Global Biochar Market Segmentation, Technology (Pyrolysis, Gasification, and Hydrothermal Carbonization) Feedstock (Agricultural Residues, Forestry and Wood Waste, Animal Manure, Biomass Plantation, and Others), End Use (Soil Conditioner, Animal Farming, Electricity Generation, Heat Generation, Water Treatment, Building, Household, Textiles, and Others) – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2032
Biochar Market Analysis
The biochar market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of its environmental benefits and its role in sustainable agriculture. Biochar, a form of charcoal produced by pyrolyzing organic material, enhances soil fertility, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and helps with waste management. The market is fueled by demand in agriculture, where biochar is used to improve soil quality and boost crop yields. In addition, biochar is gaining traction in carbon sequestration efforts, as it stores carbon for long periods. Government initiatives supporting climate change mitigation and rising interest in renewable energy further contribute to the market's expansion.
Biochar Market Size
Global biochar market is expected to reach USD 3,790.06 million by 2032 from USD 727.31 million in 2024, growing with a substantial CAGR of 23.2% in the forecast period of 2025 to 2032. In addition to the insights on market scenarios such as market value, growth rate, segmentation, geographical coverage, and major players, the market reports curated by the Data Bridge Market Research also include import export analysis, production capacity overview, production consumption analysis, price trend analysis, climate change scenario, supply chain analysis, value chain analysis, raw material/consumables overview, vendor selection criteria, PESTLE Analysis, Porter Analysis, and regulatory framework.
Biochar Market Trends
“Increasing Awareness of its Environmental Benefits”
Increasing awareness of biochar's environmental benefits is driving its adoption globally. Biochar, produced by pyrolyzing organic waste, helps reduce carbon emissions by sequestering carbon in the soil for long periods. It also improves soil health, enhancing fertility and water retention, which supports sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, biochar aids in waste management by converting agricultural residues into a valuable product. As awareness grows, more industries and farmers are recognizing its potential to mitigate climate change, improve food security, and promote sustainable farming practices. Educational campaigns and government initiatives are helping accelerate the adoption of biochar as an eco-friendly solution.
Report Scope and Market Segmentation
|
Attributes
|
Biochar Ingredients Key Market Insights
|
|
Segments Covered
|
|
|
Countries Covered
|
U.S., Canada, and Mexico, Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Switzerland, Turkey, Belgium, Netherlands and Rest of Europe, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Australia & New Zealand and Rest of Asia-Pacific, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., Egypt, Israel and Rest of Middle East and Africa
|
|
Key Market Players
|
Biochar Now (U.S.), Oregon Biochar Solutions (U.S.), Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation (U.S.), Carbon Gold Ltd (U.K.), Swiss Biochar (Switzerland), Pacific Coast Carbon (U.S.), LLC, Standard Biocarbon Corporation (U.S.), Genesis Enterprises, Inc (U.S.), WAKEFIELD BIOCHAR (U.S.), Carbonis (Germany), Arstaeco (India), Black Owl Biochar (U.S.), PYROPOWER (Netherlands), Terra Char (U.S.), American BioChar Company (U.S.), Bioforcetech Corp. (U.S.), Green Man Char (Australia), MASH Makes (India), ARTi (U.S.), and Zhengzhou kelin water purification material co.,ltd. (China)
|
|
Market Opportunities
|
|
|
Value Added Data Infosets
|
In addition to the insights on market scenarios such as market value, growth rate, segmentation, geographical coverage, and major players, the market reports curated by the Data Bridge Market Research also include import export analysis, production capacity overview, production consumption analysis, price trend analysis, climate change scenario, supply chain analysis, value chain analysis, raw material/consumables overview, vendor selection criteria, PESTLE Analysis, Porter Analysis, and regulatory framework.
|
Biochar Market Definition
Biochar is a form of charcoal produced by heating organic material, such as agricultural waste, in the absence of oxygen through a process called pyrolysis. This results in a stable, carbon-rich substance that can be used to improve soil quality, enhance crop yields, and sequester carbon. Biochar is valued for its ability to retain nutrients, improve water retention, and reduce soil acidity, making it beneficial for sustainable agriculture. Additionally, it helps mitigate climate change by storing carbon in the soil for long periods, preventing the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Biochar also aids in waste management.
Biochar Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Rising Demand For Sustainable Agricultural Practices
The rising demand for sustainable agricultural practices is a key driver behind the growing adoption of biochar in agriculture. As the global population increases and the effects of climate change intensify, there is an urgent need for farming practices that can improve crop yields, enhance soil health, and reduce environmental impact. Traditional farming methods often rely heavily on chemical fertilizers and intensive irrigation, leading to soil degradation, reduced biodiversity, and higher greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, biochar offers a promising alternative by promoting long-term soil fertility while addressing several environmental concerns.
Biochar, a stable form of carbon produced by heating organic material in a low-oxygen environment (pyrolysis), has shown multiple benefits for agricultural soils. When applied to soil, biochar enhances its structure, improves water retention, and increases nutrient availability. This results in healthier crops and reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, which are costly and contribute to soil acidification and pollution. Moreover, biochar can sequester carbon in the soil for centuries, mitigating the effects of greenhouse gas emissions.
The growing awareness of the environmental and economic benefits of biochar has spurred its adoption in sustainable farming practices. Governments, environmental organizations, and agricultural stakeholders are increasingly promoting biochar as a tool for climate-smart agriculture. Additionally, biochar production from agricultural and forestry waste offers a value-added solution to waste management, making it a versatile and circular solution for farmers. The increasing demand for organic and eco-friendly food products further reinforces the market potential for biochar in agriculture, as it aligns with consumers' preferences for sustainably grown food. Consequently, biochar is becoming an essential component of modern, sustainable farming systems aimed at boosting productivity while minimizing ecological footprints.
- Government Policies Promoting Carbon Sequestration and Climate Mitigation
Government policies promoting carbon sequestration and climate mitigation play a crucial role in the growth of the biochar market. As nations increasingly recognize the urgency of addressing climate change, there is a strong push for policies that incentivize carbon capture and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Biochar, a key carbon sequestration method, fits squarely into these efforts due to its ability to store carbon in the soil for long periods, potentially offsetting a significant portion of global CO2 emissions.
Governments around the world have begun to incorporate carbon sequestration strategies into their climate action plans, with biochar often featured as a promising solution. For example, in the European Union and the United States, policies that promote sustainable agricultural practices and carbon storage through soil amendments are gaining traction. These policies may include tax incentives, grants, and subsidies for farmers and landowners who adopt carbon sequestration technologies such as biochar application.
In addition to financial incentives, carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, encourage industries to reduce their carbon footprints. By assigning a cost to carbon emissions, these policies indirectly create demand for carbon removal technologies like biochar, which can be used to offset emissions and earn carbon credits. This has led to the development of carbon markets where biochar producers can potentially generate revenue by selling carbon credits, further supporting the economic viability of biochar production.
International climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, have also set ambitious targets for reducing global emissions, prompting governments to explore and fund innovative solutions for carbon capture. As these policies evolve, the biochar market is expected to benefit from increased research funding, regulatory support, and a growing emphasis on climate mitigation strategies.
Opportunities
- Expanding Agricultural Applications For Improved Soil Fertility And Productivity
The expanding agricultural applications for biochar to improve soil fertility and productivity are significant drivers of growth for the global biochar market. As farmers and agricultural businesses face challenges related to soil degradation, declining fertility, and environmental sustainability, biochar has emerged as a highly effective, eco-friendly solution. Biochar, when added to soil, helps enhance its structure and nutrient content. The porous nature of biochar increases the soil’s water retention capacity, making it particularly beneficial in regions with arid or water-scarce conditions. This enhanced water retention also helps mitigate drought effects, improving crop yields during dry periods. Furthermore, biochar acts as a reservoir for nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth. By improving nutrient retention, biochar reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can be both costly and harmful to the environment.
Biochar’s alkaline nature can also help neutralize acidic soils, improving the availability of nutrients and creating a more favorable environment for plant growth. This makes it especially useful for soils that are overly acidic due to heavy rainfall or overuse of synthetic fertilizers. As a soil amendment, biochar has been shown to improve crop productivity by increasing nutrient cycling, microbial activity, and root development. The increased microbial activity helps break down organic matter and release nutrients more efficiently, ensuring plants have access to a balanced supply of nutrients. Additionally, biochar’s impact on soil structure encourages deeper root penetration, allowing plants to access nutrients and water from a larger volume of soil.
In agriculture, the growing focus on sustainability and carbon sequestration has also driven biochar’s adoption. Biochar acts as a carbon sink, storing carbon in the soil for hundreds to thousands of years, thus contributing to climate change mitigation. This dual benefit—improving soil fertility while sequestering carbon—aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Innovations In Biochar Applications
Beyond its well-known agricultural applications, biochar is increasingly being recognized for its diverse potential in various industries, driving the growth of the global biochar market. These innovations extend biochar’s benefits into environmental remediation, energy production, water treatment, and even construction materials, positioning it as a versatile and sustainable solution to pressing global challenges. Biochar’s high surface area and porous structure make it an excellent adsorbent for pollutants. It has been successfully used in the treatment of wastewater, removing heavy metals, organic compounds, and toxins. Biochar's ability to trap harmful chemicals and improve water quality has led to its adoption in both industrial and municipal wastewater treatment facilities, helping mitigate water contamination issues.
Biochar's carbon-rich composition makes it an effective tool for long-term carbon storage. As a stable form of carbon, biochar can sequester carbon in soils for hundreds or even thousands of years, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. This has increased its appeal in carbon credit markets, where it can be used to offset greenhouse gas emissions, thus driving investment in biochar production. Biochar can be integrated into bioenergy systems, particularly in the form of biochar pellets or briquettes for heat generation. When produced through pyrolysis, biochar itself can be used as a renewable energy source for heating or electricity generation, offering an alternative to fossil fuels. It also improves the energy efficiency of biomass combustion by reducing smoke emissions, making biochar-based fuels cleaner than traditional wood or coal.
Recent innovations have explored using biochar as an additive in concrete, bricks, and other construction materials. Incorporating biochar into these materials can enhance their insulation properties, reduce their carbon footprint, and improve their overall strength. The use of biochar in construction supports the trend towards sustainable building practices and green construction technologies.
Restraints/Challenges
- Limited Awareness and Education on Biochar Benefits
Limited awareness and education about biochar's benefits are significant challenges hindering its widespread adoption across various sectors, including agriculture, environmental management, and climate change mitigation. Despite its potential to improve soil health, sequester carbon, and reduce waste, many stakeholders—such as farmers, landowners, policymakers, and the general public—remain unfamiliar with biochar or its advantages. This lack of awareness can slow the transition to more sustainable practices and prevent biochar from reaching its full potential.
In the agricultural sector, biochar is recognized for its ability to enhance soil fertility, improve water retention, and increase crop yields, particularly in nutrient-poor or degraded soils. However, many farmers are unaware of its potential benefits and may be hesitant to adopt biochar due to unfamiliarity or concerns about its effectiveness. The lack of information about proper application methods and the long-term advantages of biochar often results in a reluctance to invest in its use, especially given the financial constraints faced by smallholders and rural communities.
Similarly, policymakers and environmental professionals may not fully understand the role biochar can play in carbon sequestration. Biochar’s ability to lock carbon in a stable form for hundreds to thousands of years presents a cost-effective means of mitigating climate change, but this message has not been widely communicated or integrated into national and international climate policies. As a result, biochar is often overlooked in favor of other carbon removal technologies.
To address these challenges, increased education and outreach are essential. This can include training programs, workshops, and informational campaigns targeted at farmers, environmentalists, policymakers, and the public. Universities, research institutions, and industry groups can collaborate to conduct studies and share data that demonstrate the effectiveness of biochar. Raising awareness and educating stakeholders about the long-term economic and environmental benefits of biochar will be critical to its broader adoption.
- Lack of standardization and quality control in biochar production processes
The lack of standardization and quality control in biochar production processes presents a significant challenge to the global biochar market. Biochar, a form of charcoal produced through the pyrolysis of organic materials, has gained attention for its potential in carbon sequestration, soil enhancement, and waste management. However, the variability in production methods and the absence of uniform quality standards hinder its widespread adoption and market growth.
One of the key issues is the diversity of feedstocks used to produce biochar. Different organic materials, such as agricultural waste, forestry residues, and even municipal waste, result in biochar with varying chemical properties, physical characteristics, and effectiveness in applications. This inconsistency complicates the ability to evaluate and compare the performance of biochar products, especially in critical sectors like agriculture, where biochar’s soil health benefits are highly dependent on its composition.
Without clear industry standards, producers may prioritize cost-efficiency over quality, leading to biochar that fails to meet the expected performance for specific uses, such as soil amendment or carbon sequestration. Additionally, the lack of standardized testing methods and certifications makes it difficult for consumers to assess the quality and environmental impact of biochar products. This uncertainty undermines consumer confidence and limits large-scale investments. The absence of regulatory frameworks also complicates the scaling of biochar as a climate change mitigation tool. Governments and environmental agencies require standardized metrics to evaluate the carbon sequestration potential of biochar, ensuring that it can be integrated into carbon credit programs or sustainability initiatives. Without these frameworks, biochar production remains fragmented, impeding the market’s growth and its contribution to global sustainability efforts.
Impact and Current Market Scenario of Raw Material Shortage and Shipping Delays
Data Bridge Market Research offers a high-level analysis of the market and delivers information by keeping in account the impact and current market environment of raw material shortage and shipping delays. This translates into assessing strategic possibilities, creating effective action plans, and assisting businesses in making important decisions.
Apart from the standard report, we also offer in-depth analysis of the procurement level from forecasted shipping delays, distributor mapping by region, commodity analysis, production analysis, price mapping trends, sourcing, category performance analysis, supply chain risk management solutions, advanced benchmarking, and other services for procurement and strategic support.
Expected Impact of Economic Slowdown on the Pricing and Availability of Products
When economic activity slows, industries begin to suffer. The forecasted effects of the economic downturn on the pricing and accessibility of the products are taken into account in the market insight reports and intelligence services provided by DBMR. With this, our clients can typically keep one step ahead of their competitors, project their sales and revenue, and estimate their profit and loss expenditures.
Global Biochar Market Scope
The market is segmented on the basis of technology, feedstock, end use. The growth amongst these segments will help you analyze meagre growth segments in the industries and provide the users with a valuable market overview and market insights to help them make strategic decisions for identifying core market applications.
Technology
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
- Hydrothermal Carbonization
Feedstock
- Agricultural Residues
- Forestry and Wood Waste
- Animal Manure
- Biomass Plantation
- Others
End Use
- Soil Conditioner
- Animal Farming
- Electricity Generation
- Heat Generation
- Water Treatment
- Building
- Household
- Textiles
- Others
Global Biochar Market Regional Analysis
The market is analyzed and market size insights and trends are provided by country, technology, feedstock, and end use as referenced above.
The countries covered in the market are U.S., Canada, and Mexico, Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Switzerland, Turkey, Belgium, Netherlands and Rest of Europe, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Australia & New Zealand and Rest of Asia-Pacific, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America South Africa, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., Egypt, Israel and Rest of Middle East and Africa.
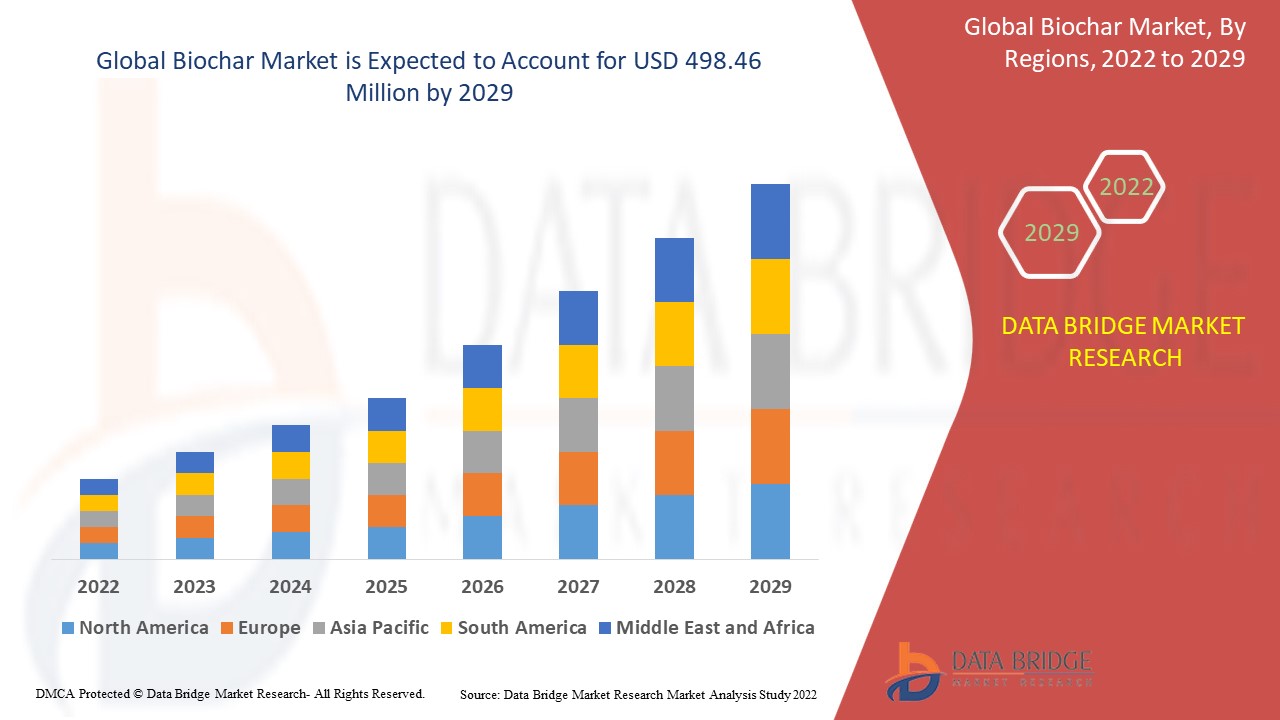
North America dominates the global biochar market due to strong environmental regulations, government incentives, advanced agricultural practices, and growing awareness of biochar's benefits in carbon sequestration and sustainable farming.
Asia Pacific is emerging in the global biochar market due to increasing agricultural demand, government support for sustainable farming, rising environmental awareness, and the need for waste management solutions in rapidly growing economies.
The country section of the report also provides individual market impacting factors and changes in regulation in the market domestically that impacts the current and future trends of the market. Data points like down-stream and upstream value chain analysis, technical trends and porter's five forces analysis, case studies are some of the pointers used to forecast the market scenario for individual countries. Also, the presence and availability of global brands and their challenges faced due to large or scarce competition from local and domestic brands, impact of domestic tariffs and trade routes are considered while providing forecast analysis of the country data.
Global Biochar Market Share
The market competitive landscape provides details by competitors. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, global presence, production sites and facilities, production capacities, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies' focus related to market.
Global Biochar Market Leaders Operating in the Market Are:
- Biochar Now (U.S.)
- Oregon Biochar Solutions (U.S.)
- Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation (U.S.)
- Carbon Gold Ltd (U.K.)
- Swiss Biochar (Switzerland)
- Pacific Coast Carbon LLC (U.S.)
- Standard Biocarbon Corporation (U.S.)
- Genesis Enterprises Inc (U.S.)
- WAKEFIELD BIOCHAR (U.S.)
- Carbonis (Germany)
- Arstaeco (India)
- Black Owl Biochar (U.S.)
- PYROPOWER (Netherlands)
- Terra Char (U.S.)
- American BioChar Company (U.S.)
- Bioforcetech Corp. (U.S.)
- Green Man Char (Australia)
- MASH Makes (India)
- ARTi (U.S.)
- Zhengzhou kelin water purification material co.,ltd. (China)
SKU-