In recent years, the healthcare landscape has undergone a profound transformation with the advent of telemedicine. This revolutionary approach to healthcare delivery utilizes telecommunications technology to provide remote medical services, breaking down geographical barriers and enhancing accessibility to quality healthcare. As the world grapples with global health challenges, telemedicine has emerged as a powerful tool, offering innovative solutions to improve patient care, reduce healthcare costs, and streamline medical processes. This article delves into the growing impact of telemedicine, supported by facts, data, and statistics, while exploring the future prospects it holds for modern medicine.
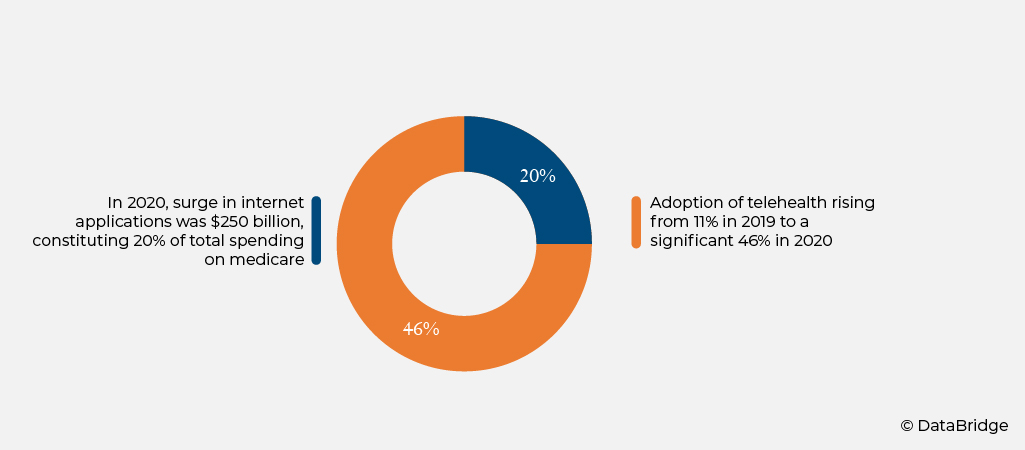
In 2020, the healthcare sector had experienced a notable surge in internet applications, with virtual care anticipated to reach $250 billion, constituting 20% of total spending on medicare, Medicaid, and commercial payer services. The swift adoption of telehealth is evident in the increase of consumers accessing telehealth services, rising from 11% in 2019 to a significant 46% in 2020. This shift highlights the growing reliance on virtual care solutions and their increasing importance in the healthcare landscape. Notably, the market is buoyed by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases globally, with general consultations playing a pivotal role. This transformative shift toward virtual care reflects a growing recognition of the benefits of telemedicine in enhancing healthcare accessibility and delivery while meeting the evolving needs of patients in an increasingly interconnected world.
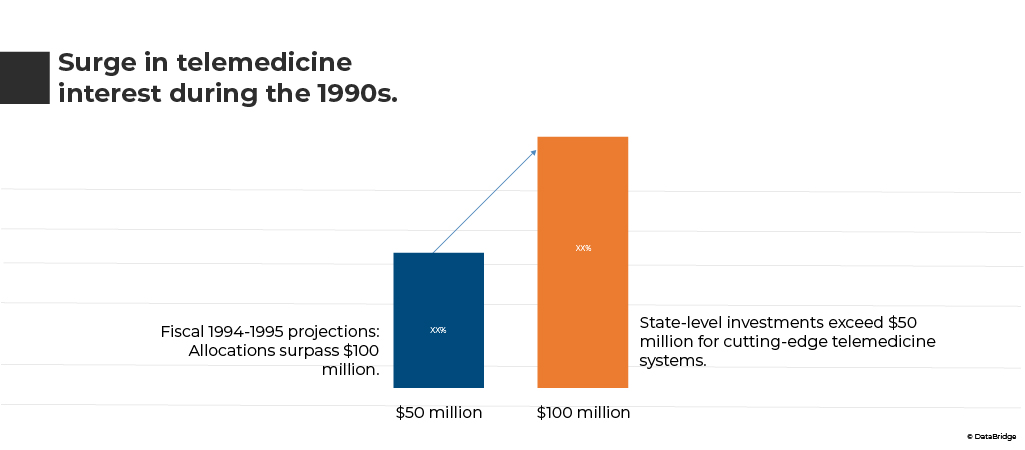
Telemedicine is broadly defined as the utilization of telecommunications technologies to deliver medical information and services. While this encompasses various applications such as telephone consultations, facsimile transmission, and distance education, the term has increasingly become synonymous with remote electronic clinical consultations. The 1990s witnessed a surge in interest in telemedicine, with substantial financial commitments from state and federal authorities. In fiscal 1994-1995, allocations for telemedicine and related technologies were projected to surpass $100 million. Notably, over 13 federal agencies, including the US Department of Commerce, Health Care Financing Administration (HCFA), Office of Rural Health Policy, and the Department of Defense, embarked on telemedicine research and demonstration programs. At the state level, substantial investments exceeding $50 million were dedicated to constructing cutting-edge telemedicine systems. This momentum underscores the growing recognition of telemedicine's potential in transforming healthcare delivery and promoting accessibility to medical services across the United States.
Versatile Communication Channels in Telemedicine
Three primary mediums of communication within telemedicine include video conferencing, telephone consultations, and secure messaging platforms.
Video Conferencing: This medium enables real-time, face-to-face interactions between healthcare providers and patients, allowing for a comprehensive assessment, visual examination, and discussion of medical concerns. It enhances the quality of remote consultations by incorporating visual cues and facilitating a more personalized healthcare experience.
Telephone Consultations: Traditional yet effective, telephone consultations involve audio communication between healthcare professionals and patients. This medium is particularly valuable for discussions, follow-ups, and addressing non-emergent medical issues, offering a convenient and accessible means of healthcare delivery, especially in areas with limited internet connectivity.
Secure Messaging Platforms: Asynchronous communication through secure messaging platforms allows patients to interact with healthcare providers at their convenience. This includes exchanging text messages, images, and documents, promoting ongoing communication, sharing updates, and addressing non-urgent queries in a secure and timely manner.
These diverse communication channels within telemedicine contribute to its versatility, making healthcare services more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered.
The Future Prospects of Telemedicine
As telemedicine continues to evolve, its future prospects are filled with promise. Several factors contribute to the ongoing growth and development of telemedicine, shaping its role in the future of healthcare.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI): The integration of AI in telemedicine holds great potential for improving diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, helping healthcare providers make more informed decisions and enhancing the overall quality of care.
Expansion of Remote Patient Monitoring: The increasing prevalence of wearable devices and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies allows for continuous monitoring of patients' vital signs and health metrics. This real-time data enables healthcare providers to intervene promptly in case of deviations from normal parameters, preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.
Telemedicine in Specialized Fields: Telemedicine is extending its reach into specialized medical fields, such as dermatology, psychiatry, and cardiology. Remote consultations with specialists allow patients to access expertise that may not be readily available in their local areas, fostering a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach to healthcare.
Global Healthcare Collaboration: Telemedicine facilitates cross-border collaboration among healthcare professionals, enabling the exchange of knowledge and expertise on a global scale. This collaboration can lead to advancements in research, treatment modalities, and the development of innovative healthcare solutions.
Improved Regulatory Frameworks: As the benefits of telemedicine become more evident, regulatory frameworks are evolving to support and govern its implementation. Clear guidelines and regulations will contribute to the widespread acceptance and integration of telemedicine into mainstream healthcare.
Patient Satisfaction in Traditional Healthcare: Implications for Evolving Telemedicine Integration
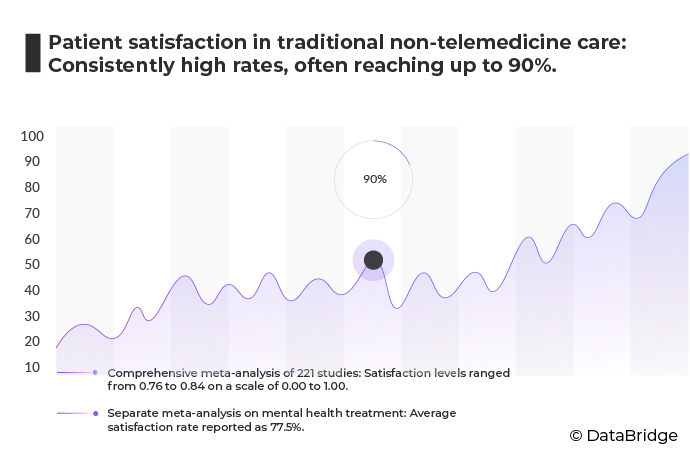
Patient satisfaction studies in traditional non-telemedicine care consistently show high rates, often reaching up to 90%. In a comprehensive meta-analysis of 221 studies, satisfaction levels ranged from 0.76 to 0.84 on a scale of 0.00 to 1.00. These findings underscore a robust and predominantly positive perception of traditional healthcare services among patients.
Moreover, a separate meta-analysis focused on over 50 studies examining patient satisfaction in mental health treatment reported an average satisfaction rate of 77.5%. These findings underscore the broad contentment with care in the context of mental health services. However, it's important to note that patient satisfaction is not uniform across all types of care and can be influenced by various contextual factors.
The variability in patient satisfaction is evident in studies where it was observed to be influenced by the type of care provided and the specific context in which it was delivered. Different healthcare modalities, specialties, and settings may elicit varying levels of satisfaction among patients.
While traditional non-telemedicine care has generally demonstrated high levels of patient satisfaction, the evolving landscape of healthcare, marked by the integration of telemedicine, prompts further investigation into how patient satisfaction may be influenced in comparison to traditional models. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing healthcare delivery and ensuring patient-centered approaches in both traditional and emerging healthcare modalities.
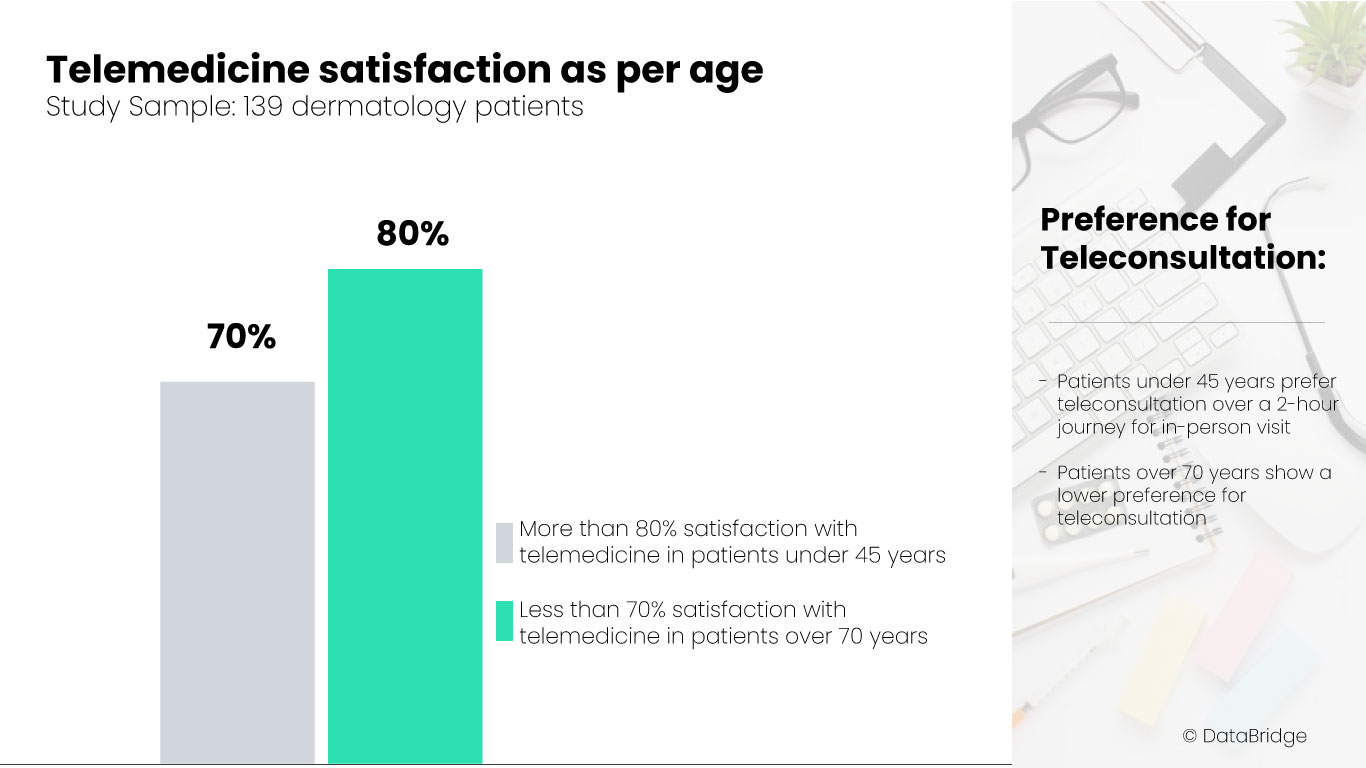
In a study assessing 139 dermatology patients, the research revealed that younger patients were more satisfied with telemedicine than their older counterparts. Specifically, more than 80% of patients under 45 years preferred teleconsultation over a 2-hour journey for an in-person visit, while less than 70% of patients over 70 years shared the same preference. Interestingly, no significant differences were noted based on education level, proximity to the hospital, or the nature of the examination (new or follow-up).
The Pandemic's Impact on Telemedicine Adoption
The COVID-19 pandemic has undeniably acted as a catalyst in propelling the adoption of telemedicine to unprecedented heights. Companies across the globe have witnessed a surge in telemedicine visits, with a notable increase in demand for video consultations. This surge is not only driven by the necessity of maintaining social distance but also by the need to limit exposure to potential infections, especially for healthcare professionals. Consequently, an escalating number of individuals are turning to telemedicine consultations as a safer and more convenient alternative.
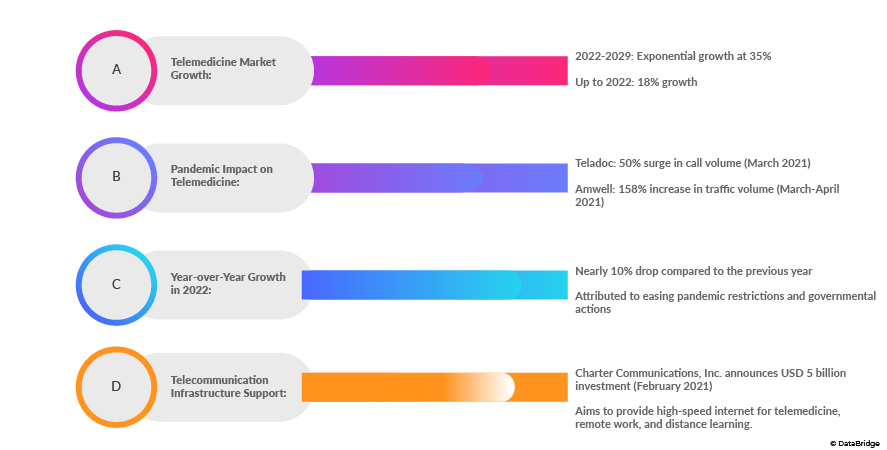
The statistics paint a compelling picture of the telemedicine boom. From 2022 to 2029, the market is expected to grow at ab exponential growth rate of 35%, a stark contrast to the 18% growth observed up to 2022. The impact of the pandemic is evident in the substantial increase in telemedicine utilization. In March 2021, Teladoc reported a staggering 50% surge in call volume within just one week, reflecting the rapid and widespread adoption of telemedicine services. Similarly, Amwell recorded a remarkable 158% increase in traffic volume between March and April 2021, underscoring the growing reliance on virtual healthcare solutions.
The global landscape of telemedicine was not confined to a specific region. In China, Ali Health, JD Health, and We Doctor responded to the pandemic by offering online telemedicine services tailored to address COVID-19 concerns. This strategic move reflected the adaptability of telemedicine platforms to cater to specific healthcare needs during a crisis. Simultaneously, in Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI), in collaboration with Line and Medpeer, initiated free remote consultation services in March 2021, highlighting telemedicine solutions' global reach and utility.
Despite the remarkable growth, the telemedicine market had experienced nearly 10% drop in year-over-year growth in 2022 compared to the previous year. This temporary decline is attributed to factors such as the easing of global pandemic restrictions, evolving guidelines, and various governmental actions to address the aftermath of the crisis. However, this setback is anticipated to be short-lived, with the market projected to resume its growth trajectory by mid-2022.
The response to the increased demand for telemedicine goes beyond the healthcare sector. Charter Communications, Inc. took a significant step by announcing a USD 5 billion investment plan in February 2021. The plan aimed to provide high-speed internet connections to lower-density rural towns, thereby facilitating telemedicine, remote work, and distance learning, among other applications. This strategic investment underscores the recognition of the critical role that robust internet infrastructure plays in supporting the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
Telemedicine, a revolutionary approach to healthcare, offers several benefits and drawbacks
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Telemedicine enhances healthcare access, especially for individuals in remote or underserved areas, by enabling virtual consultations and medical services.
- Cost-Efficiency: It reduces healthcare costs for both providers and patients by minimizing the need for physical infrastructure, travel, and hospital visits.
- Patient Convenience: Telemedicine provides convenience through virtual consultations, eliminating the need for patients to travel and wait in clinics, resulting in time and resource savings.
- Continuity of Care: It ensures continuous patient care, particularly for those with chronic conditions, by enabling remote monitoring, follow-ups, and timely interventions.
- Pandemic Response: Telemedicine proved invaluable during public health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, by facilitating healthcare services while minimizing the risk of infection.
- Drawbacks:
- Technological Barriers: Limited internet access, lack of digital literacy, and inadequate technology infrastructure can hinder the adoption of telemedicine, especially in rural or developing areas.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Transmitting sensitive health information over digital networks raises concerns about data security and patient privacy, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures.
- Diagnostic Limitations: Some medical conditions may require in-person examinations or diagnostic tests that cannot be adequately conducted through virtual consultations.
- Regulatory Challenges: Varying regulations and reimbursement policies across regions can pose challenges for the consistent implementation and growth of telemedicine services.
- Impersonal Interaction: Telemedicine lacks the personal touch of face-to-face interactions, potentially impacting the doctor-patient relationship and the quality of communication.
In navigating these benefits and drawbacks, the ongoing evolution of telemedicine requires careful consideration of technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and patient-centered approaches to ensure its effective integration into mainstream healthcare.
Conclusion
Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in modern healthcare, addressing longstanding challenges and paving the way for a more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system. Supported by a wealth of data and statistics, the impact of telemedicine is evident in improved healthcare access, cost savings, and enhanced patient outcomes.
As technology continues to evolve, the future prospects of telemedicine look promising, with the integration of AI, 5G, VR, and RPM unlocking new possibilities for healthcare delivery. However, addressing regulatory, ethical, and privacy considerations will be crucial to ensure the responsible and ethical deployment of these technologies.
The revolutionizing journey of telemedicine is not without challenges, but the collective efforts of healthcare providers, policymakers, and technology innovators hold the key to harnessing its full potential. As we stand on the cusp of a new era in healthcare, the continued exploration and integration of telemedicine will undoubtedly shape the future of medicine and contribute to building a healthier and more connected world.