The liver, often referred to as the body's chemical powerhouse, undertakes numerous essential functions vital for maintaining overall health. From detoxification to metabolism regulation, the liver's significance cannot be overstated. Consequently, any disruption in its function can trigger various health issues. Liver function tests (LFTs) emerge as indispensable tools for evaluating liver health and diagnosing various diseases associated with liver dysfunction. This article delves into the critical role of liver function tests in assessing health and diagnosing diseases.
Understanding Liver Function
Before delving into liver function tests, it's crucial to comprehend the diverse functions performed by the liver. The liver aids in digestion by producing bile, which facilitates fat digestion and absorption. It metabolizes nutrients, detoxifies harmful substances, and synthesizes proteins crucial for blood clotting and other bodily functions. Additionally, the liver stores glycogen for energy and regulates blood sugar levels. Given these vital roles, any impairment in liver function can have far-reaching consequences on health.
Liver Function Tests: An Overview
Liver function tests encompass a several blood tests aimed at assessing liver health and functionality. These tests measure various enzymes, proteins, and substances in the blood indicative of liver health. Common components of liver function tests include alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin, and albumin levels.
ALT and AST are enzymes primarily found within liver cells. Elevated levels of these enzymes in the bloodstream indicate liver cell damage or inflammation. ALP is an enzyme present in various tissues throughout the body, including the liver, bones, and bile ducts. Elevated ALP levels may suggest liver or bone disorders. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. Elevated bilirubin levels can indicate liver dysfunction or problems with bile flow. Albumin is a protein synthesized by the liver, and decreased levels may indicate liver damage or disease.
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the liver function test market which was USD 33.4 billion in 2021, is expected to reach USD 57.39 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 7.00% during the forecast period 2022 to 2029.
To know more about the study, visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-liver-function-test-market
Understanding Common Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests (LFTs) consist of a battery of blood tests aimed at assessing the health and functionality of the liver. These tests provide valuable insights into liver function and help diagnose various liver diseases. Here's a closer look at some of the common liver function tests:
- Alanine Transaminase (ALT) and Aspartate Transaminase (AST): ALT and AST are enzymes found in liver cells, but they are also present in smaller amounts in other tissues. When liver cells are damaged, these enzymes leak into the bloodstream, causing elevated levels. ALT is sometimes referred to as SGPT, while AST is known as SGOT. Elevated ALT and AST levels may indicate liver damage or disease, although AST can also be elevated due to muscle damage.
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): ALP is an enzyme found in the liver, bone, and other tissues. Elevated ALP levels may suggest liver damage or disease, such as a blocked bile duct, or certain bone diseases. ALP is crucial for breaking down proteins in the body.
- Albumin and Total Protein: Albumin is a protein produced by the liver and is essential for various bodily functions, including fighting infections. Lower-than-usual levels of albumin and total protein may indicate liver damage or disease, as well as gastrointestinal or kidney-related conditions.
- Bilirubin: Bilirubin is a substance produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. Elevated levels of bilirubin may indicate liver damage or disease, as well as conditions such as a blockage of the liver ducts or certain types of anemia.
- Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and L-lactate Dehydrogenase (LD): GGT and LD are enzymes found in the blood, with elevated levels potentially indicating liver or bile duct damage. However, elevated LD levels can also be caused by various other conditions.
- Prothrombin Time (PT): PT measures the time it takes for blood to clot. Increased PT may suggest liver damage, although it can also be influenced by blood-thinning medications such as warfarin.
Understanding the significance of these common liver function tests is crucial for diagnosing liver diseases and assessing overall liver health. Regular monitoring and interpretation of these tests allow healthcare providers to intervene promptly and formulate appropriate management strategies to ensure optimal liver function and overall well-being.
Significance of Liver Function Tests in Health Assessment
Liver function tests are instrumental in assessing overall health and detecting early signs of liver dysfunction. Routine screening with liver function tests can aid in the early detection and management of liver diseases, thus preventing potential complications. For instance, elevated ALT and AST levels may be the first indicators of liver inflammation or injury, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly. Similarly, abnormal bilirubin levels may signal liver or bile duct disorders that require further investigation.
Moreover, liver function tests can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of certain medications and treatments. Certain drugs can have hepatotoxic effects, meaning they can cause liver damage. Monitoring liver function through regular tests enables healthcare providers to adjust medication dosages or switch to alternative treatments if necessary, thereby safeguarding liver health while ensuring effective management of underlying conditions.
Detecting and Diagnosing Liver Diseases
Liver function tests play a pivotal role in detecting and diagnosing various liver diseases, ranging from fatty liver disease to viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming increasingly prevalent, driven by factors such as obesity and metabolic syndrome. Elevated ALT levels are often the initial indicator of NAFLD, prompting further evaluation through imaging studies or liver biopsies for confirmation.
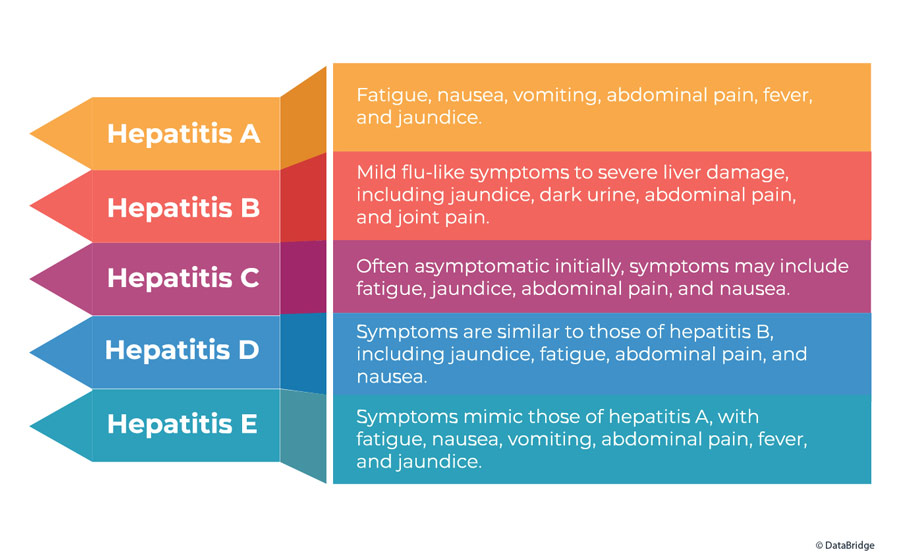
Viral hepatitis, caused by hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, and E), is another major concern worldwide. Liver function tests help identify hepatitis infections by detecting elevated liver enzymes and abnormal bilirubin levels. Subsequent serological tests can determine the specific type of hepatitis virus responsible for the infection, guiding treatment decisions.
Chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, can also be detected through liver function tests. As liver damage progresses, levels of liver enzymes may fluctuate, and other markers of liver function, such as albumin levels, may decline. These changes in liver function test results can provide valuable insights into the severity and progression of liver disease, helping healthcare providers formulate appropriate management strategies.
Liver function tests are also indispensable in monitoring patients with liver diseases, enabling healthcare providers to track disease progression, assess treatment efficacy, and detect complications such as liver failure or portal hypertension.
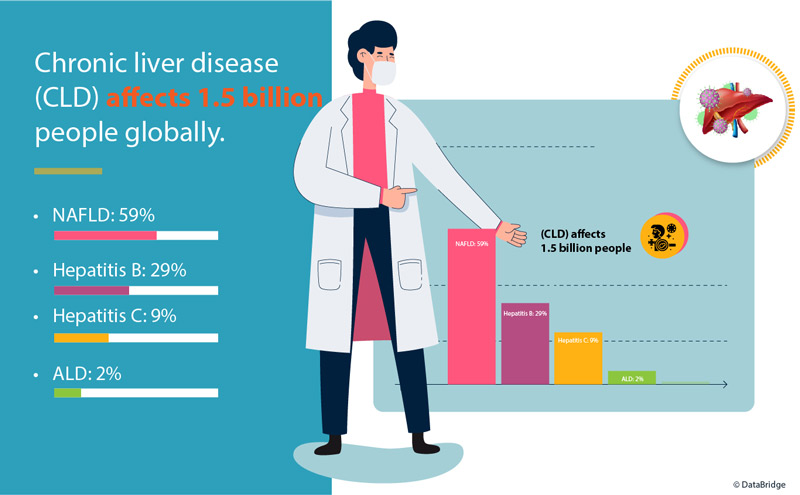
Chronic liver disease (CLD) represents a significant global health challenge, impacting approximately 1.5 billion individuals worldwide. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) stands out as the most prevalent, affecting 59% of cases, followed by hepatitis B (29%), hepatitis C (9%), and alcoholic liver disease (ALD) (2%). Concurrently, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a pressing concern, afflicting around 2 billion people annually, resulting in 1 million fatalities.
Given this formidable burden of liver diseases, there's a projected surge in demand for liver disease diagnostics products. This demand surge is expected to drive substantial growth in the liver disease diagnostics market. With increased emphasis on early detection and management, coupled with rising awareness of liver diseases' prevalence and severity, the market for diagnostic tools and technologies catering to liver diseases is anticipated to witness significant expansion. Such growth not only reflects the pressing need for effective diagnostics but also underscores the imperative of addressing liver diseases comprehensively on a global scale.
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Liver
The COVID-19 pandemic has not only posed a significant threat to respiratory health but has also raised concerns about its impact on various other organ systems, including the liver. While the primary manifestation of COVID-19 involves respiratory symptoms, emerging evidence indicates a notable association between COVID-19 and liver injury.
Liver involvement in COVID-19 can present in diverse ways, ranging from mild abnormalities in liver function tests to severe hepatocellular injury and cholestasis, with potential progression to liver failure in severe cases. Elevated levels of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) have been consistently observed in COVID-19 patients, indicative of liver inflammation and damage.
The underlying mechanisms contributing to liver injury in COVID-19 are multifaceted. One plausible mechanism involves the direct invasion of liver cells by the SARS-CoV-2 virus through the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is abundantly expressed in liver cells. This direct viral invasion can lead to hepatocellular injury and subsequent liver dysfunction. Moreover, the systemic inflammatory response triggered by COVID-19, characterized by cytokine release syndrome, can exacerbate liver inflammation and impair hepatic function. Additionally, hypoxia resulting from severe respiratory compromise in critically ill patients can further compromise liver function.
Furthermore, individuals with pre-existing liver conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), viral hepatitis, or cirrhosis may be at a heightened risk of experiencing more severe liver injury from COVID-19. Conversely, COVID-19-induced liver injury can exacerbate pre-existing liver conditions, potentially leading to worse clinical outcomes and increased mortality rates.
The clinical implications of COVID-19-associated liver injury extend beyond the acute phase of illness. Long-term liver complications, including the development or exacerbation of chronic liver diseases such as fibrosis and cirrhosis, are areas of ongoing investigation. The long-lasting consequences of COVID-19-related liver injury may significantly impact the overall morbidity and mortality rates among affected individuals.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought about additional challenges concerning liver health, particularly in the context of increased alcohol consumption during periods of lockdowns and social isolation. A research study published in December 2021 indicates a substantial surge, with alcohol consumption in the United States escalating by up to 25%. This surge poses a grave long-term threat, significantly elevating the burden of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD)-related morbidity and mortality.
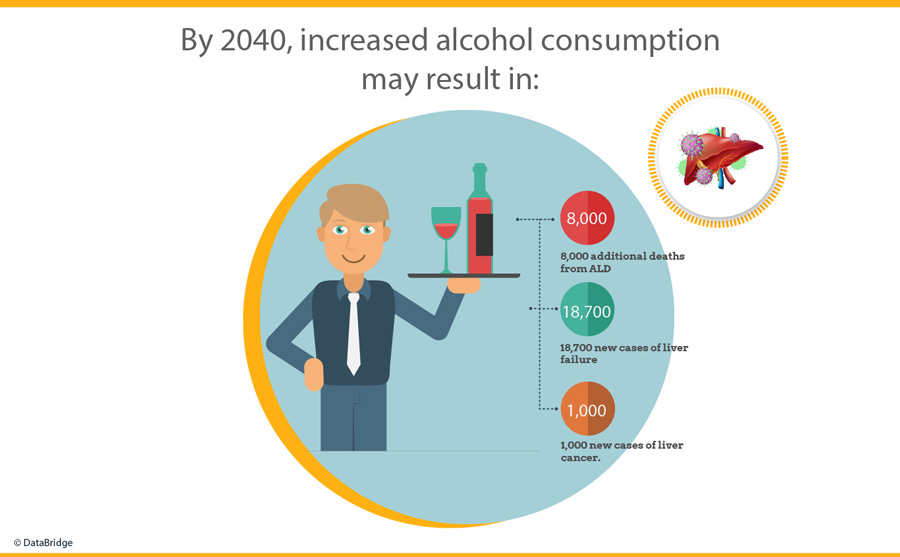
Projections suggest that by 2040, this increase in alcohol consumption could lead to an additional 8,000 deaths from ALD, 18,700 cases of liver failure, and 1,000 cases of liver cancer. These projections underscore the urgent need for advanced diagnostic tools to meet the escalating demand for medical attention. Enhanced diagnostic capabilities are crucial for early detection and intervention, facilitating timely and appropriate medical care for individuals at risk of ALD-related complications.
In conclusion, liver function tests (LFTs) stand as indispensable tools in assessing overall health and diagnosing various liver diseases. With the liver's central role in maintaining bodily functions, any disruption in its function can have profound consequences on health. LFTs, by measuring enzymes, proteins, and substances indicative of liver health, provide valuable insights into liver function and aid in the early detection and management of liver diseases. The significance of LFTs is particularly highlighted in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, where liver involvement has emerged as a notable concern. As liver diseases continue to pose significant global health challenges, the demand for advanced diagnostic tools is projected to rise. Enhanced diagnostic capabilities not only enable early detection but also facilitate timely intervention, ultimately contributing to improved outcomes and reduced morbidity and mortality rates associated with liver diseases.