What exactly is Dementia?
Dementia is a very sensitive disease that is more common as people grow older. Approximately one-third of all people aged 85 years or older may have some form of dementia. However, there are few cases wherein many people live into their 90s and beyond without any signs of dementia.
It is the loss of cognitive functioning which includes thinking, remembering, and reasoning and it effects to such an extent that it interferes with a person's day-to-day life. There are many people with dementia who cannot control their emotions, and as a result their personalities may change. It can range in terms of severity, starting from the mildest stage, when it just starts to affect the brain functioning slowly, to the most severe stage, when the person must depend completely on others for basic living activities.
Our DBMR team has investigated the global dementia - alzheimer disease market and witnessed that the market to account to grow at a CAGR of 10% in the above mentioned forecast period. The rise in prevalence of Alzheimer's across the globe is among the important factor expected to intensify the growth and demand of dementia - alzheimer disease market. North America region leads the dementia - Alzheimer disease market owing to the rise in awareness regarding Alzheimer's disease in the U.S. and the increase in the prevalence of Alzheimer's disease,
To know more about the study, please visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-dementia-alzheimer-disease-market
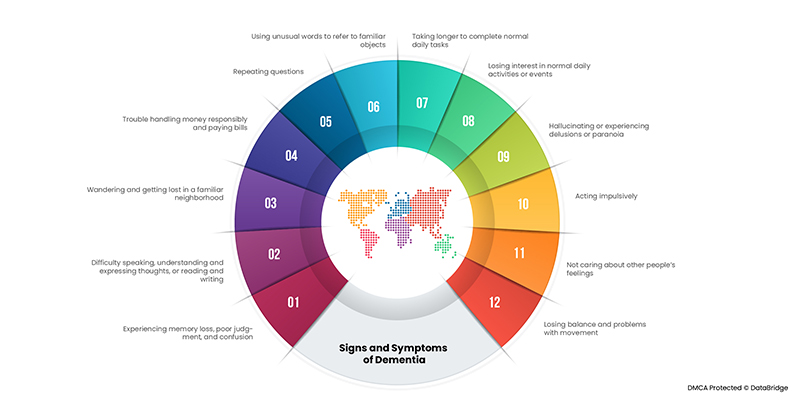
Signs and Symptoms
There are varied signs and symptoms that are associated with dementia. People with dementia lose their healthy neurons, or nerve cells, as in they stop working. Although almost everyone loses some neurons with each passing age, but people with dementia experience far greater loss. Here is a list of varied signs and symptoms that are associated with dementia:
Causes of Dementia
Neurodegenerative disorders lead to progressive and irreversible loss of neurons and brain functioning. Alzheimer's disease is caused by the irregular buildup of two proteins called amyloid and tau. Deposits of amyloid, called plaques, build up around brain cells. Deposits of tau form "tangles" within brain cells. As brain cells become affected by Alzheimer's, chemical messengers also decrease, which is involved in sending messages, or signals, between brain cells.
The most common causes of dementia include:
Degenerative neurological diseases. These include:
- Parkinson's disease
- Huntington's disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- Few types of multiple sclerosis.
Our DBMR team has investigated global parkinson's disease market and witnessed that the prevalence of parkinson's disease among population across the globe acts as one of the major factors driving the growth of parkinson's disease market. North America dominates the Parkinson's disease market due to the increasing occurrence of the disorder and well-developed healthcare infrastructure. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness high growth during the forecast period of 2021-2028 due to the presence of untapped market and supportive government policies in the region.
To know more about the study, please visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-parkinsons-disease-market
Vascular disorders which affect the blood circulation in your brain.
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Long-time alcohol or drug use
- Infections of the central nervous system, which include meningitis, HIV, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Certain types of hydrocephalus, a buildup of fluid in the brain
Few of the reversible causes of dementia include:
- Alcohol or substance use disorder
- Subdural hematomas, blood clots beneath the outer covering of the brain
- Tumors
- Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
- Low levels of thyroid hormones, called hypothyroidism
- Low blood sugar, which is known as hypoglycemia
- Metabolic disorders such as a vitamin B12 deficiency
- HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders
Our DBMR team has investigated the global post-bariatric hypoglycemia (PBH) treatment market and witnessed that the increase in the prevalence of obesity globally is escalating the growth of post-bariatric hypoglycemia (PBH) treatment market. North America dominates the post-bariatric hypoglycemia (PBH) treatment market due to the high prevalence of obesity within the region. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness high growth during the forecast period of 2021 to 2028 because of the high population in the region.
To know more about the study, please visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-post-bariatric-hypoglycemia-pbh-treatment-market
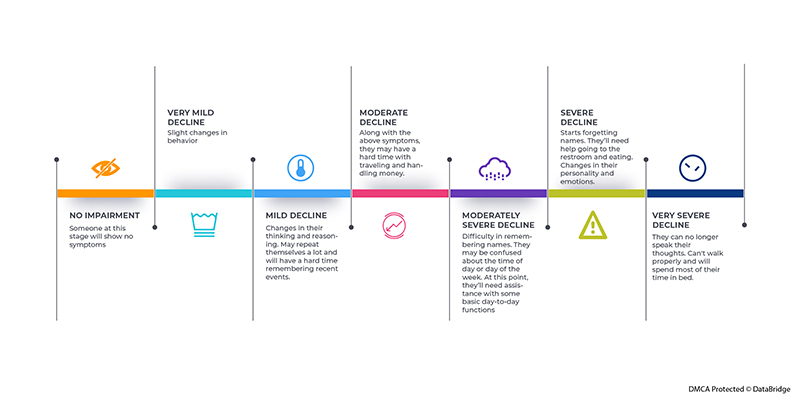
Stages of Dementia
There are varying stages of dementia that is explained below:
Prevalence of Dementia
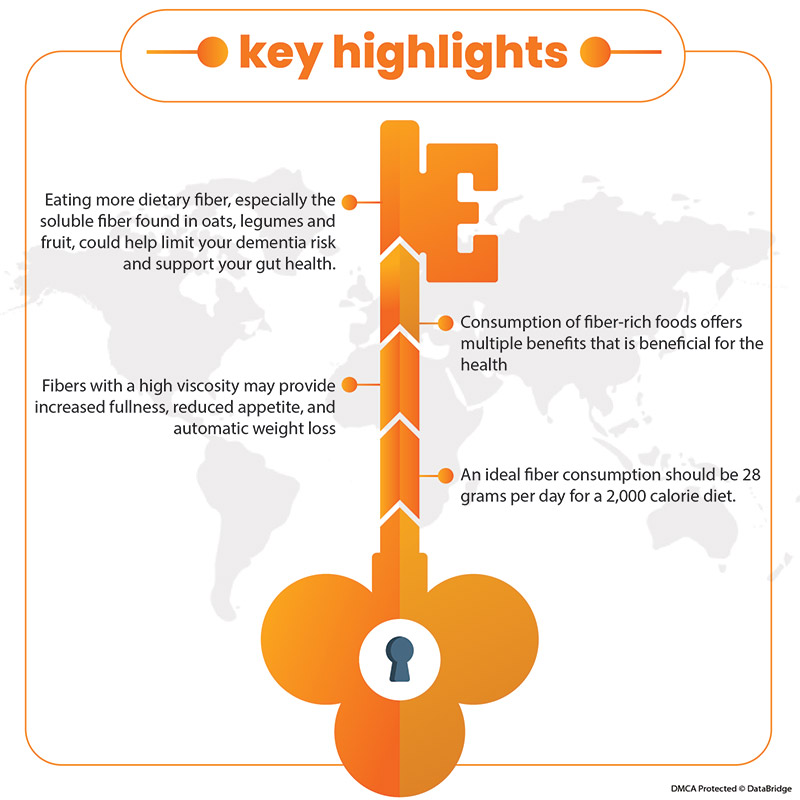
The overall prevalent cases that include diagnosed and undiagnosed cases of dementia in both men and women are set to rise high over the next decade, reaching upto 12,000,000 by 2028. A recent Japanese study published in early February said that a diet high in fiber is related to a minimized risk of dementia later in life. If indulging oneself in a high-fiber diet becomes a standard recommendation to aid in preventing dementia, researchers expect that total incident cases of dementia could reduce among older adults in Japan.
Worldwide, approximately 55 million people have dementia, with over 60% living in low- and middle-income countries. With the increasing population of the elderly in nearly every country, this number is expected to rise to 78 million in 2030 and 139 million in 2050.
Importance of Fiber Diet in the Prevention of Dementia
Whole plant foods are good for the body's functionality, especially because of the fibers. Increasing evidence shows that adequate fiber intake may benefit digestion and reduce chronic disease risk. Fiber can be categorized into dietary, which can normally be defined as "nondigestible carbohydrates and lignin found in plants." Dietary fiber is further broken down into soluble and insoluble fiber. Another type is functional fiber which is extracted from natural foods or produced synthetically and only exists in isolation. Fiber is essential for the body; most of us fall short of the ideal quantity of fiber, consuming only about 9 to 11 grams daily. Many nutritionists recommend that women should consume 35 grams of fiber and that men should be 38 grams of fiber.
The latest FDA nutrition label recommends that the ideal fiber consumption should be 28 grams per day for a 2,000 calorie diet.
New research suggests another potential significant benefit. A high-fiber diet may trigger a chemical cascade that leads to reduced inflammation in the brain, implying age-related cognitive decline and memory loss, as well as a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Since this is a mouse study, it has the caveat that it "has not been tested in humans yet", but the results are significant when we first look at the fiber-to-brain connections. The researchers started by looking at a short-chain fatty acid called butyric acid, produced by bacteria ferment fiber in the gut. It has been shown to enhance memory in rodents.
To investigate whether a high-fiber diet produces similar effects to the butyrate dosage form, the researchers fed young and aged mice high-fiber and low-fiber diets, tested the butyrate's blood levels, and measured the intestinal level. The results showed that a high-fiber diet had comparable effects to drugs by increasing butyric acid and other short-chain fatty acids in both young and aged mice. found that it reduced intestinal inflammation in mice to levels indistinguishable from young mice. The researchers then genetically tested the mice and found that mice fed a high-fiber diet also had less inflammation in the brain's immune cells, known as microglia, which make up about 15% of all cells in the brain. Microglial inflammation is thought to be one of the main causes of age-related cognitive decline.
There are several benefits associated with fiber consumption:
- Digestion Becomes Smoother
Fiber-rich foods, including beans and legumes, whole grains, berries, and nuts, help in easing out the digestion process. It's been researched that soluble fiber combines with water to form a gel-like substance that creates bulk. A diet rich in high fiber will promote more regular digestion and less constipation.
- Acceleration of Zero Calories
With the consumption of double fiber intake from 12 to 24 grams per day, one can burn more calories, as per the recent research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Our body cannot digest fiber but it attempts to burn calories in the process and boosts the metabolism. Approximately all that burnout would result in a 10-pound loss per year.
- Lowering of Cholesterol
Soluble fiber, specifically, has been associated with lower LDL cholesterol levels. Soluble fiber can be found in barley, oat bran, strawberries and apples. Fiber has absorbent properties, which helps bind the circulating cholesterol and then eliminate it from the body.
- Accelerates Energy
A high-fiber diet can be a great savior for an instant energy boost. Eating fiber and protein together balances blood glucose, providing the body with sustained energy throughout the day.
- For Glowing Skin
Fiber maintains toxins in the blood, thus eliminating them through the digestive tract instead of the pores, which can make your skin brighter and clearer. Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants that might help to fight aging, such as artichokes, pears, and broccoli.
- Decreases Inflammation
Fiber is a prebiotic which plays a vital role in gut health and is essential for battling inflammation and lowering overall disease risk. As per the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition study, fiber works as a natural protective armor against C-reactive protein (CRP), which is a sign of acute inflammation.
- Reduces Bloating
Drinking at least three liters of water daily can avoid aches and unsettled stomach aches. It will lead to complete and regular bowel movements. One of the primary benefits of fiber is that it surges stool bulk, which eventually aids in preventing constipation and bloating, which is a great sign of relief from irritable bowel syndrome.
- Stabilization of blood sugar
Foods that are rich in fiber take longer to digest; hence blood sugar doesn't show dramatic fluctuation as it does with refined carbohydrates. Fiber slows down digestion and stabilizes blood sugar levels, curbing sugar cravings and sustaining energy. Balancing is a crucial thing with regard to the fiber consumption. For instance, when indulging in something lower-fiber, such as pancakes, if we balance out with a handful of sliced pears or a medium sliced banana, it will show a good result.
- Lowering of Hypertension
Improving the cholesterol levels and decreasing inflammation, fiber can really help in reducing heart disease risk and also lower down the blood pressure levels.
- Decreases Chances of Cancer
Fiber causes constant cell turnover, which is found to be beneficial in terms of digestion and colon health in preventing tumor growth. In addition, fiber helps reduce levels of circulating estrogen, which has been proven to reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Our DBMR team has investigated global colorectal cancer treatment market and witnessed that increased number of genetic mutation disorders and adoption of unhealthy lifestyle that increases the risk evolving colorectal cancer also boost up the global colorectal cancer treatment market growth. North America dominates the colorectal cancer treatment market share due to increasing healthcare and R&D expenditure and global players on novel technology or formulation of existing drugs.
To know more about the study, please visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-colorectal-cancer-treatment-market
List of Few High Fiber Foods:
Various high fiber foods are available in the market, but the general population is unaware of it. Here are a few high fiber foods listed below:
- Pears:
The pear is a popular fruit that is both tasty and nutritious and is considered to be one of the best fruit sources of fiber.
Fiber content: 5.5 grams or 3.1 grams per 100 grams
- Strawberries
Strawberries are a delicious, healthy option that can be eaten fresh. It is full of vitamin C, manganese, and various powerful antioxidants.
Fiber content: 3 grams in 1 cup of fresh strawberries, or 2 grams per 100 grams
- Apples
Apples are relatively high in fiber. People like it, especially like them in salads.
Fiber content: 4.4 grams or 2.4 grams per 100 grams
- Carrots
Carrots are liked by many because its tasty, crunchy, and highly nutritious. It's rich in vitamin K, vitamin B6, magnesium, and beta carotene, an antioxidant that gets turned into vitamin A in the body
Fiber content: 3.6 grams in 1 cup of raw carrots, or 2.8 grams per 100 grams
- Brocolli
Broccoli is a type of cruciferous vegetable that is loaded with vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, B vitamins, potassium, iron, and manganese and contains antioxidants and potent cancer-fighting nutrients. Compared to other vegetables, broccoli is also relatively high in protein,
Fiber content: 2.4 grams per cup, or 2.6 grams per 100 grams
- Lentils
Lentils are among the most nutritious foods and common food. They are very high in protein and loaded with many important nutrients.
Fiber content: 13.1 grams per cup of cooked lentils, or 7.3 grams per 100 grams
- Legumes
Most legumes are rich in protein, fiber, and various nutrients. They are among the world's cheapest sources of quality nutrition if properly prepared.
Other high fiber legumes include:
- Cooked black beans: 8.7 grams
- Cooked lima beans: 7 grams
- Baked beans: 5.5 grams
- Cooked edamame: 5.2 grams
- Oats
Oats are one of the healthiest grain foods that is known in recent times. They are very high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They contain a powerful soluble fiber called beta glucan, leaves major health benefits on blood sugar and cholesterol levels. It is very easy to make and is becoming more common among working professionals.
Fiber content: 16.5 grams per cup of raw oats, or 10.1 grams per 100 grams
- Almonds
Almonds are a popular type of tree nut with many nutrients such as healthy fats, vitamin E, manganese, and magnesium. It can also be made into almond flour for baking with a dose of extra nutrients.
Fiber content: 4 grams per 3 tablespoons, or 13.3 grams per 100 grams.
- Dark Chocolates
Dark chocolate is one of the most delicious foods that is liked by the majority of the population. It is high in nutrients and is one of the most antioxidant- and nutrient-rich foods. If one chooses dark chocolate with a cocoa content of 70–95% or higher and avoid products loaded with added sugar, they will be highly beneficial.
Fiber content: 3.1 grams in a 1-ounce piece of 70–85% cacao, or 10.9 grams per 100 grams
- Brussels Sprouts
The Brussels sprout is quite relatable with broccoli. They are very high in vitamin K, potassium, folate, and potent cancer-fighting antioxidants.
Fiber content: 3.3 grams per cup or 3.7 grams per 100 grams.
- Avocado
The avocado is a type of fruit which is loaded with healthy fats. They are very high in vitamin C, E,potassium, magnesium, and other B vitamins. They also have numerous health benefits such as losing weight, increasing immunity and such.
Fiber content: 10 grams in 1 cup or 6.7 grams per 100 grams
Few Tips for Increasing Dietary Fiber in the Diet
- Add fiber to your diet slowly
- Too much fiber at once can cause cramping, bloating, and constipation
- When adding fiber to your diet, ensure you drink enough water (at least 64 ounces or 8 cups per day) to prevent constipation from drinking
- Choose products that list whole grains as the first ingredient, not enriched flours
- Whole grains are whole grains, but wheat flour is not
- Choose whole grain bread that contains 2 to 4 grams of fiber per slice
- Choose grains that contain at least 5 grams of fiber per serving
- Choose raw fruits and vegetables instead of juices and eat the skins
- Try alternative fiber options such as whole grain buckwheat, whole grain couscous, quinoa, bulgur, wheat germ, chia seeds, hemp seeds, lentil pasta, and edamame pasta, among others
- Popcorn is whole grain
- For a healthier snack, try low-fat without butter. Bran is sprinkled over soups, cereals, baked goods, spaghetti sauces, ground beef, and casseroles
- Bran also goes well with orange juice
- Use dried peas, beans, and legumes in main dishes, salads, or side dishes such as rice or pasta
- Add dried fruit to yogurt, cereal, rice, and muffins
- Try brown rice and whole wheat pasta
Besides these factors, the addition of fiber supplements is also another factor that can lead to benefit of the body's functionality by normalizing constipation and diarrhea. It is mentioned below:

Soluble fiber was particularly effective in preventing dementia compared to insoluble fiber. The inverse association was more pronounced with soluble fiber intake and was restricted to dementia without a history of stroke. Potatoes, but not vegetables or fruits, showed similar associations for high-fiber foods. In Japanese culture, potatoes are not considered vegetables as in the United States. For this reason, the researchers decided to distinguish between potatoes and vegetables. Potato starch is also very different from vegetables. Foods high in soluble fiber include black beans, lima beans, lentils, chickpeas, edamame beans, barley, flaxseeds, chia seeds, Brussels sprouts, sweet potatoes, avocados, broccoli, beets, and pears.
Conclusion:
Dementia is a very crucial disease that affects almost the majority of the elderly population. Many preventive measures are available for these patients, but apart from the basic treatment, natural measures are working wonders for these patients. Having a diet rich in fiber helps in preventing dementia. In many developing countries, such as U.S. and Australia, people doesnot consume as much fiber as they should. Including more dietary fiber, especially the soluble fiber found in oats, legumes, and fruit, could help reduce dementia risk and support gut health. To increase the intake of fiber-rich foods, one can snack on high-fiber foods, like raspberries, apples, and crispy chickpeas. In addition, instead of choosing for refined breading on the chicken or fish, one may coat them in crushed wheat bran or oats to keep things moving and outsource the benefits of fiber. These are a few examples that can help increase fiber in the diet.