibration ensures that the sensors provide accurate and reliable data
- Data Collection and Analysis: Establish mechanisms for collecting and analyzing the data generated by smart packaging technologies. This may involve implementing systems for data capture, storage, and analysis. Data analysis can provide valuable insights into consumer behavior, product performance, and supply chain optimization
- Connectivity and Communication: If applicable, ensure that the smart packaging solution is connected to appropriate networks or devices for data transmission and communication. This may involve integrating with cloud-based platforms, mobile applications, or backend systems to enable real-time data exchange and interaction with consumers or other stakeholders
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing and validation of the smart packaging solution to ensure its functionality, reliability, and compatibility with the intended use. This may involve simulated testing, real-world trials, and feedback from consumers or other stakeholders
- Deployment and Implementation: Once the smart packaging solution has been tested and validated, it is ready for deployment. This involves integrating smart packaging into the production and supply chain processes. Train relevant personnel on the usage and benefits of the smart packaging solution
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the performance of the smart packaging solution and conduct regular maintenance as needed. This includes monitoring sensor functionality, data accuracy, and addressing any issues or malfunctions that may arise
- Continuous Improvement: Evaluate the effectiveness of the smart packaging solution and seek opportunities for continuous improvement. Collect feedback from customers, track key performance indicators, and explore advancements in smart packaging technologies to stay updated and enhance the solution over time
By following these steps, companies can successfully implement smart packaging solutions that align with their objectives, enhance their operations, and provide value to customers.
Why Companies Prioritize Smart Packaging?
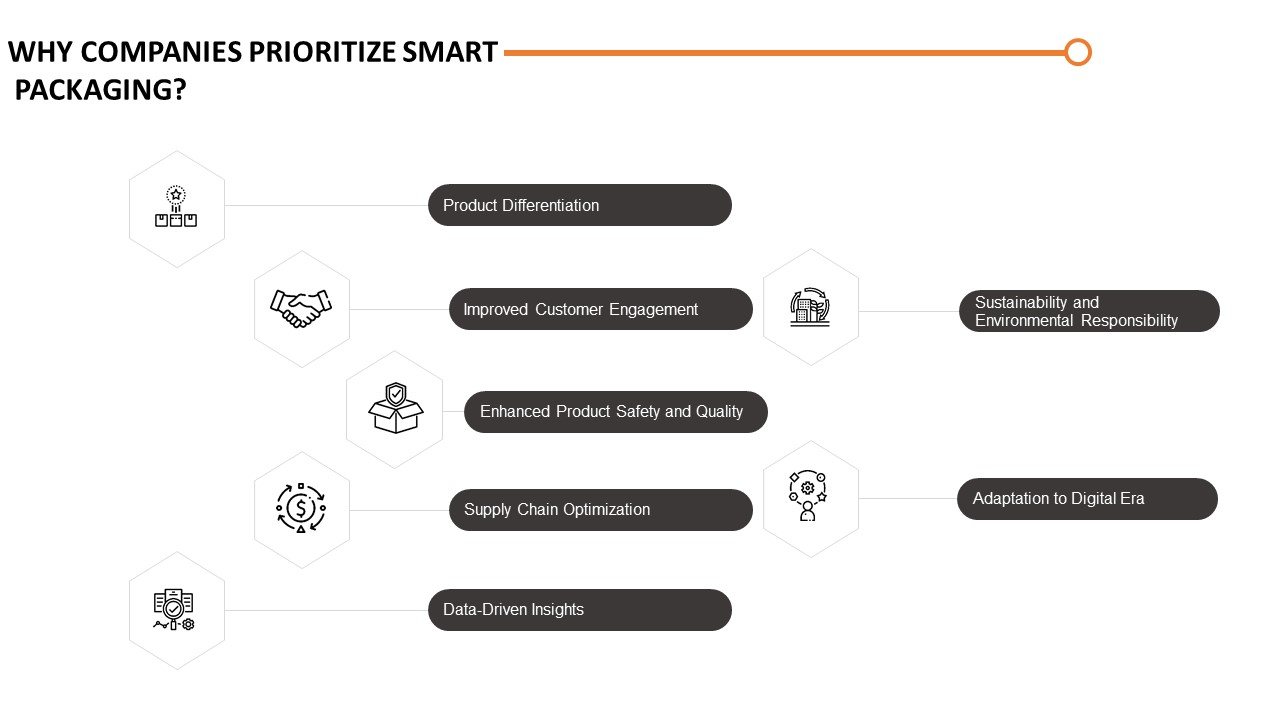
- Product Differentiation: Smart packaging sets a company apart from its competitors by offering unique and innovative features. It allows businesses to provide added value to consumers, enhancing the overall product experience and giving them a competitive edge in the market
- Improved Customer Engagement: Smart packaging enables companies to engage with consumers on a deeper level. Interactive features such as augmented reality, QR codes, or personalized messages create memorable experiences, strengthen brand loyalty, and foster long-term customer relationships
- Enhanced Product Safety and Quality: By incorporating sensors and indicators, smart packaging helps ensure that products are safe, fresh, and of high quality. This focus on product integrity reassures consumers and builds trust in the brand, leading to increased customer satisfaction and repeat purchases
- Supply Chain Optimization: Smart packaging technologies provide real-time visibility and traceability throughout the supply chain. This enables companies to streamline logistics, reduce costs, prevent theft or counterfeiting, and improve inventory management, ensuring products reach customers efficiently and on time
- Data-Driven Insights: Smart packaging generates valuable data about consumer behavior, product usage, and supply chain performance. By collecting and analyzing this data, companies can gain valuable insights that inform decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and identify opportunities for growth and innovation
- Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: Many companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices. Smart packaging allows businesses to optimize packaging materials, reduce waste, and promote eco-friendly initiatives. This aligns with consumer expectations and corporate social responsibility, enhancing brand reputation and attracting environmentally conscious customers
- Adaptation to the Digital Era: As technology continues to advance, companies need to adapt to the digital era. Smart packaging leverages technologies such as IoT, RFID, and mobile connectivity, integrating products into the digital ecosystem. This allows businesses to stay relevant, embrace digital transformation, and meet the evolving needs of tech-savvy consumers
By focusing on smart packaging, companies can gain a competitive advantage, enhance customer engagement, ensure product safety and quality, optimize supply chain operations, leverage data-driven insights, promote sustainability, and adapt to the digital age. These benefits contribute to business growth, customer loyalty, and long-term success.
Smart Packaging is Utilized by Various Types of Buyers

Several companies across different industries have adopted smart packaging solutions to enhance their products and operations. Here are some examples:
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G has embraced smart packaging technologies in various ways. For instance, they developed the Oral-B SmartSeries toothbrush, which connects to a mobile app through Bluetooth technology. The app provides real-time feedback on brushing habits, encouraging better oral hygiene
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola introduced smart packaging with its "Share a Coke" campaign. They printed individual names on their bottles to create a personal connection with consumers. This approach leveraged the power of personalization and engagement to enhance the overall customer experience
- Nestlé: Nestlé has been exploring smart packaging solutions for improved supply chain visibility and consumer engagement. They have implemented technologies such as QR codes and blockchain to provide detailed product information, traceability, and authentication to consumers
- Diageo: Diageo, a leading spirits company, has integrated NFC technology into its packaging. Consumers can tap their smartphones on the packaging to access interactive content, cocktail recipes, and brand information, creating an engaging and interactive experience
- Amcor: Amcor, a global packaging solutions provider, offers smart packaging solutions that incorporate sensors to monitor and ensure product freshness, integrity, and tamper-evidence. Their technologies help extend shelf life, reduce waste, and enhance consumer confidence
- Unilever: Unilever has explored smart packaging options in various product categories. For instance, they have developed connected packaging for their personal care products, allowing consumers to access information, tips, and personalized offers through QR codes or NFC technology
- Microsoft: Microsoft has utilized smart packaging for their gaming console, Xbox. The packaging includes NFC (Near-Field Communication) tags that can be scanned to download relevant content, connect with online communities, and access additional features and services
It's important to note that the adoption of smart packaging is not limited to these companies alone. Many other companies across industries such as food and beverage, healthcare, logistics, and fashion are incorporating smart packaging solutions to provide unique experiences, improve product safety, optimize supply chain operations, and enhance customer engagement.
To know more about the sustainable packaging research study in terms of qualitative and quantitative research on the present and what impact on future, driving factors driving the market demand in the near future, industry challenges, and market growth potential for sustainable packaging market kindly visit the below mention website link.
Smart Packaging Offers Significant Benefits to Customers in the Business Realm
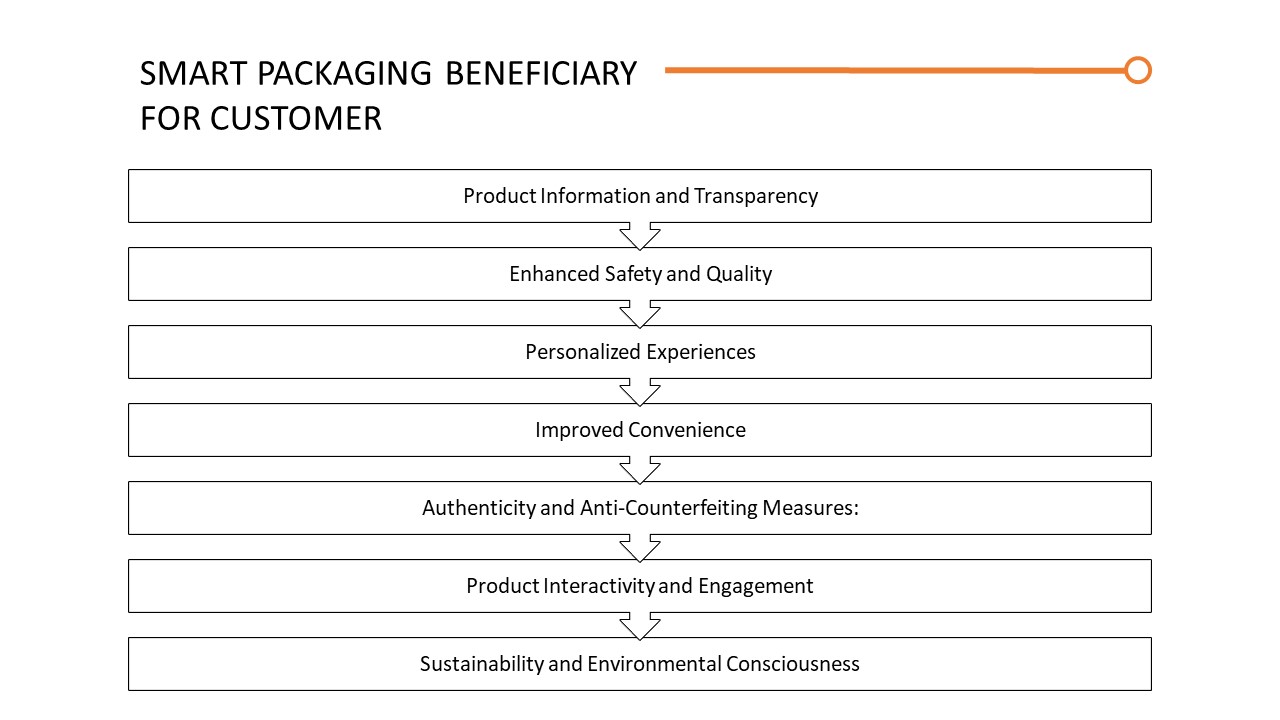
Smart packaging offers several benefits to customers, enhancing their overall experience and providing added value. Here are some ways in which smart packaging is beneficial for customers:
- Product Information and Transparency: Smart packaging allows customers to access detailed information about the product, such as ingredients, nutritional values, manufacturing processes, and certifications. This transparency helps customers make informed choices based on their preferences and dietary requirements.
- Enhanced Safety and Quality: Smart packaging technologies, such as temperature and freshness sensors, can ensure that perishable products, such as food and pharmaceuticals, are safe and of high quality. Customers can trust that the product they purchase is fresh, properly stored, and within its expiration date.
- Personalized Experiences: Smart packaging can offer personalized experiences through features like QR codes, NFC tags, or augmented reality. Customers can access customized content, recommendations, or promotions that cater to their specific needs and preferences, creating a more tailored and engaging experience.
- Improved Convenience: Smart packaging can enhance convenience for customers. For example, packaging with resealable or portion control features helps to maintain product freshness and reduce waste. Smart packaging can also provide easy access to product instructions, usage tips, or troubleshooting information, making it more convenient for customers to use and maintain the product.
- Authenticity and Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: Smart packaging incorporates technologies like QR codes, holograms, or RFID tags that allow customers to verify the authenticity of the product. This helps protect customers from counterfeit goods and ensures that they are purchasing genuine and safe products.
- Product Interactivity and Engagement: Smart packaging can create interactive experiences for customers, such as games, contests, or access to exclusive content. This engagement fosters a deeper connection with the brand and enhances the overall product experience.
- Sustainability and Environmental Consciousness: Many customers are increasingly concerned about sustainability. Smart packaging solutions that optimize materials, reduce waste, and promote eco-friendly practices resonate with environmentally conscious customers, providing them with a sense of contributing to a greener future.
In summary, smart packaging benefits customers by providing them with detailed product information, ensuring safety and quality, offering personalized experiences, enhancing convenience, enabling authentication, fostering engagement, and aligning with their sustainability preferences. These benefits contribute to a positive customer experience, increased satisfaction, and loyalty towards the brand.
Smart Packaging Is Making A Positive Environmental Impact In The Business Landscape
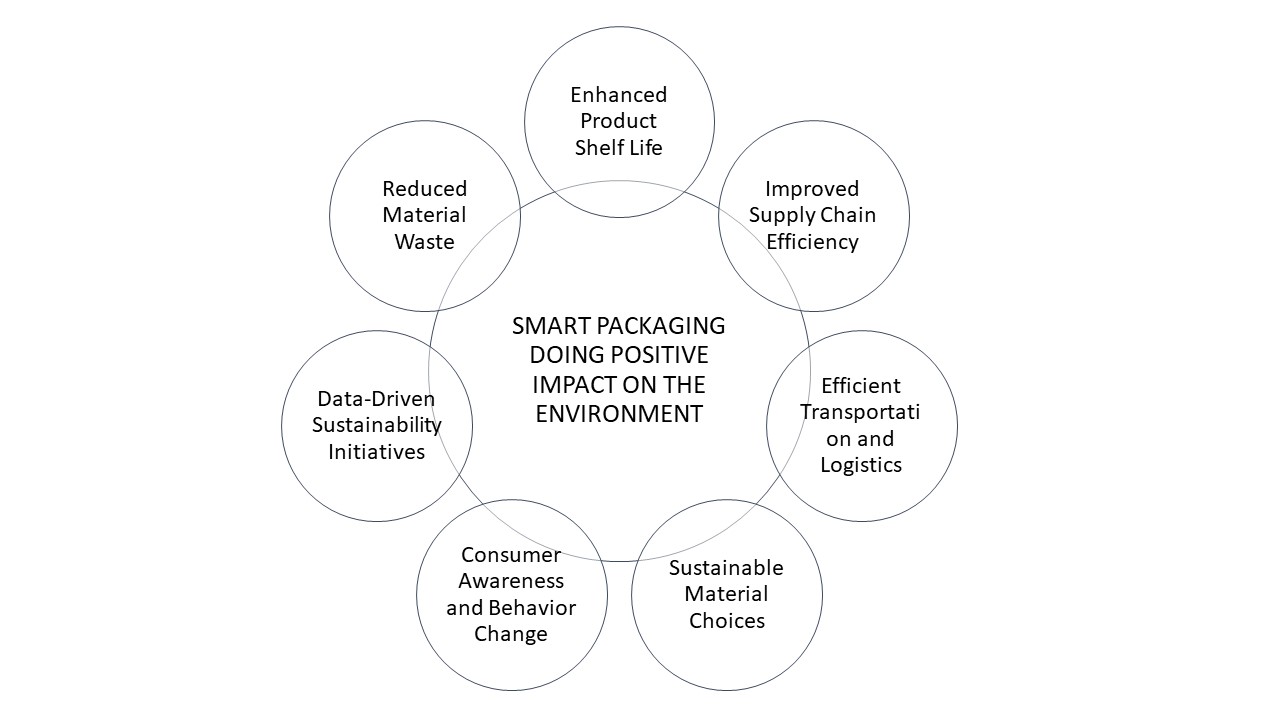
- Reduced Material Waste: Smart packaging technologies can optimize material usage, leading to reduced waste. By accurately measuring and portioning products, smart packaging minimizes excess packaging material, resulting in less overall waste generation.
- Enhanced Product Shelf Life: Smart packaging solutions, such as temperature and humidity sensors, can help maintain optimal storage conditions for perishable goods. This extends the shelf life of products, reducing the likelihood of spoilage and waste.
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Smart packaging with tracking technologies, like RFID or IoT sensors, enables real-time monitoring of product movement and storage conditions throughout the supply chain. This helps prevent product losses, damage, or expiration, reducing waste and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
- Efficient Transportation and Logistics: Smart packaging technologies provide data on package dimensions, weight, and content, enabling better optimization of transportation and logistics. This can lead to reduced fuel consumption, lower carbon emissions, and minimized environmental impact associated with transportation.
- Sustainable Material Choices: Many smart packaging solutions incorporate eco-friendly and sustainable materials. For example, companies are increasingly using biodegradable or recyclable materials in smart packaging designs, reducing the reliance on single-use plastics and promoting a circular economy.
- Consumer Awareness and Behavior Change: Smart packaging can raise consumer awareness about environmental issues by providing information about sustainable practices, recycling instructions, or eco-friendly alternatives. This awareness can lead to positive changes in consumer behavior, encouraging recycling, responsible disposal, and more sustainable consumption patterns.
- Data-Driven Sustainability Initiatives: Smart packaging generates valuable data on consumer behavior, product usage, and supply chain performance. Companies can analyze this data to identify opportunities for sustainability improvements, such as optimizing packaging designs, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impacts across the entire product lifecycle.
By incorporating smart packaging solutions, companies can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing material waste, improving supply chain efficiency, utilizing sustainable materials, promoting consumer awareness, and leveraging data for sustainability initiatives. These efforts help minimize the environmental footprint associated with packaging and contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Smart Packaging Can Play a Crucial Role in Building Brand Value in the Business
Smart packaging can play crucial role in building a brand by providing unique and engaging experiences for consumers. Here are some ways in which smart packaging can help in brand building:
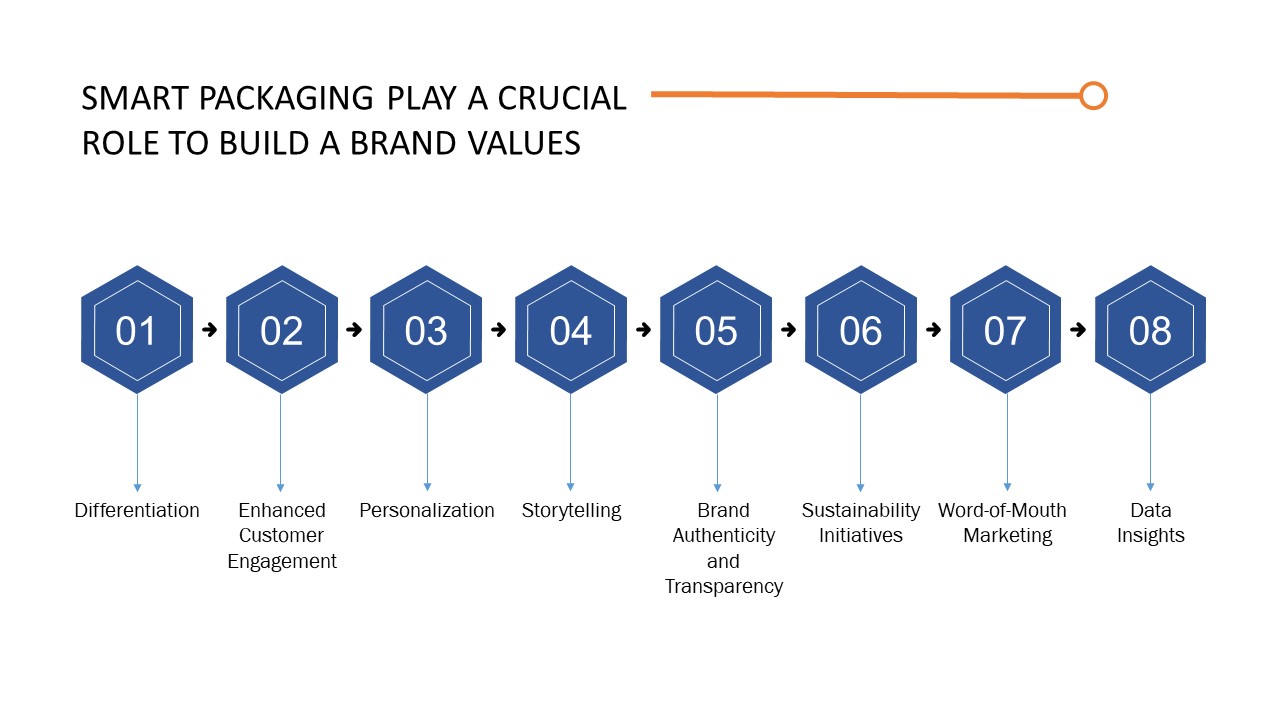
- Differentiation: Smart packaging sets your brand apart from competitors by offering innovative and interactive features. It creates a memorable and distinctive experience for consumers, making your brand stand out in a crowded market place.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Smart packaging enables direct interaction with consumers. Through technologies like augmented reality, QR codes, or NFC, consumers can access additional product information, personalized offers, and engaging content. This fosters a deeper connection between the brand and the consumer, increasing engagement and brand loyalty.
- Personalization: Smart packaging allows for personalized experiences by collecting data on consumer preferences and behaviors. This data can be leveraged to provide tailored recommendations, offers, or promotions. Personalization creates a sense of exclusivity and enhances the overall brand experience
- Storytelling: Smart packaging can be used as a storytelling medium to communicate the brand's values, mission, and product origins. By incorporating multimedia elements like videos or interactive graphics, brands can effectively convey their narrative and create an emotional connection with consumers
- Brand Authenticity and Transparency: Smart packaging can incorporate authentication technologies such as NFC or block chain, ensuring product authenticity and traceability. This enhances consumer trust by demonstrating the brand's commitment to quality, safety, and transparency
- Sustainability Initiatives: Smart packaging can support a brand's sustainability efforts by incorporating eco-friendly materials, providing recycling instructions, or promoting responsible consumption. Brands that prioritize sustainability can leverage smart packaging to communicate their environmental commitment and attract eco-conscious consumers
- Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Memorable and innovative smart packaging experiences can generate positive word-of-mouth marketing. Consumers are likely to share their unique interactions with the packaging on social media, leading to increased brand exposure and awareness
- Data Insights: Smart packaging generates valuable data on consumer behavior, preferences, and usage patterns. Brands can analyze this data to gain insights into consumer trends, refine marketing strategies, and develop new product offerings, ultimately strengthening the brand's position in the market
It's important to ensure that the implementation of smart packaging aligns with the brand's identity and adds value to the consumer experience. Additionally, brands should communicate the benefits and features of smart packaging effectively to create awareness and maximize its impact on brand building.
The Future Outlook for Smart Packaging in the Business Arena
The future of smart packaging holds significant potential for revolutionizing various industries and enhancing consumer experiences. Here are some possible advancements
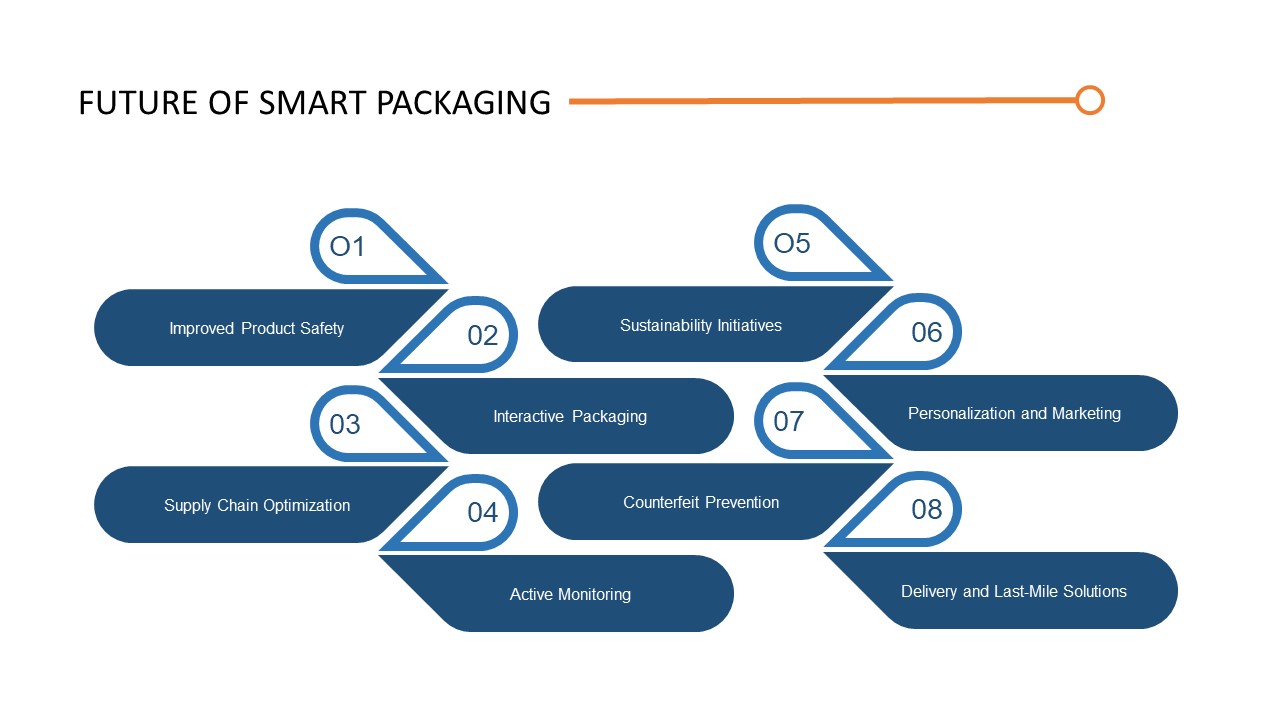
- Improved Product Safety: Smart packaging can incorporate sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors. This enables real-time tracking and alerts for potential issues like spoilage or contamination, ensuring product safety and reducing waste.
- Interactive Packaging: With the integration of augmented reality (AR) and near-field communication (NFC) technologies, smart packaging can provide interactive experiences. Consumers can access additional product information, personalized recommendations, and even play games or watch videos related to the product.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Smart packaging can enable enhanced traceability throughout the supply chain. By integrating technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) or QR codes, companies can efficiently track and monitor products from manufacturing to distribution, improving inventory management and minimizing losses.
- Active Monitoring: Smart packaging can actively monitor product usage and provide real-time updates. For example, pharmaceutical packaging can remind patients to take their medication and track adherence. Similarly, food packaging can provide expiration date notifications and suggest recipe ideas based on the contents.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Smart packaging can contribute to sustainability efforts by integrating eco-friendly materials and reducing waste. For instance, it can use biodegradable or compostable materials, provide portion control to minimize overconsumption, and offer smart recycling instructions.
- Personalization and Marketing: Smart packaging can enable personalized marketing campaigns by utilizing data analytics. It can collect consumer preferences, track usage patterns, and provide targeted promotions or recommendations. This can enhance customer engagement and brand loyalty.
- Counterfeit Prevention: Smart packaging can incorporate anti-counterfeiting measures, such as tamper-evident seals or embedded authentication technologies like blockchain. This ensures product authenticity and protects consumers from purchasing counterfeit goods.
- Delivery and Last-Mile Solutions: Smart packaging can streamline the delivery process and enhance the last-mile experience. It can include features like built-in tracking, temperature control for perishable goods, or even autonomous delivery capabilities, ensuring efficient and secure delivery.
It's important to note that while these advancements hold significant potential, the actual adoption and implementation of smart packaging will depend on various factors, including technological advancements, cost-effectiveness, consumer acceptance, and regulatory considerations.
3 “C” Analysis
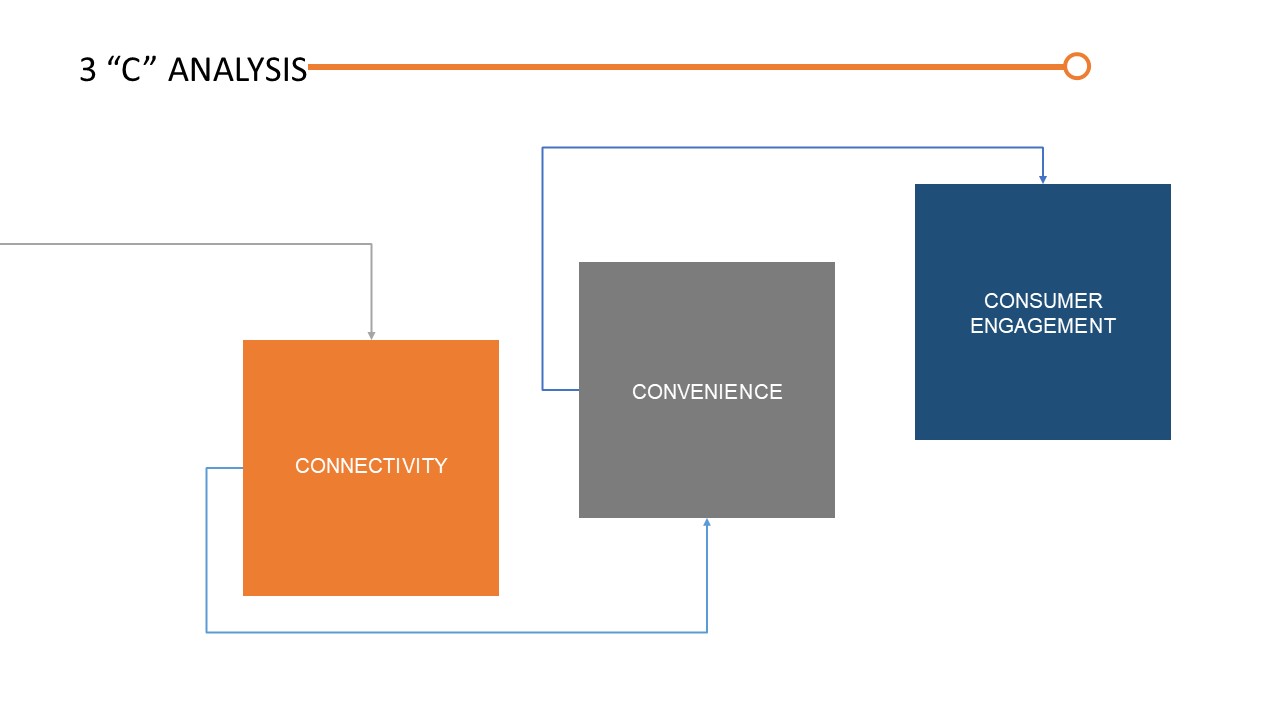
Connectivity:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart packaging utilizes IoT technologies to connect physical products with the digital world. It enables real-time data collection, communication, and interaction between the packaging and external devices or networks. Connectivity enhances supply chain visibility, enables product tracking, and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Sensor Integration: Smart packaging incorporates various sensors to monitor and collect information about the product's condition, such as temperature, humidity, or freshness. These sensors provide valuable data that can be used to ensure product quality, optimize logistics, and enhance safety.
- Wireless Communication: Smart packaging often leverages wireless communication technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) or NFC (Near Field Communication) to enable seamless interactions between the packaging and external devices, such as smartphones or scanners.
Convenience:
- User-Friendly Design: Smart packaging should be designed with ease of use in mind. It should be intuitive and require minimal effort or technical knowledge from consumers to access its functionalities
- Time and Effort Savings: Smart packaging solutions aim to simplify and streamline processes for consumers. For example, it can offer convenient ways to open, reseal, or dispense products, reducing the need for additional tools or packaging accessories
- On-the-Go Accessibility: In today's fast-paced lifestyle, smart packaging can cater to the needs of on-the-go consumers. It can provide portability, portion control, and easy consumption, enabling convenience in various settings like travel or outdoor activities
Consumer Engagement:
- Interactive Elements: Smart packaging can engage consumers through interactive features such as augmented reality (AR), QR codes, or personalized messages. These elements enhance the user experience and create a deeper connection between the consumer and the product or brand
- Product Information and Transparency: Smart packaging can provide consumers with detailed product information, such as ingredients, origin, or sustainability credentials. This transparency builds trust and allows consumers to make informed purchasing decisions aligned with their preferences or values
- Customized Experiences: Smart packaging can enable personalized experiences through tailored content or offers. By leveraging consumer data and preferences, companies can deliver targeted promotions, recommendations, or loyalty programs, enhancing consumer engagement and brand loyalty
Considering these three "C" factors helps businesses in developing smart packaging solutions that prioritize connectivity, convenience, and consumer engagement. By focusing on these aspects, companies can create innovative packaging experiences that add value to both consumers and the overall brand proposition.
The Transformation of Smart Packaging in the Logistics Sector

Smart packaging plays a crucial role in the logistics industry by integrating advanced technologies to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and provide better tracking and monitoring capabilities. Here are several ways in which smart packaging helps in the logistics industry:
Influence of Smart Packaging on the Logistics Industry
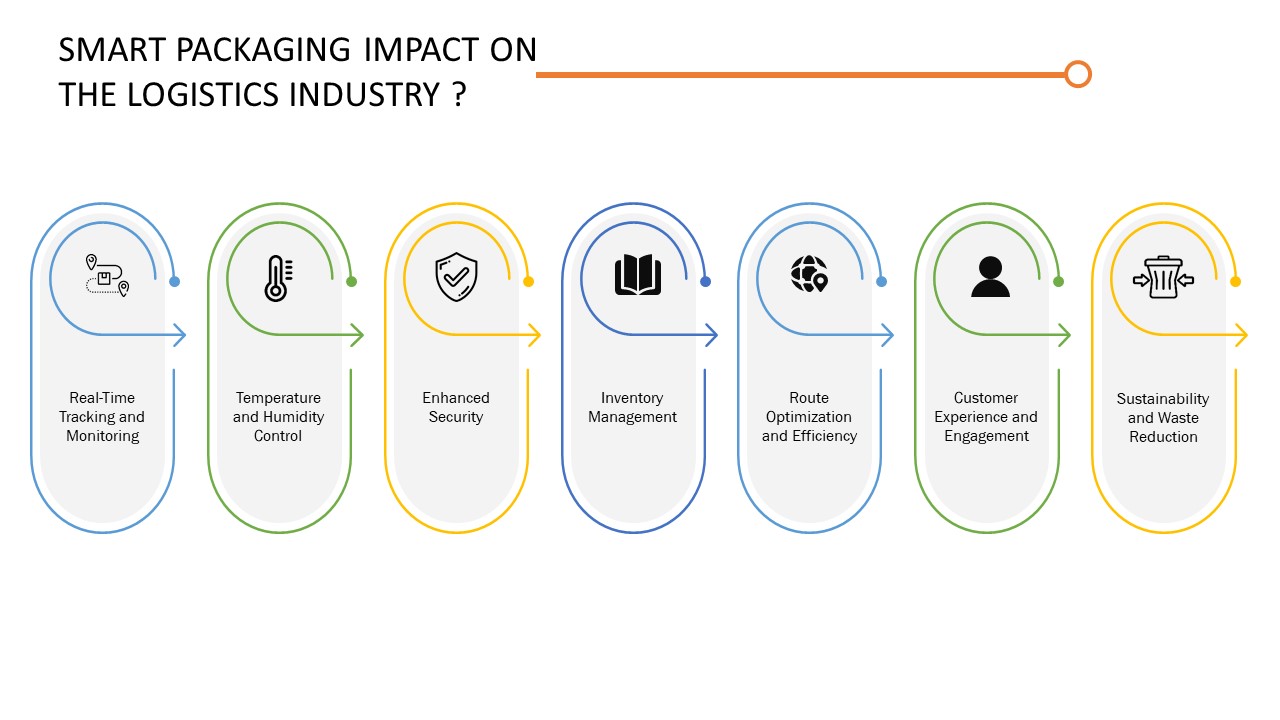
- Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring: Smart packaging incorporates technologies like RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), GPS (Global Positioning System), and sensors to enable real-time tracking and monitoring of packages throughout the supply chain. This allows logistics companies to have complete visibility and control over the location and condition of the packages, reducing the risk of loss, theft, or damage.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Smart packaging can include sensors that monitor and maintain specific temperature and humidity levels for temperature-sensitive or perishable goods. This is particularly important for industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages, where maintaining the right conditions is crucial. Monitoring the environmental conditions in real-time helps prevent spoilage, quality degradation, and regulatory compliance issues.
- Enhanced Security: Smart packaging incorporates features like tamper-evident seals, authentication tags, or anti-counterfeiting measures to ensure the integrity and security of goods during transit. Any tampering attempts can be detected and reported, reducing the risk of theft and unauthorized access.
- Inventory Management: Smart packaging can be equipped with sensors that automatically update inventory systems when packages are received, shipped, or moved. This streamlines the inventory management process, enabling real-time inventory visibility and reducing the likelihood of stockouts or overstocking.
- Route Optimization and Efficiency: By leveraging data from smart packaging, logistics companies can analyze shipping patterns, identify bottlenecks, and optimize routes. This helps streamline logistics operations, reduce transportation costs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Customer Experience and Engagement: Smart packaging can provide interactive features like QR codes or augmented reality (AR) capabilities, enabling customers to access additional product information, promotions, or personalized messages. This enhances the customer experience and increases engagement, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Sustainability and Waste Reduction: Smart packaging can facilitate sustainable practices by optimizing package sizes, reducing excess materials, and promoting recycling. By monitoring and optimizing packaging usage, logistics companies can minimize waste, reduce carbon footprint, and contribute to environmental conservation efforts.
Overall, smart packaging enables logistics companies to make data-driven decisions, streamline operations, enhance security, and provide a better customer experience. By leveraging advanced technologies, it helps create a more efficient and sustainable supply chain ecosystem.
To know more about the global temperature controlled packaging solutions research study in term of qualitative and quantitative research on present and what impact on future, driving factors driving the market demand in the near future, industry challenges, and market growth potential for temperature controlled packaging market kindly visit the below mention website link.
Conclusion
In the packaging industry, smart packaging represents a paradigm shift. It is an essential instrument for firms/companies in the contemporary market because of its capacity to increase product safety, increase consumer interaction, and promote sustainability. Smart packaging is positioned to revolutionize industries and contribute to a more effective and environmentally sustainable future as technology develops. However, for it to be widely used, issues including cost, privacy worries, and infrastructure requirements must be resolved. Smart packaging is a promising and fascinating area for both businesses and consumers despite these obstacles.