HIGLIGHTS:
The U.S. supported Ukraine with $46 billion in military and non-military aid between January and May 2022
The European Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom have all imposed severe financial and economic sanctions against Russia
China and India did not denounce or support the attack
Fig.1: Bilateral Aid to Ukraine between January 24 and May 10, 2022 ($ Billions)
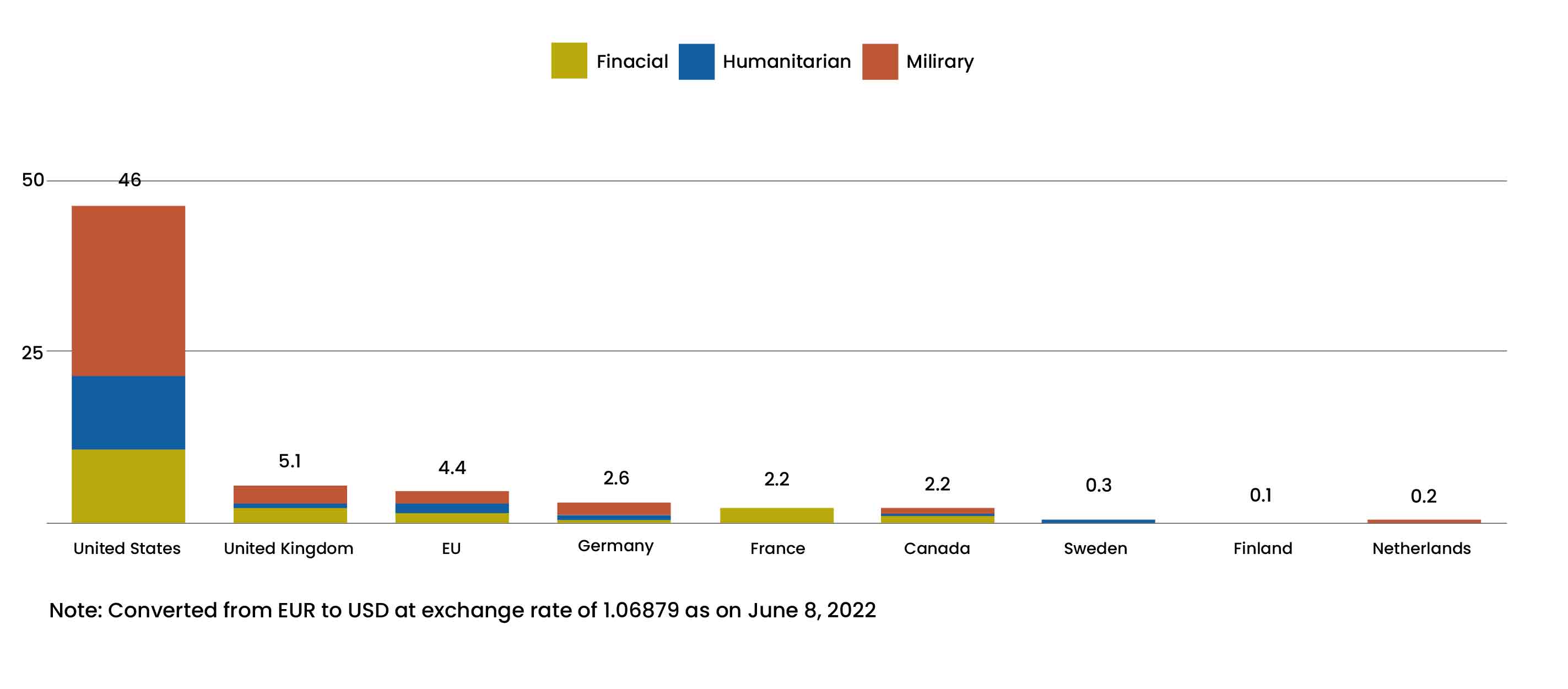
Source: GlobalData
To understand the global response and impact to the war, it is essential to comprehend the relations between these countries. A brief recap of their relations in the 20th century is discussed below:
- 1918- After years of fighting involving numerous nations and forces, Ukraine declared independence from Russia. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk grants international acknowledgment of its independence and sovereignty. Later, independent Ukraine was overthrown by Soviet armies. In 1921, the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic is established, and the Soviet Union annexes Ukraine the following year.
- 1932 and 1933- Millions of people die in a famine in 1932 and 1933 brought on by Stalin's collectivization policies, primarily ethnic Ukrainians in the so-called "bread basket" of the Soviet Union. The name of the catastrophe, "Holodomor," comes from the Ukrainian term meaning "famine."
- 1939-1944- Poland and Romania cede what is now western Ukraine to the Soviet Union between 1939 and 1944. Later, the Soviet Union is invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany and the Axis powers, wreaking havoc on Ukraine.
- 1991- Ukraine proclaims its independence, with 92 percent of voters supporting the decision in a referendum. Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus signed an agreement formally acknowledging the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
The relations between the two countries became hostile in February 2014. This indicates that tension had been brewing between the two former republics of the Soviet Union for almost a decade now, ultimately leading to Russia's invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022. A timeline of events in short, as mentioned below would allow a more precise picture to this:
Timeline of Russia-Ukraine Conflict
2014- In February, protesters in Ukraine overthrew President Viktor Yanukovych. He had been supportive of Russia's objectives. More than 100 people were killed during the revolution in demonstrations centered on the Maidan, or Main Square, in the Ukrainian capital of Kiev. Following this pro-western uprising, the interim administration eventually signed a trade agreement with the E.U. that was regarded as a first step toward enlisting in the organization. At the conclusion of the Euromaidan protests in February 2014, the Revolution of Dignity, also known as the Euro-Maidan Revolution, occurred in Ukraine. Deadly clashes between protesters and security forces in Kyiv led to the removal of elected President Viktor Yanukovych and the overthrow of the Ukrainian government. Russia then annexed the Crimean Peninsula. Later, the Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic declared their independence, supported by secessionists in eastern Ukraine. They invade Ukraine and start a war. The secessionist conflict was still ongoing in the eastern region known as Donbas. After that, it moves West. Over the course of the fight, almost 13,000 Ukrainian military and civilians perished. For years, the front lines had hardly moved.
2014-2015- The Minsk Accords are a set of ceasefire agreements signed by Russia, Ukraine, France, and Germany. These agreements are seen as vague by many. The Minsk agreements were a set of international accords that aimed to end the conflict in Ukraine's Donbas. The first, referred to as the Minsk Protocol, was drafted in 2014 by the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), Russia, and the Trilateral Contact Group on Ukraine, with mediation provided by the presidents of France and Germany in what is known as the Normandy Format. The agreement was signed on September 5, 2014, in Minsk, Belarus, by members of the Trilateral Contact Group and the then-leaders of the self-declared Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) and Luhansk People's Republic, without acknowledging their official status (LPR). This pact sought to put into effect an immediate ceasefire after numerous prior attempts to stop the combat in the area. The Minsk II agreement, which was signed on February 12, 2015, was a revision and update of the original Minsk accord because it failed to put an end to fighting. This agreement included a number of actions, such as a ceasefire, the removal of heavy weapons from the front line, the release of prisoners of war, constitutional reform in Ukraine that granted certain Donbas regions self-government, and the reestablishment of control of the state border to the Ukrainian government. Fighting decreased after the agreement was signed, but it was never totally resolved, and its terms were never fully carried out. The parties to the Normandy Format concurred that Minsk II will continue to serve as the cornerstone of any ensuing peace agreement.
April 2019- Volodymyr Zelensky, a former comedian, was elected president of Ukraine with a sizable majority on a platform of restoring Donbas to the country and establishing peace with Russia. With 43% of the party-list vote in the parliamentary election of July 21, 2019, Zelenskyy's political party, Servant of the People, became the first single-party majority in contemporary Ukrainian history. 254 of the 424 seats were won by his party. Zelenskyy pledged to end Ukraine's protracted conflict with Russia during his presidential campaign, and he has made an effort to communicate with Vladimir Putin of Russia. In 2021, tensions between his administration and Russia increased, reaching a peak in February 2022 with the beginning of the current full-scale Russian invasion. Zelenskyy proclaimed martial law in all of Ukraine and a general mobilization of the armed forces once the invasion began. He has received tremendous recognition from the international community for his leadership during the crisis and has been dubbed a symbol of the Ukrainian resistance. Zelenskyy has been rated as one of Ukraine's greatest presidents in public polls.
2021–2022- Russian President Vladimir V. Putin tries to stop Ukraine from moving closer to the U.S. and its allies. Mr. Putin wants "security guarantees," such as NATO's promise that Ukraine won't ever join the organization and that it will withdraw its soldiers from nations that joined after 1997. Given the strong cultural ties between Russia and Ukraine, many Russians consider Kyiv to be the cradle of their country. The main goal of the Russian leader was to invade Ukraine, overthrow its government, and end Ukraine's aspirations to join NATO, a Western defensive alliance. He gave up trying to take over the Ukrainian capital Kyiv after a month of failures and shifted his attention to the east and south of the country. He declared his intention to "demilitarize and de-Nazify Ukraine" when he began the invasion on February 24. His goal was to defend those he claimed had been the targets of the Ukrainian government's eight years of intimidation and genocide. Assuring Ukraine's neutrality was shortly added as a new goal.
AMERICA'S RESPONSE TO THE CONFLICT:
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has sparked heated discussion in America about how the U.S. should react and how much the attack threatens democracy. There have been concerns regarding the nature of the Biden administration's response, the degree to which the Russian attack has energized popular support for NATO, and whether the war has put an end to the post-Cold War era as we have known it. It has also sparked debate over how much the recent partisan split in America has been weakened due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Some stats and figures in this regard are:
- Ukraine has received $13.6 billion in military and non-military aid, and Congress is currently debating an extra $40 billion. at least 3,000 additional U.S. soldiers were sent to Poland, Germany, and Romania
- At least 3,000 additional U.S. soldiers were sent to Poland, Germany, and Romania. In the event that a NATO Rapid Response Force is activated, 8,500 US troops have been placed on high alert
- Even if most Americans do not simply believe Russia to be an adversary or Ukraine to be a full ally, Americans see Ukraine as far more favorable than Russia. According to the University of Maryland Critical Issues Poll, a total of 34% of respondents, including 30% of Republicans and 40% of Democrats, define Russia as an enemy, 38% as a "unfriendly country," and 24% as neither friendly nor unfriendly. 19% of people think of Ukraine as an ally, while 54% of people say it is a "friendly country," and 25% think it is neither friendly nor unfriendly
- Even if the war continues, substantial bipartisan majorities continue to be opposed to sending American troops to Ukraine. 65% of people, including 68% Republicans and 62% Democrats, oppose deploying soldiers. The Ukrainian army should be provided with military hardware, according to a vast majority, 83%. Similarly, 89% of respondents support maintaining strict sanctions against Russia
- Americans are divided in their opinions along party lines but generally see the U.S. reaction to the Ukraine issue positively compared to adversely. 49% of Republicans and 69% of Democrats say they have a favorable opinion of how the United States has responded, while 31% of Republicans and 13% of Democrats have an unfavorable opinion. Another 20% are neutral, expressing neither support nor opposition. 51% of Americans believe that the United States responded "appropriately," whereas 56% of Republicans believe that the United States has "underreacted." President Joe Biden's decision to stop importing Russian energy has the approval of two-thirds of Americans, including 56% of Republicans and 80% of Democrats.
FIG.2: Monthly average prices of crude oil and natural gas, Jan 2018-Mar 2022
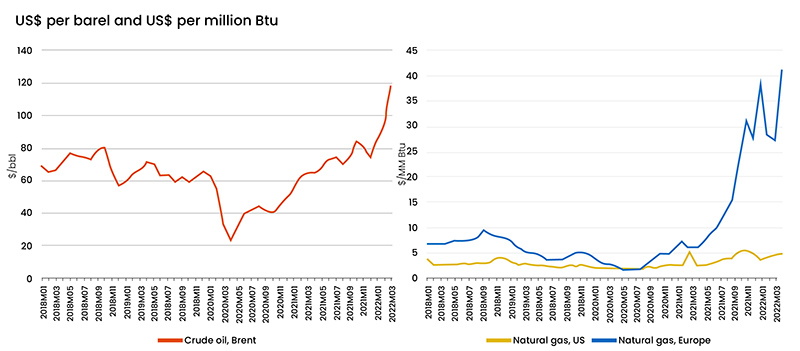
Source: World Economic Forum
Chart 2 demonstrates the sharp increase in fuel prices across the globe. Prior to the Ukraine War, this began in 2020. A barrel of oil cost $118 in March 2022, which is 38 percent more than in January 2022 and 81 percent more than the previous year. On March 8, the daily oil price peaked at $128 per barrel, but by April 1, it had dropped to just $104 per barrel. The WTO explains that natural gas prices differ between areas. Between January and March, the price of natural gas in Europe increased by 45 percent to $41 per million Btu (a unit of heat content). The WTO reports that prices in the United States have "generally stayed low," at about $4.9 per million Btu.
The oil and gas composites market was valued at USD 1,986.00 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 2956.66 million by 2029, registering a CAGR of 5.10% during the forecast period of 2022-2029. The market report curated by the Data Bridge Market Research team includes in-depth expert analysis, import/export analysis, pricing analysis, production consumption analysis, and climate chain scenario. The oil and gas composites market is segmented on the basis of resin type, fiber type, product type and application.
To know more, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-oil-and-gas-composites-market
EUROPEAN UNION'S RESPONSE TO THE CONFLICT:
Strong economic penalties, in line with U.S. policy, prohibiting the sale or supply of aircraft and related equipment to Russian airlines, as well as dual-use and oil-related technology. Limiting Russian diplomats' access to the E.U. and those complicit in Russia's invasion of Ukraine, the E.U. will actively give lethal weapons to Ukrainian soldiers as part of a $500 million military aid package, marking the first time that has ever been done. The 27-member European Union (E.U.) has reacted to Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 with unparalleled cohesion and swiftness. Congress is interested in E.U. policy responses and coordination with the United States because the EU is a significant partner of the United States. Sanctions imposed included:
- Putting travel and asset freezes on 1,091 Russian leaders, lawmakers, and other elites, and freezing the assets of 80 businesses (Russian President Vladimir Putin and Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov are subject only to asset freezes).
- Extending sanctions already in place against Russia's financial industry, limiting interactions with the Central Bank, and preventing access to its reserve holdings.
- Russian imports of liquor, coal, steel and other raw commodities will all be banned starting in August 2022.
- Prohibiting the shipment of luxury items to Russia as well as specific exports in the aviation, maritime, technological, and oil refining industries (such as semiconductors).
- Extending the reach of export restrictions on products and technologies with dual uses.
- Through the European Peace Facility, the E.U. has announced a total of €1 billion (about $1.1 billion) in funding for military aid to Ukraine (EPF). This budget includes funds for lethal equipment for the first time, totaling €900,000,000 ($987,000,000); the remaining €100,000,000 ($110,000,000) goes toward nonlethal supplies. Equipment delivery is the responsibility of the member states, who may be compensated from the EPF for assistance rendered since the beginning of 2022.
- Approximately 60% of the 4.5 million refugees from Ukraine have arrived in Poland. In order to grant Ukrainian nationals and other legal residents of Ukraine instant residency rights and access to benefits throughout the E.U., the E.U. has created a temporary protection mechanism.
- The E.U. has sent emergency supplies in kind and humanitarian aid of €550 million (about $598 million) to Ukraine and its neighbors. The E.U. promised to provide an additional €1 billion in aid for refugees and internally displaced people on April 9, 2022.
- President Biden promised to work with "international partners" to increase LNG supplies to the E.U. this year while he was in Brussels on March 24–25, 2022. He also plans to increase yearly U.S. LNG shipments through 2030. Additionally, Biden stated that the United States will accept up to 100,000 Ukrainian refugees and emphasized the tight cooperation between the United States and the European Union in this area.
- Since 2015, U.K. has been in Ukraine offering instruction and non-combat supplies. They sent Ukraine 2000 NLAW anti-tank missiles in 2022 and said in March that they would give Ukraine a Starstreak anti-air system. Economic sanctions against Russian banks, oligarchs, officials, and companies have been implemented by the U.S. and the E.U., although more slowly. Germany has vowed to adhere to the NATO goal of spending 2% of GDP on defense. A 110 billion euro ($100 billion) off-budget modernization fund will also be established. Prior regulations that restricted their participation in armed conflicts and the delivery of deadly equipment to a nation at war have been reversed. Scholz, the chancellor, declared that Ukraine would receive 500 Stinger missiles and 1,000 AT missiles.
- Rarely, both Finland and Sweden have waived their neutrality and given the Ukraine military support.
- Finland has donated 70,000 field rations, 1,500 rocket launchers, 150,000 rounds, 2,500 assault rifles, and 2,500 rocket launchers.
- Sweden has given over 5,000 anti-tank weapons (most likely Carl-Gustaf and NLAW systems).
- In the past, France has provided Ukraine with $60 million in lethal military hardware, and as of late, they have committed to providing a further €300 million in lethal hardware, including anti-tank, anti-aircraft, and "digital weapons" systems.
ASIA-PACIFIC'S RESPONSE TO THE CONFLICT:
Southeast Asian nations have reacted to the Russian invasion of Ukraine in a variety of ways, from outright denunciation to continuous abstention. The relationship with China is crucial in this context in terms of geopolitics. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) responded to the Ukraine War very feebly. The statement from the ASEAN foreign ministers advocated for peaceful negotiation and dialogue but avoided using the phrases "Russia" or "invasion." This is in keeping with the association's guiding principles of balancing between larger states and not meddling in the internal affairs of other nations. In addition, Russia is Southeast Asia's top weaponry supplier, according to data from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, and a significant trading partner. Some important takeaways are:
- China has not denounced or supported the attack, citing its fundamental foreign policy tenet that it does not meddle in countries' domestic affairs. China, however, has made it clear that it is prepared to mediate a ceasefire and maybe even go further to end the war through diplomacy.
- India has neither denounced nor approved the attack, despite China's Foreign Minister Wang Yi signaling China's support for Ukraine's sovereignty. With Prime Minister Modi referring to Putin as a "dear friend," they have a close relationship with Russia. A significant portion of India's military hardware is Russian in origin. However, despite widespread expectations, India was one of the 34 countries in the U.N. to abstain from a vote denouncing Russia's invasion.
- With Laos and Vietnam abstaining, nine out of the eleven nations voted in support of the first U.N. resolution. Only the Philippines and Timor Leste voted in favor of the resolution to ban Russia from the Human Rights Council; the majority of Southeast Asian nations abstained.
- Singapore's response to the sanctions and its outright rejection of Russia's conduct was the region's most robust response, and it demonstrated the little state's importance and dedication to the global order. In Southeast Asia, Singapore has the best-equipped military and the most significant military budget per capita. Other nations, especially important states such as Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia, have made more careful public statements.
- The tacit removal of the head of the army-owned television channel "Channel 5", which had been representing strongly pro-Russian positions and spreading false information in its programs until late March, is a striking illustration of the efforts made by Thailand's authorities to maintain their neutrality. In Thailand, much of the old elite support Russia's war of aggression, similar to Myanmar, while younger pro-democracy activists sharply denounce Russian policies.
- At the March 2, 2022, special session of the United Nations General Assembly, the Northeast Asian democracies Japan and South Korea denounced the Russian invasion of Ukraine in late February. Fundamentally, this was a value-based choice. Both nations consider themselves to be a part of the international coalition of democratic forces.
- However, political elites and the general public in both countries are greatly influenced by the regional political climate at the same time. On the one hand, North Korea is feared as an aggressive and evasive neighbor who is developing its nuclear arsenal and conducting frequent ballistic missile tests. On the other hand, Japan at least has territorial disputes with the two dominant nations in the area, China and Russia, which pose a threat of escalation in a time of crisis. Such ideas of threat were made real by the attack on Ukraine.
- China is by far the most significant trading and investment partner for both nations, although there are also close economic links with Russia. The Japanese government has joined Western sanctions against Russia. Energy imports are an exception, as they are in Europe, despite Japan's not relying on Russia to the same extent as Germany. At first, South Korea tried to avoid endangering its economic goals in trading with Russia by imposing sanctions. However, since February, the U.S. has applied significant political pressure to the government to join in with broad trade penalties against Russia.
- Leading governments of the E.U., the U.S., and their coalition allies have been pushing for strong sanctions against Russia since the start of the war in Ukraine. These nations are not at all pleased with New Delhi's impartial stance. Their message is crystal clear: India needs to be more aggressive with Russia. Many ambassadors from other countries, including those from the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, and the Netherlands, have recently visited India. The "West" is urging India to adopt a more "principled" stance toward Russia, change its stance at the U.N. and other international forums, stop purchasing oil from Russia, and even forgo a trade agreement with it based on the rupee and the ruble that might work around the sanctions.
- India's position on the situation in Ukraine is based on "an immediate cessation of violence and cessation of hostilities," "a return to the path of dialogue and diplomacy," and "a global order based on international law, the UN Charter, and respect for the territorial integrity and sovereignty of all states," according to Indian Foreign Minister S. Jaishankar. Jaishankar stated that decisions about such issues in India's foreign policy would be made in accordance with national interests and under the direction of his nation's thoughts, perspectives, and interests. In resolutions passed by the U.N. Security Council and General Assembly denouncing Moscow's conduct, India has consistently refrained from voting. However, India's Prime Minister Narendra Modi has had discussions with President Putin and Zelenskyi about what India "might do to urge a suspension of hostilities" and conversation to resolve and de-escalating tensions. On Ukraine's request, humanitarian aid and medical supplies shipments have been dispatched there.
- India's reaction to the Ukraine War is not expected to change, despite Western pressure and India's basic and increasing proximity to the West. This is due to the intricate and strong geopolitical factors and national interests at play. The emphasis on "conversation and diplomacy" reveals India's perspective on the conflict: According to India, a geopolitical struggle between NATO and Russia originates in the post-Cold War security system.
- Even the political opposition in India has praised the Indian government for its stance, which is unusual. The diplomatic "friendship" between India and Russia dates back to the 1950s; despite the fact that the two countries relations have not been the same for a number of years, Russia has supported India when other nations have not. For instance, Russia has frequently defended India's interests at the U.N. through its veto power, notably concerning the Kashmir problem. During the Cold War, when the United States partnered with Pakistan, Russia (or the Soviet Union at the time) stood solidly with India. The vast majority of Indians also supports the current stance of the Indian government toward Russia.
The refractories market is expected to witness market growth at a rate of 4% in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. Data Bridge Market Research report on the refractories market provides analysis and insights regarding the various factors expected to be prevalent throughout the forecast period while providing their impacts on the market's growth. The refractories market is segmented on the basis of product type, alkalinity, manufacturing process, fusion temperature, form, and end user. Some of the major players operating in the refractories market are RHI Magnesita, Vesuvias, Imerys, Saint Gobain S.A., Ruitai Materials Technology Co., Ltd., Harbison Walker International, Coorstek, Inc., IFGL Refractories Ltd., Refratechnic Cement GmbH, and HarbisonWalker International among others.
To know more, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/russia-refractories-market









