Blockchain technology is a game-changer that has the ability to revolutionize not just one or two industries but the whole business environment. Blockchain applications can precisely identify serious and even dangerous errors in the medical profession. As a result, it can potentially increase the performance, security, and transparency of medical data sharing in the healthcare system. Medical institutions can use this technology to obtain insight and improve the analysis of medical records.
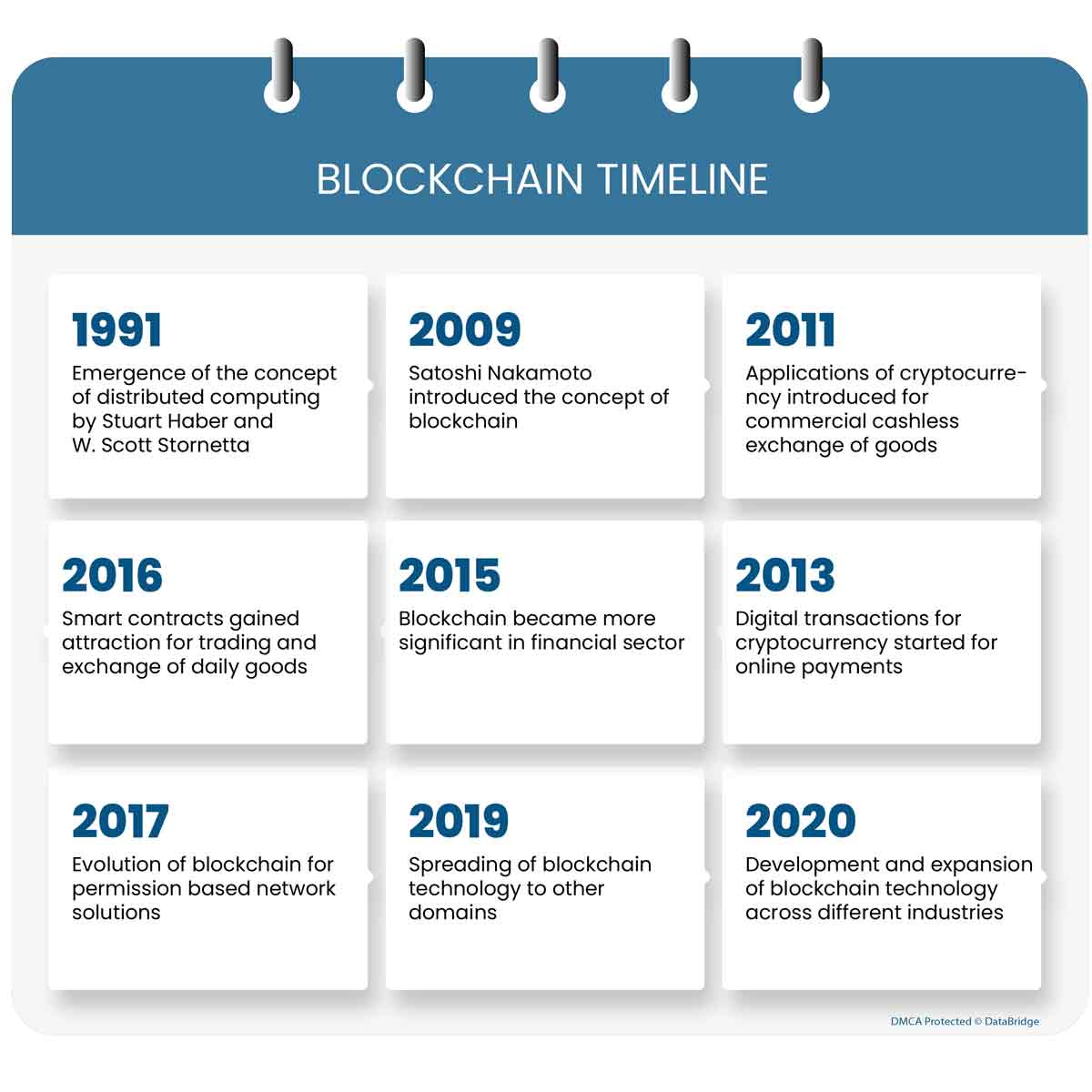
Timeline of the Revolution of Blockchain
What is a Blockchain?
The term "blockchain" refers to a shared, immutable record of a sequence of transactions, each of which is made up of one block and held together by cryptographic keys. These keys or signatures are maintained in shared ledgers and connected by a network of nodes or processes. Each node maintains a copy of the entire chain, which is constantly synchronized and updated. The most revolutionary aspect of blockchain, which is delivered through a carefully balanced mix of advanced cryptography and built-in incentives (in the form of Bitcoin or other crypto-tokens), is that it does away with the need for a centrally controlling authority and instead distributes power among all participants within the blockchain ecosystem. One of the main benefits of a decentralized system is that end-users, especially consumers, would have much more transparency and control over how their data is used. Hence, one of the long-term goals of disruptive blockchain-enabled companies is to decentralize the data economy, reclaiming power from top companies that centralize large datasets for the competitive benefit and instead of controlling how personal and legalized data is used in the hands of individuals and organizations.
This concept is still more theoretical than practical, and it could take a decade or more to come to fruition, if at all. However, over the last few years, blockchain has proven to solve real, but far more specific issues around data reliability and accessibility – such as bad user interfaces, scalability issues, and the need for greater privacy to protect enterprise IP – and has proven to solve real but far more specific issues around data reliability and accessibility.
Need of Blockchain in Healthcare
It has become a great advantage in the healthcare sector in recent decades. In the healthcare system, a blockchain network stores and shares patient data across hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, pharmacies, and clinicians. Blockchain applications can precisely identify serious and even dangerous errors in the medical profession. As a result, it has the potential to increase the performance, security, and transparency of medical data sharing in the healthcare system. Medical institutions can use this technology to obtain insight and improve the analysis of medical records.
Blockchain would play a crucial role in transforming the healthcare sector. In addition to this, the scenario of the health system is moving towards a patient-centered approach, mainly focusing on two main aspects:
- Accessible services
- Appropriate healthcare resources at all times
Until now, data privacy, sharing, and interoperability are the most serious issues in population health management. The solution to this dilemma is to use blockchain. This technology improves security, data interchange, interoperability, integrity, and real-time updating and access when properly implemented. Data security is also a major concern, particularly in the domains of personalized medicine and wearables. The future of big data heavily relies on the technological ambits that ensure data security. Data certainly is the new oil as businesses - big or small aim to leverage it to drive revenues and ROIs. This is also resulting in the fast proliferation of data points that are highly vulnerable if not secured effectively. Patients and medical workers require a secure and simple method of recording, sending, and consulting data through networks; consequently, Blockchain technology is used to address these problems.
Our DBMR team has analyzed and investigated the big data security market and witnessed that the increasing volume of business data generated from multiple sources and the demand for scalable high-security solutions in increasing cyber-attacks are the major drivers associated with it. The major players involved are Oracle, Microsoft, Symantec Corporation, IBM Corporation, and Amazon Web Services.
To know more about the study, kindly visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-big-data-security-market
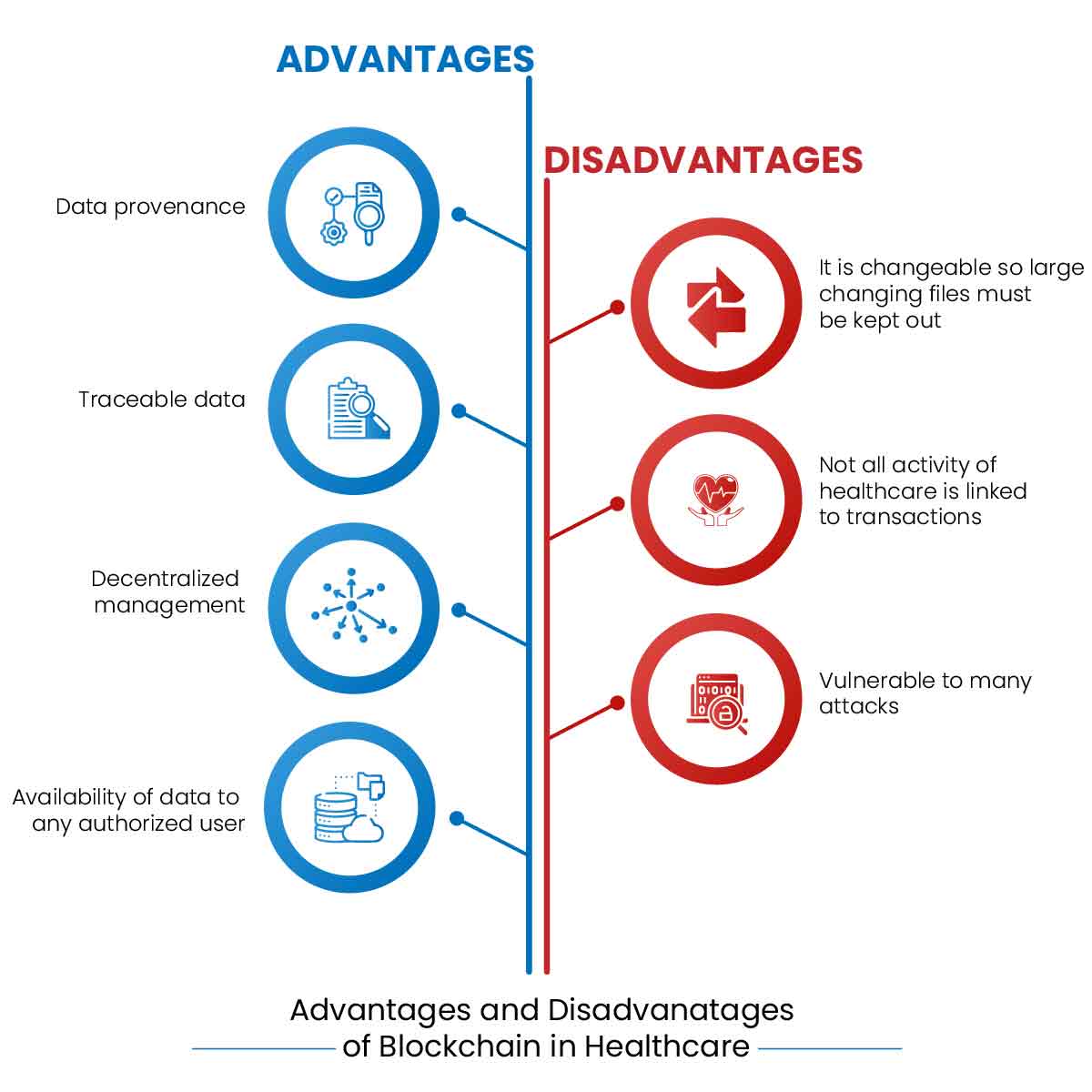
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain in Healthcare
Although the technology of blockchain is becoming more common in the recent scenario but still along with the applications, some disadvantages are also associated with it. Blockchain can be applied to many areas of healthcare, but all healthcare activities are non-transactional. However, because the data contained in the public blockchain is public, you cannot use the public blockchain to store personal information such as health records. This transparency requires providers to consider privacy considerations to ensure protected health information (PHI). Blockchain technology should not be used indiscriminately in healthcare as its data is immutable. You can exclude large files and files that change frequently. All identification data should be removed from the chain. In addition to this, blockchain technology is vulnerable to some types of attacks but provides built-in protection from other types. Blockchain code is open to zero-day attacks, bugs, and social engineering. Therefore, you should pay close attention to information security, especially when used in the medical field. However, the advantages associated with blockchain overpower the disadvantages of the technology.
The applications that blockchain technology holds in the healthcare sector are enormous. There are indefinite applications that this technology withholds that make it a boon to the industry.
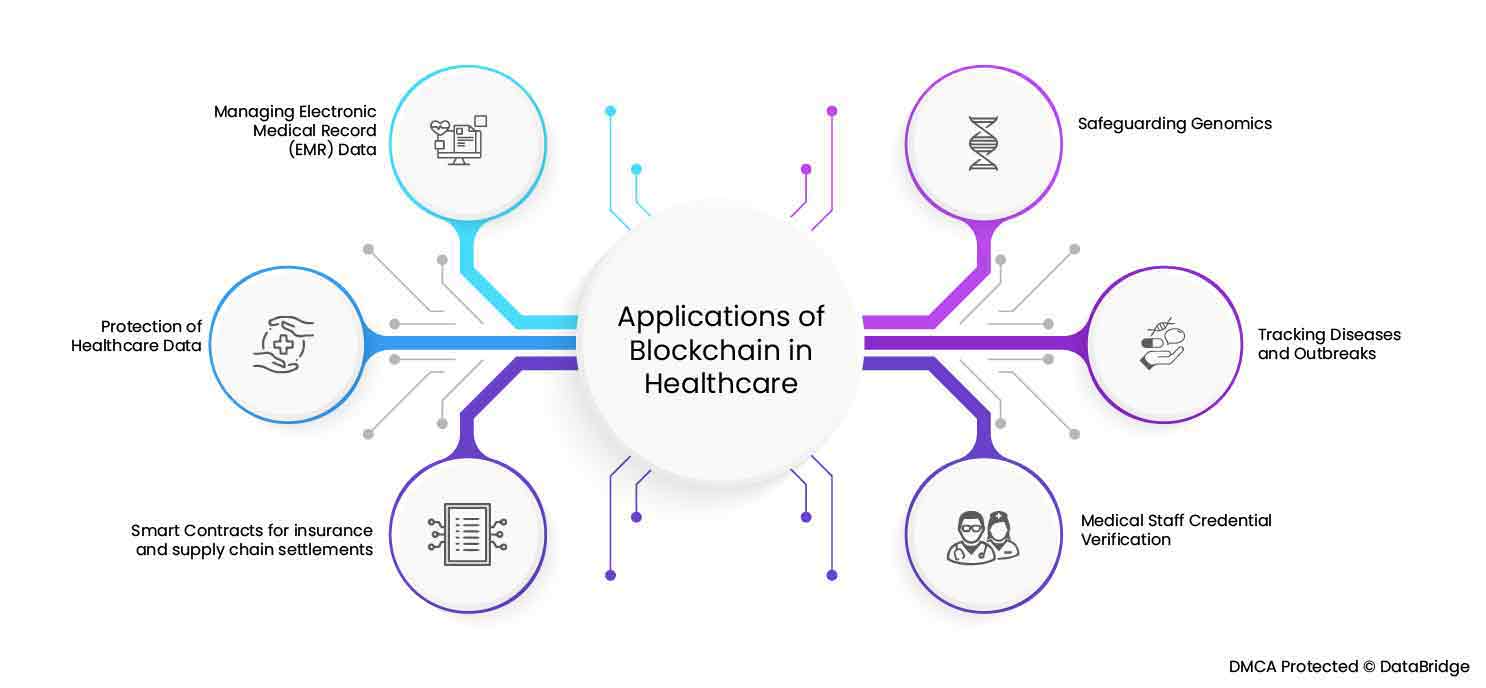
A nationwide blockchain network for electronic medical records will increase efficiency and improve patient health in the long run. In particular, a blockchain is a mutually immutable record of transactions created from a block of connected transactions and held in a digital booklet. Medical details such as patient life, medical device logs, and temperature of medical products can be recorded at the time of shipment to the medical field.
Blockchain makes the entire prescribing process transparent, from manufacturing to pharmacy shelves. Congestion, cargo direction and speed can all be tracked using IoT and blockchain. It offers the possibility to efficiently plan procurement to prevent confusion and shortages in clinics, pharmacies and other healthcare facilities that use certain drugs. The use of blockchain-based digital frameworks helps ensure that logistics data avoids uncontrolled adjustments. Increase trust and prevent records, payments and illegal handling of medicines by different people interested in buying medicines.
Disputes over chargeback claims for prescription drugs and other products by sharing digital contracts between manufacturers, retailers, and healthcare providers in blockchain ledgers, rather than having each player sign a contract for their own version. It can be significantly reduced. Shared smart contracts can be used to manage a patient's health insurance policy. As with other use cases, as this data becomes digitized and easily accessible, insurers can use more sophisticated analysis to optimize health outcomes and costs.
Blockchain technology can be used to track the experience of medical professionals in the same way that it can be used to track the provenance of a medical good. Trusted medical institutions and healthcare organizations can log the credentials of their staff, which helps to streamline the hiring process for healthcare organizations.
The exceptional capabilities of blockchain can aid in real-time disease reporting and the identification of disease patterns that can help identify its origin and transmission parameters.
With many market players bringing DNA sequencing to the individual, genomic data theft has become a topic of major concern. Blockchain can help to prevent this, and even provide an online marketplace where scientists can buy genomic information for research purposes. With improved blockchain security and systems that promote synchronized transactions, blockchain services could be used to enhance the management of healthcare data.
Our DBMR team has analyzed and investigated the electronic medical records(EMR) market and it was witnessed that the market was valued at USD 29,092.13 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 47,640.2 million by 2029, registering a CAGR of 7.30% during the forecast period of 2022-2029. North America dominates the electronic medical records (EMR) market because of the favorable insurance policies, presence of well-established healthcare and leading market players within the region. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period of 2022 to 2029 due to the developing healthcare infrastructure and government initiatives to encourage physicians to adopt electronic health records within the region.
To know more about the study, kindly visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-electronic-medical-records-emr-market
Besides these factors, the healthcare industry must be educated about the security system. Security and trust are the most common worries shared by businesses in the existing system when it comes to information shared between different entities. Information can be entered at any point along the communication chain, causing trust concerns, particularly in the healthcare industry. There are also issues with numerous vendors holding unvalidated versions of the same patient data, leading in various mistakes, inconsistencies, and incompleteness. It's no surprise that healthcare professionals are concerned, given stories of security breaches, personal data tampering, and the ever-present hacking threat. This technology could be the solution to many of these issues because blockchains are cryptographically secure, and the data they contain can be authenticated using digital signatures that are unique to each individual.
Role in Clinical Trials:
Blockchain technology has a role in the aspect of clinical trials as well. In clinical trials, blockchain technology addresses issues or obstacles of false results and data disintegration that do not match the aims and objectives of the research study. Blockchain will strengthen trust in clinical trials. The business analysis platform investigates the evolving market dynamics so that the healthcare sector understands the possibilities. The management of medicines on the blockchain is just another chance to build and monitoring the chain from the manufacturer to the customer by incorporating Blockchain credibility. In relation to clinical trials, decentralization means that they are not done in a single central location. Instead, multicenter collaborative research can also use connected technology to allow participants and investigators to report remotely while remaining within the overall structure of scientific and regulatory controls. Decentralization of clinical trials is one of the essential practices in place to ensure the continuation of clinical research during a pandemic. As a result, electronically submitted patient reports (ePRO) and many other remote solutions are becoming increasingly common. Not only do these approaches generate large amounts of data, as in typical studies, but in many cases, participants may not participate in regular direct follow-up visits with healthcare professionals. Therefore, it also requires robust governance.
Blockchain can keep a tab on the number of repetitive tasks that is associated with the trials via smart contracts and e-contact forms. It amplifies and highlights the importance of integrated systems. Having a unified platform with various capabilities is one significant feature of a blockchain-based clinical process.
However, as W. Clement Stone correctly said, "To every disadvantage, there is a corresponding advantage." One of the important aspect to consider associated with blockchain is the replication rate. Limitations arise in blockchain networks once the data volumes start scaling up. For instance, if 20,000 patients needs to be enrolled and the data needs to be replicated across 1,000 sites, primarily because of the capabilities of current technology. However, some data limitations still exist, which may not necessarily be the case in the future as technologies continue to evolve. In addition to this, blockchain systems require good internet connectivity, so in a rural community, running this technology might pose a problem, and hence implementing such systems can become a challenge.
Our DBMR team has analyzed and investigated the clinical trials market and witnessed that clinical trials market is expected to gain market growth in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. Data Bridge Market Research analyses the market to grow at a CAGR of 5.15% in the above-mentioned forecast period. North America dominates the market due to increasing research and development and rising adoption of new technologies in clinical research. Asia-Pacific is expected to show a rapid and lucrative growth rate in the forecast period owing to the increasing availability of large patient pool facilitating easy recruitment of candidates.
To know more about the study, kindly visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-clinical-trials-market
Dimension of IoT Security in Blockchain
Internet of things (IoT) security can be summarized as the technological segment that is primarily focused on safeguarding connected devices and networks in the internet of things (IoT). One of the biggest trends in digital health is the adoption of remote monitoring solutions. It uses all types of sensors to measure a patient's vital signs to give doctors a deeper understanding of the patient's health and enable more preventative and prophylactic care. However, security is a major issue in the Healthcare IoT, ensuring that patient data is both private and secure and has not been tampered with to generate erroneous information. The connected device may be reliable in an emergency. It is also important that the support system is highly resistant to attacks that interfere with multiple services in order to alert elderly caregivers in the event of a fall or heart attack.
Blockchain encryption allows only authorized parties to access the personal data stored in the blockchain as a unique hash function (a different hash function is created each time the source data is modified, and the user Must have a specific set of encryption keys in order to decode the hash function (to the source data). Once patient data is recorded in the blockchain ledger (as a hash function), it is nearly impossible to tamper with, as all stored copies need to be accessed. Although blockchain has the potential to improve IoT security in healthcare, these use cases are still in the early stages of development and it is not yet clear whether blockchain is the best tool for deployment. Blockchain is worth considering for digital health companies looking for ways to keep remote surveillance devices safe, but only as part of a much broader end-to-end security strategy.
Our DBMR team has analyzed and investigated the IoT Security market and witnessed that the major factors that are expected to boost the internet of things (IoT) security market in the forecast period are the rise in the number of ransomware attacks on the IoT devices to be a critical threat around the world. In addition to this, North America dominates the internet of things (IoT) security market due to the widespread deployment of IoT devices across numerous domains and countries. Furthermore, implementing governing frameworks will further boost the internet of things (IoT) security market in the region during the forecast period. Asia-Pacific is projected to observe significant amount of the internet of things (IoT) security market due to the increase in the mobile workforce.
To know more about the study, kindly visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-internet-of-things-iot-security-market
Blockchain Improves IoT Security. How?
The scanario with normal IoT devices does not lie in the fact that it will eradicate all kinds of attack and will authenticate the system well. That is the present scenario that the IoT devices are facing today. With the addition of blockchain into the IoT devices, the server gets authenticated and it helps to prevent the target attack.
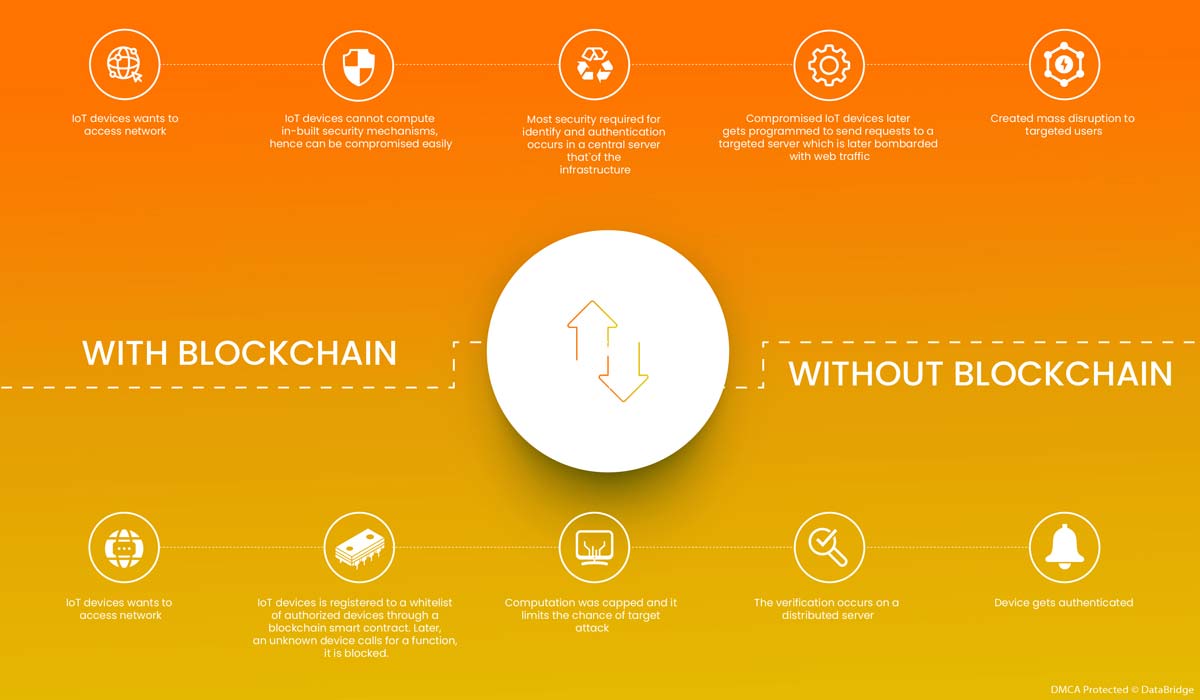
Comparison of two scenarios of Iot Devices that is used in a particular transaction, without or with blockchain
Blockchain Market Overview
Using blockchain in healthcare can protect patient data and improve the overall experience. It also prevents data misuse to prevent it further outbreaks of harmful diseases. Here, is a list of few companies that is associated with blockchain.
- Akiri- Located in Foster City, Akiri manages a network-as-a-service specifically designed for the healthcare sector, assisting in protecting patient health data throughout transportation. The Akiri system is a network and protocol that sets policies and configures data layers while instantly confirming the sources and destinations of data. It does not store any data of any sort. Akiri makes sure that medical information is safe and accessible only to those with the proper permissions at the appropriate times.
- BurstIQ- The technology from BurstIQ enables healthcare organizations to manage vast amounts of patient data safely and securely. With careful adherence to HIPAA regulations, it can store, sell, share, or license data thanks to blockchain technology. The business leverages blockchain to enhance the sharing and utilization of medical data. BurstIQ's platform, which has complete and up-to-date information about individuals' health and healthcare activity, could aid in the detection of opioid and other prescription drug abuse.
- MedicalChain- Located in London, Medicalchain's blockchain preserves the accuracy of medical records by creating a single point of truth. Doctors, hospitals, and laboratories can all request patient information with a traceable origin that keeps the patient's identity safe from prying eyes. The blockchain-based platform used by Medicalchain preserves a record of origin and safeguards patient identification. Medicalchain announced the launch of MyClinic.com in May 2018. MyClinic is a telemedicine platform that allows patients to videoconference with their doctors and pay for those consultations using "MedTokens."
- GuardTime- Being an indutry of cybersecurity or blockchain, Blockchain integration into government and healthcare organisations' cybersecurity strategies is assisted by Guardtime. It recently inked a partnership with a private healthcare provider in the United Arab Emirates to add blockchain to its data privacy systems. The company played a key role in helping to implement blockchain in Estonia's healthcare systems. Guardtime uses blockchain technology in cybersecurity applications, including healthcare. Recently, Guardtime and Verizon Enterprise Solutions collaborated to roll out several platform services based on the Keyless Signature Infrastructure (KSI) Blockchain from Guardtime.
Our DBMR team has analyzed and investigated the cybersecurity market and witnessed that the market was valued at USD 217.90 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 551.18 billion by 2029, registering a CAGR of 12.30% during the forecast period of 2022-2029. North America dominates the cybersecurity market because of the presence of prominent security vendors within the region. Asia-Pacific (APAC) is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period of 2022 to 2029 due to the development of a strong cyber defense ecosystem in the region.
To know more about the study, kindly visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cybersecurity-market
- Chronicled- Located in San Fransisco, The Mediledger Project, a ledger system devoted to the security, privacy, and effectiveness of medical supply chains, was established by Chronicled in 2017. A blockchain network called Chronicle is deployed to guarantee secure delivery and thorough examination of drug shipments. Results from Chronicled's recent MediLedger Project, according to the business, demonstrate that their blockchain-based system "can act as the interoperable system for the pharmaceutical supply chain" and "can meet the data privacy standards of the pharmaceutical industry itself."
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention- Being a Government agency located in Atlanta, Georgia, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating the blockchain to monitor diseases similar to the supply chain. According to US government agencies, blockchain timestamps, peer-to-peer health reports, and data processing capabilities help report illness outbreaks in real-time. By examining the traces of reported outbreaks, scientists can find the origin of the disease and patterns that help control the disease. The CDC can also use the blockchain to track opioid epidemics. The CDC uses the blockchain to monitor illnesses and report outbreaks in real-time. IBM is working with the CDC to develop a blockchain-based surveillance system that allows public health agencies to collect patient and prescribing data more effectively.
- EncrypGen- Located in Coral Springs, Florida, EncrypGen Gene-Chain is a blockchain-based platform that facilitates the retrieval, sharing, storage, purchase, and sale of genetic information. The company protects user privacy by allowing other members to purchase genetic information using secure and traceable DNA tokens. Member companies can use genetic information to build genetic knowledge and develop the industry. The company's blockchain platform makes it easy to find, share, store and purchase genetic information. EncrypGen plans to extend user profiles with self-reported medical and behavioral data. David Koepsell, co-founder, and CEO of the company, said he is working on integrating blockchain payments and testing platforms, as well as forming partnerships with testing companies, analysis software developers, and more.
- Coral Health uses blockchain to accelerate care processes, automate management processes, and improve health. By incorporating patient information into distributed ledger technology, the company connects doctors, scientists, laboratory technicians, and health authorities faster than ever before. Coral Health also implements smart contracts between patients and healthcare professionals to ensure accurate dates and treatments. Coral's blockchain technology accelerates care, automates management processes, and employs smart contracts between patients and physicians.
Blockchain technology reduces complexity, enables unreliable collaboration, and creates unique opportunities for building secure and unchanging information. To shape the future of blockchain, companies are considering mapping and merging the blockchain ecosystem, establishing a blockchain framework for early adopters, and supporting consortiums for dialogue and discovery. One of the most exciting aspects of blockchain technology is the foundation of growth and modularity it provides. While the initial implementation faces the same limitations as of today's technology, blockchain openness will drive and support industry-wide progress over the next few years. Many exciting and creative blockchain solutions have emerged from pioneering companies around the world, but this is just the beginning.
Conclusion:
There are varied applications of blockchain in healthcare owing to inherent encryption and decentralization. It is useful in accelerating the security of patients' electronic medical records, it helps to promote the monetization of health information and help to counterfeit combat medicines. Different healthcare fields can change with Blockchain technology; areas like healthcare, digital agreements allowed by intelligent contracts constitute one of blockchain's most critical applications. The Blockchain potential in healthcare depends primarily on adapting associated advanced technologies in the ecosystem. It includes system tracking, healthcare insurance, medicines tracing, and clinical trials. This technology can well be used to improve patient history management, especially for tracking and the insurance mediation process, accelerating clinical actions with optimized data maintenance. Thus, it can be said that this technology would significantly enhance and eventually revolutionize how patients and physicians treat and use clinical records and improve healthcare services.









