In the realm of modern dentistry, technology has revolutionized the way dental professionals operate, collaborate, and deliver care. The advent of digital tools and techniques has streamlined processes, enhanced precision, and significantly improved patient outcomes. One of the most notable advancements facilitated by digitalization is the seamless collaboration between dentists and dental laboratories. This article explores the digital evolution in dentistry, focusing on how it has transformed the relationship between dentists and laboratories, leading to more efficient workflows and superior results.
The Shift towards Digital Dentistry
Traditional methods in dentistry often involved manual processes, such as taking physical impressions, which were time-consuming, prone to errors, and sometimes uncomfortable for patients. However, with the rise of digital dentistry, these limitations have been overcome. Digital technologies such as intraoral scanners, computer-aided design (CAD), and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) have become integral components of contemporary dental practice.
Intraoral scanners have replaced traditional impression materials, allowing dentists to capture highly accurate 3D images of patient's teeth and oral structures quickly and comfortably. These digital impressions can be instantly transmitted to dental laboratories, eliminating the need for physical molds and reducing turnaround times significantly.
CAD/CAM technology enables the design and fabrication of dental restorations with unparalleled precision and efficiency. Dentists can use CAD software to design crowns, bridges, veneers, and other prosthetic devices digitally based on the patient's unique anatomy and treatment requirements. Subsequently, CAM systems utilize this digital data to mill restorations from high-quality materials such as ceramics or resins, ensuring optimal fit, aesthetics, and functionality.
Enhanced Collaboration between Dentists and Laboratories
The integration of digital tools has transformed the collaboration between dentists and dental laboratories into a seamless and highly efficient process. Instead of mailing physical impressions or dental models, dentists can now share digital files instantly with laboratories, regardless of geographical distance. This real-time communication accelerates the treatment planning and production phases, enabling faster turnaround times and improved patient satisfaction.
Moreover, digital platforms and software solutions facilitate effective communication and collaboration between dentists and laboratory technicians. Dentists can convey their treatment preferences, clinical notes, and specific instructions digitally, ensuring clarity and precision in the fabrication process. Similarly, laboratory technicians can provide feedback, seek clarification, and make modifications to digital designs in collaboration with dentists, fostering a collaborative partnership focused on delivering optimal outcomes for patients. For instance, dental professionals can transmit treatment preferences and clinical notes digitally, ensuring precise fabrication. Similarly, technicians can offer feedback and collaborate on digital designs, fostering a partnership dedicated to achieving optimal patient outcomes through seamless communication and collaboration.
Unlock insights! Dive into Dental Lab market trends with Data Bridge Market Research. Gain actionable data for informed decisions.
Explore now https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-dental-lab-market
The Role of Virtual Treatment Planning
Digital dentistry enables virtual treatment planning, allowing dentists and laboratory technicians to visualize and plan complex cases with unprecedented accuracy. Through advanced software solutions, clinicians can simulate various treatment scenarios, assess different prosthetic options, and evaluate potential outcomes before initiating treatment. This virtual planning process enhances predictability, minimizes risks, and enables more informed decision-making, ultimately leading to superior clinical results.
Furthermore, virtual treatment planning facilitates interdisciplinary collaboration between different dental specialties. Dentists, orthodontists, periodontists, and oral surgeons can collaborate seamlessly to develop comprehensive treatment plans for complex cases involving multiple dental issues. This interdisciplinary approach ensures a coordinated and patient-centered approach to care, optimizing treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
The Impact of Digital Dentistry on Patient Care:
The digital revolution in dentistry has had a profound impact on patient care, enhancing both the quality and convenience of dental treatments. Patients benefit from shorter appointment times, as digital impressions eliminate the need for traditional impression materials, which can be messy and uncomfortable. Moreover, the use of CAD/CAM technology enables same-day restorations, allowing patients to receive crowns, veneers, or bridges in a single visit without the need for temporary restorations or multiple appointments.
Additionally, the precision and accuracy afforded by digital workflows result in superior clinical outcomes and aesthetics. Digital designs can be customized to match the patient's natural dentition seamlessly, ensuring a precise fit and optimal function. Furthermore, patients appreciate the ability to preview their proposed treatment outcomes through virtual simulations, enabling them to make informed decisions about their dental care.
The Future of Digital Dentistry:
As technology progresses, the future of digital dentistry appears increasingly promising. Innovations such as 3D printing, artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR) are set to redefine the field, unlocking fresh avenues for innovation and enhancement, and heralding a new era of possibilities for dental care.
3D printing technologies enable the fabrication of dental prosthetics, surgical guides, and orthodontic appliances with unprecedented speed and precision. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of clinical data to assist dentists in treatment planning, diagnosis, and outcome prediction, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of dental procedures. AR applications can provide real-time visualization and guidance during dental surgeries, improving precision and reducing procedural errors.
In a recent survey conducted in the field of implant dentistry, insights were gathered from 70 technicians regarding their practices and collaborations with dentists. Here are the key findings:
When it comes to creating diagnostic wax-ups, technicians reported that dentists consistently request them 13% of the time. This figure rises to 36% for complicated occlusion problems and 51% for esthetic issues.
In terms of impression trays, 56% of impressions were taken with custom trays, while 37% were taken with stock plastic trays, and 7% with stock metal trays. For the open tray technique, 87% of technicians reported using custom trays, and 87% were asked to fabricate custom trays for impressions with three or more implants.
Impressions were predominantly taken at implant level (79%), with 83% of impression copings being screw-retained, 11% snap-on, and 6% press-fit caps. Technicians reported that dentists provided the majority of impression copings and implant replicas.
In terms of casting reference models, more than 20% of technicians always cast a reference model in addition to the working cast, with 60% doing so at the dentist's request and 17% never casting reference models.
Regarding gingival replicas, 87% of technicians fabricated them on the working cast, primarily for restorations involving the anterior segments (12%), while only 1% used them solely in posterior segments.
All technicians reported mounting working casts in articulators, with 80% doing so for any restoration and 20% specifically for restorations of three or more missing teeth. Close to 60% used semi-adjustable articulators, while 41% used free plane/hinge-type articulators. Bite registrations were received by 91% of technicians regardless of the number of missing teeth or implants.
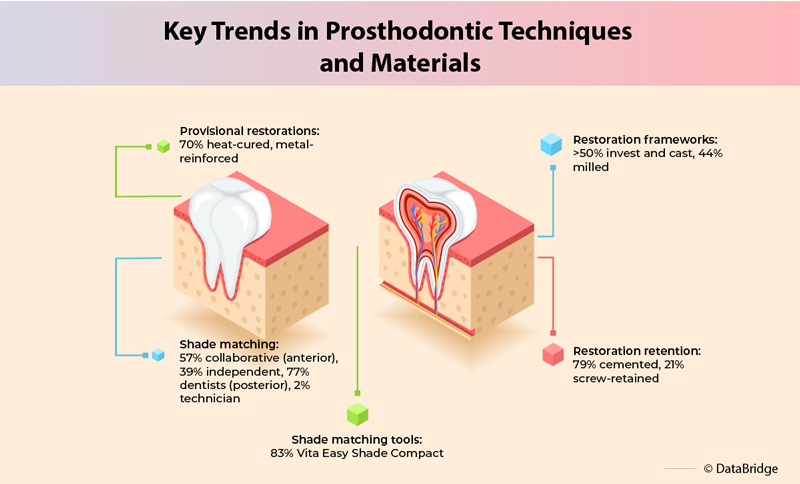
Nearly 70% of technicians fabricated heat-cured, metal-reinforced, acrylic provisional restorations, especially when restoring three or more units, where reinforcement was provided by 91% of technicians.
Impression copings were commonly splinted together or to the impression tray, and abutment selection was carried out by 72% of technicians. When a misfit occurred in the metal framework, 94% of technicians asked dentists to retake impressions.
For shade matching, 57% of technicians collaborated with dentists in the anterior segments, while 39% matched shades independently. In posterior segments, shade matching was primarily done by dentists (77%), although in 2% of cases, technicians completed individualized color and shade matching.
When special lighting was used for shade matching, Vita Easy Shade Compact was the preferred tool for 83% of technicians. The fabrication of fixed restoration frameworks was mostly done by investing and casting of metal alloy (more than half), while 44% used milled frameworks. The majority of fixed restorations were cement-retained, with 21% being screw-retained.
Conclusion
The digital evolution in dentistry has ushered in a new era of precision, efficiency, and collaboration, transforming the way dental professionals deliver care and interact with patients. Through the seamless integration of digital technologies, dentists and dental laboratories can collaborate more effectively, resulting in faster turnaround times, superior clinical outcomes, and enhanced patient satisfaction. As technology continues to evolve, the future of digital dentistry holds immense promise for further advancements, ultimately benefiting both dental professionals and their patients.