Electronic health records were used to store and retrieve clinical data and other documents as early as 1965. Most healthcare organizations have migrated from paper to electronic health records over time, allowing the idea of interoperability to develop and expand. Before understanding the concept in detail, let us discuss a few highlights about electronic health records as below:

Fig.1 Benefits of EHR
- Better Care Quality- Quick access to patient records by EHR makes it possible to treat patients more effectively. They improve the practice's operational effectiveness while also assisting with treatment effectiveness. On the side of the healthcare provider, most EHR gives doctors access to health analytics that support pattern recognition, diagnosis prediction, and therapy recommendation. Instead of depending solely on trial-and-error techniques, these analytics produce more effective overall patient results the first time. Patient portals, which patients can access, provide them with access to past medical data such as lab and imaging results, prescriptions, diagnoses, and more. Patients and doctors can connect by exchanging notes, instant messages, and even video calls.
- Increased efficiency- Physicians can use the built-in templates in EHR to record frequent patient complaints or difficulties. These templates are frequently customized to match particular specializations or a doctor's unique requirements. EHR platform use of artificial intelligence (AI) is increasing. It aids doctors in making diagnoses and deciphering patient histories. A few businesses have also added voice recognition functionality so that suppliers can speak questions to the platforms. For most healthcare institutions and medical specializations, e-prescribing is now considered normal. Depending on their locations, several healthcare organizations around the nation are now required to write prescriptions electronically. This lowers the prevalence of opioid abuse and addiction among regulated substances. From the point of care, prescriptions can be electronically transmitted to the pharmacy. Further, this system enables the physician to monitor any possible drug-to-drug or drug-to-allergy interactions that may or may not occur due to ongoing patient treatment.
- Accurate Patient Data- Electronic files were initially introduced as a replacement for paper medical records to make storing and accessing patient information more accessible. Still, they also provide several other benefits. One benefit of electronic record storage is the absence of the possibility of sensitive data being stolen, lost, damaged, or altered. Digital records can also eliminate mistakes and errors brought on by illegibility and illegible handwriting. Doctors can update patient information in real-time to provide other healthcare providers with an accurate, up-to-date patient file. Every doctor or specialist involved in a patient's care can be reached through this electronic record. Continuity is particularly beneficial since it gives doctors a thorough background of the patient's medical history, which is especially important when a patient switches providers or sees a new doctor.
- Revenue Improvement- Every company aims to increase income. The same frequently holds for healthcare companies. EHR offers capabilities for billing and payments that help manage income and guarantee payments. Claims that contain mistakes or coding flaws can be automatically cleaned up to prevent rejections. This feature helps speed up reimbursements without losing or delaying claims by increasing the percentage of insurance claims accepted the first time. EHR also makes it simple for doctors to record every detail of a patient's visit, making it simple to back up specific claims. Government agencies offer financial rewards to medical practitioners that set up and use EHR systems. Organizations can earn tens of thousands of dollars by installing a recognized solution and fulfilling the requirements for meaningful use.
- Additional Features- As medical practices grow, third-party EHR software can develop and scale up to incorporate more patients. When practices decide to join a group practice or an accountable care organization, cloud-based EHR can integrate patient populations. EHR is easily accessible thanks to online access. Users of third-party managed EHR can log in and access their data from any location with internet access. These platforms enable provider collaboration and allow patients to participate in their care. Accessibility enables healthcare professionals to address patients' inquiries and worries from any location. EHR systems are adaptable to a practice's specific requirements because every practice is unique. A practice's workflow can be customized using an EHR package, which makes switching to a new system very painless.
The discussion above directly and indirectly points to the advantages of an interoperable healthcare system. The electronic health record system falls under the extension of healthcare interoperability. The electronic exchange of patient data between various EHR systems and healthcare providers is made possible by interoperable electronic health records (EHR). The simplicity with which doctors can treat their patients is increased through healthcare interoperability, and it can also assist patients in navigating the healthcare environment. Although interoperability may be at the heart of electronic health records, there are different levels at which a healthcare organization can communicate with those providing care. Because it is intended to enhance patient outcomes and patient safety through improved healthcare communication, EHR interoperability is crucial. Medical professionals can treat patients at any point of care within their network to the best of their abilities because interoperability provides access to clinical data regardless of the caregiver's location. This is true even if the data originates outside of the health system. Better workflows, less uncertainty, and data sharing between EHR systems and healthcare stakeholders are all made possible by EHR interoperability. In the end, an interoperable environment enhances the provision of healthcare by making the appropriate data accessible to the right individuals at the appropriate time.
When the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, which provided $19.2 billion for health information technology to assist hospitals and doctors' offices in implementing electronic health records in their daily operations, was passed in 2009, this was further strengthened. To communicate, interpret, and use data cohesively through interoperability, healthcare organizations can now access and use a variety of healthcare information apps. By allowing data to be accessed within and across organizational, regional, and national boundaries, health data exchange architectures, application interfaces, and standards enable seamless mobility of information to maximize the health of as many populations as feasible internationally.
In a recent article, the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) stated that there are now four interoperability levels used within healthcare companies. These levels consist of:

Fig.2: Four Levels of Interoperability in Healthcare Systems
- Foundational (Level 1): Establishes the interconnectivity criteria necessary for one system or application to safely share data at the foundational (Level 1) level. The lowest degree of interoperability is known as easy transport. Data is securely transported from one system or device to another without being interpreted or put into a specific format. For instance, a nurse might manually enter the information from a PDF file of a patient's most recent lab results into the patient's health record.
- Structural (Level 2): Specifies how data interchange is organized and formatted, including how data fields are interpreted. All the data is standardized to a specific format when structural interoperability, or structured transport, is achieved so that various systems or devices may interpret it. This data is arranged in a specific order to enable the receiving system to recognize particular data fields automatically. Records can be consistent, consolidated, and easily move between systems, thanks to structural interoperability offered by data standards such as FHIR and HL7.
- Semantic (Level 3): Provides for common underlying models and codification of the data, using data elements with established definitions from readily accessible value sets and coding vocabularies, giving users a shared understanding and meaning. Data exchange across systems with utterly distinct data structures is done at the semantic level of interoperability, also known as semantic transport. An easy illustration is provided by imaging systems, which support a variety of specialized DICOM and non-DICOM picture formats. Without regard to the image's original format or source, semantic interoperability allows for the transfer, interpretation, and incorporation of images between different systems. However, since systems present the same information in many ways, deciding what data to gather and convey can be challenging. Because of this, some professionals argue that artificial intelligence will be required to accomplish complete semantic interoperability.
- Organizational (Level 4): Governance, policy, social, legal, and administrative issues are included in organizational (Level 4) considerations to help with secure, frictionless, and timely data communication and use both inside and between organizations, entities, and people. These elements enable end-user procedures and workflows that are integrated, shared, and based on trust. The seamless data flow between distinct organizations with various criteria, policies, and purposes is referred to as organizational interoperability. Innovations in governance, policy, and technology are required to ensure that integrated workflows, security, and consent amongst various parties are achieved at this level of interoperability. However, other experts contend that organizational interoperability rather than semantic interoperability represents the ultimate level of interoperability.
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the healthcare interoperability solutions market is expected to reach USD 139.93 million by the year 2029, at a CAGR of 8.40% during the forecast period. The advancements in software technology extend profitable opportunities to the market players in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. Additionally, a high emphasis on streamlining imaging workflows will further expand the future healthcare interoperability solutions market's growth rate. "Healthcare providers" accounts for the largest end-user segment in the healthcare interoperability solutions market owning to the presence of government mandates and rise in healthcare costs. North America dominates the healthcare interoperability solutions market because of the strong base of healthcare facilities and presence of major key players within the region. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period of 2022 to 2029 due to increased government initiatives for eHealth, rise in medical tourism, and the growing demand for quality healthcare in the region. Some of the major players operating in the healthcare interoperability solutions market are Allscripts Healthcare, LLC, Cerner Corporation, Epic Systems Corporation, Infor, iNTERFACEWARE Inc., InterSystems Corporation, Jitterbit, NXGN Management, LLC, Koninklijke Philips N.V., ViSolve Inc., Orion Health group of companies, OSP Labs, AM HEALTHCARE TECHNOLOGY, Deevita LLC, GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY, and IBM among others.
To know more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-healthcare-interoperability-solutions-market
Concept Discussion:
It has always been difficult to securely access and share health data. Health data is sensitive and needs a high level of privacy and security, which makes sharing it challenging. However, not having access to it when required could have serious consequences. Lack of interoperability can cause a population's or an individual's health needs to be misunderstood, resulting in subpar results and more expensive treatment. To simplify, below are the examples of healthcare interoperability:
- On their cellphones, consumers can purchase insurance and healthcare services.
- A web or mobile application streamlines the patient's experience throughout the customer journey and allows for more informed choices as they look for, get, and pay for care.
- Decision-makers will be able to track their routine PPE use and have accurate information during emergencies, such as pandemics, thanks to the regular entry of standardized data into an application for monitoring personal protective equipment inventory by hospital networks, suppliers, and emergency stockpiles.
- Exchange of documents takes place through federated repositories.
- Through standards-based APIs, Medicare Advantage, Medicaid and Children's Health Insurance Program FFS, Medicaid and Children's Health Insurance Program managed care, and QHPs on the FFEs can access patient healthcare claims and clinical data.
- Payers can communicate with their members via email, SMS, online portals, and post using an omni-channel platform.
- Payers respond to requests by exchanging patient data from their systems.
- On patient portals, patients can access their electronic medical records or EMRs.
- Hospitals notify other healthcare providers of events such as admission, discharge, and transfer.
- So that doctors may access patient information whenever they choose, including on their cellphones, a healthcare company keeps patient data from a chronic disease management app on virtual private servers.
- A patient's health information is shared through a mental health app with the EHR/EMR of their healthcare providers.
In the context of healthcare, interoperability refers to the prompt and secure integration and use of electronic health data to improve individual and population health outcomes. Interoperability and data sharing are going to be more and more important for providing exemplary healthcare as populations throughout the world age, and people live longer. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality in the US, at least two chronic mental or physical disorders affect two out of every three older people.
Approximately 66% of US healthcare costs are currently attributed to treating patients with numerous chronic illnesses. Health data interoperability benefits businesses in the healthcare sector in addition to assisting doctors and other healthcare professionals in getting a fuller picture of their patients. Health plans would better know their utilization rates and service demand if health information systems were more interconnected. Access to demographic data would allow government service providers to identify trends and address the needs of their constituents.
Furthermore, life science firms could use substantial datasets to facilitate quicker, more accurate research. Better interoperability would enable enterprises to cease thinking of people as patients one day, health plan members the next, and app users the next. Instead, industry decision-makers could begin examining how people obtain and use health information, regardless of its source, to promote better service models, pursue improved patient safety, and enhance the experiences of the clients they serve. Modern consumers have high standards regarding information access, and many increasingly anticipate having constant, easy access to their health and care records. To facilitate the smooth and secure sharing of electronic health information, several healthcare institutions are creating health information exchanges (HIE), specialized networks that depend on compatible technologies. Although the adoption of EHRs was a positive first step in the development of HIEs, there are still numerous obstacles to be solved before interoperability will be at the level required to reap the full benefits of HIEs. These challenges/ restraints/ demerits/ disadvantages include:
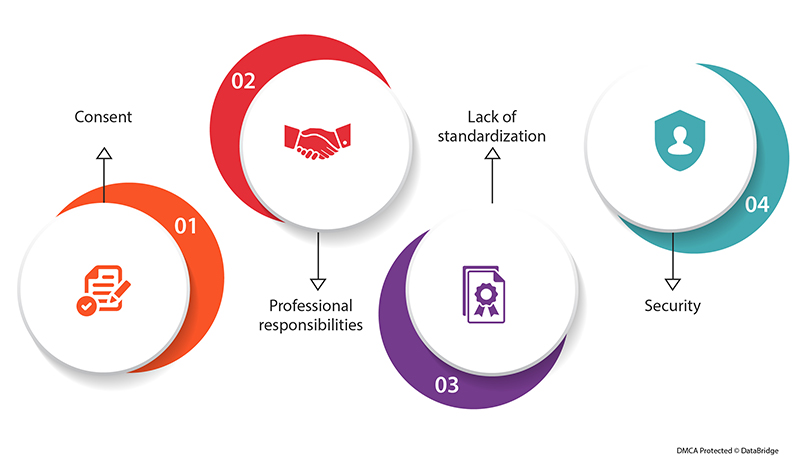
Fig.3: Challenges Ahead of Electronic Health Records Interoperability
- Consent: It's not always obvious when patient consent is required or to what degree of consent, due to the development of digital health systems that allow health information to flow freely from provider to provider. It makes sense that healthcare organizations would be cautious in this situation and err on the side of not disclosing information.
- Professional responsibilities: People must learn how to use new recordkeeping tools as they are introduced. Since EHR systems frequently support administrative and billing operations better than physicians' needs, healthcare practitioners are frequently cautious of new systems.
- Lack of standardization: Many healthcare providers and systems use customized EHR systems that can be challenging to convert to a standard format and share with others, despite standard record formats such as FHIR and HL7 becoming more prevalent and new regulations pressuring EHR vendors to provide APIs that support interoperability.
- Security: With the rise in cybersecurity attacks on healthcare systems, it can be challenging for healthcare companies to strike a balance between the requirement for patient privacy and the need to secure critical information.
Stakeholders can expect much from the interoperability scenario in the coming future. For all parties involved, healthcare interoperability has a lot to offer. It's a game-changer for the care you provide and your overall effectiveness, which is what matters most. First things first, though. Everyone, from patients to insurers, should know what it means. Following is the discussion in this regard:
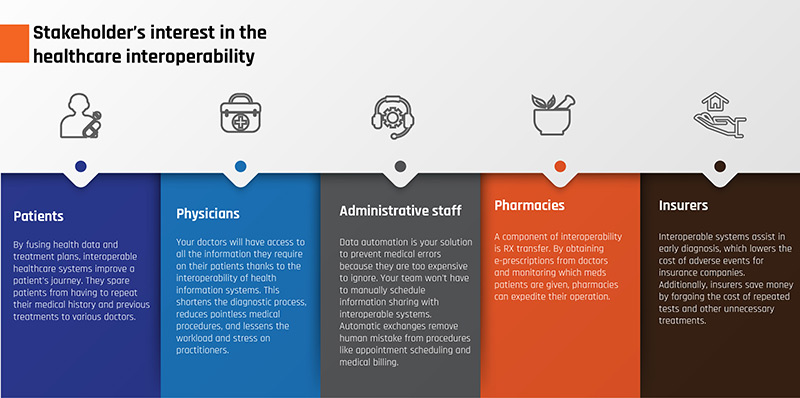
Fig.4: Stakeholder's Interest in the Healthcare Interoperability
- Patients- By fusing health data and treatment plans, interoperable healthcare systems improve a patient's journey. They spare patients from repeating their medical history and previous treatments to various doctors.
- Physicians- Your doctors will have access to all the information they require on their patient's thanks to the interoperability of health information systems. This shortens the diagnostic process, reduces pointless medical procedures, and lessens the workload and stress on practitioners.
- Administrative staff- Data automation is your solution to prevent medical errors because they are too expensive to ignore. Your team won't have to schedule information sharing with interoperable systems manually. Automatic exchanges remove human mistakes from procedures such as appointment scheduling and medical billing.
- Pharmacies- A component of interoperability is RX transfer. By obtaining e-prescriptions from doctors and monitoring patients' medications, pharmacies can expedite their operations.
- Insurers- Interoperable systems assist in early diagnosis, which lowers the cost of adverse events for insurance companies. Additionally, insurers save money by forgoing the cost of repeated tests and other unnecessary treatments.
The financial opportunity that each business has depends on the skills that they have. To enable those capabilities, though, a fundamental core must be in place. As the market grows and the solutions that can be found and built upon it become more robust, that fundamental platform will continue to develop. Each organization will need to establish its business case to determine the benefits of interoperability in healthcare, given the specific factors and conditions that are particular to that organization. Organizations should also be aware that they can't do all of these at once—or perhaps ever—so focusing on the capabilities that will have the most significant impact is essential.
The Interoperability Future in Healthcare:
The healthcare sector is well underway with automated data sharing. The power of shared data is being eagerly tapped by providers thanks to FHIR and new HIMSS interoperability initiatives. However, significant barriers to implementation still exist. For instance, some suppliers struggle with secure data transfer, while others are unsure how to standardize interoperability. Stakeholders hope to adopt innovative, interoperable healthcare solutions soon to get around these challenges. Apart from HER, the focus is now bolstering on:
- Healthcare APIs- APIs make it simpler for healthcare providers to achieve internal and cross-organizational software interoperability. They tout faster deployment times and offer patients hassle-free access to medical records, lab results, and other information. For this reason, FHIR APIs will soon be incorporated into all healthcare platforms. They also create a uniform standard for all systems, making third-party integrations easier.
- Artificial Intelligence- AI systems can process the growing volume of patient forms, clinical notes, and health records thanks to machine learning, which is at its core. They can address most of the data handling-related healthcare interoperability difficulties in this way. Additionally, AI systems provide current insights, irrespective of the data's source.
- Blockchain- Security is crucial, especially when transferring a lot of private information. Blockchain is one method for making it more secure. This approach demonstrates the untapped potential for protecting EHR data from unauthorized parties while it is transferred across systems. Additionally, blockchain can reduce the risk of data fraud when transferring EHRs with other stakeholders or within your clinic.
Standardizing data entry will be crucial for interoperability in medical information systems in the future. All players should work to create a standard that makes it simple to extract patient data, giving organizations the most pertinent and recent information. Another step to take is to centralize this data across the healthcare industry. By 2040, every contemporary healthcare company may be forced to adopt radical interoperability, where every person's unified health information will be accessible for research and therapeutic purposes. The US government's pertinent initiatives are intended to improve coordination and management, care quality, patient safety and outcomes, patient privacy and security, staff productivity, operational effectiveness, knowledge sharing, medical research, medical error rates, healthcare costs, and overall population health. There will always be a need for new software systems to communicate with one another. Interoperability and other improvements made possible by APIs are essential for organizations that want to satisfy patient demand for access to medical records, transition to value-based care, and fully utilize analytics.
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the healthcare interoperability market will exhibit a CAGR of around 12.75% for the forecast period of 2021-2028. Growing focus on patient-centric care delivery, increased usage of electronic health record (EHR) software by healthcare providers, and favorable reimbursement scenario in matured and developed markets are the major factors attributable to the growth of the healthcare interoperability market. The healthcare interoperability market is segmented on the basis of type, software type, model type, interoperability level, deployment, application and end users. The major players covered in the healthcare interoperability market report are InterSystems Corporation, Orion Health group of companies, Allscripts Healthcare LLC, Infor., Cerner Corporation, iNTERFACEWARE Inc., NXGN Management, LLC., OSPLabs, Epic Systems Corporation., Koninklijke Philips N.V, Corepoint Health, Oracle, MuleSoft, LLC, Summit Healthcare Services, Inc. and IBM among other domestic and global players.
To know more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-healthcare-interoperability-market









