In today's interconnected world, cyber security plays a critical role in safeguarding user data online. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, protecting sensitive information has become more critical than ever. Cyber security measures are implemented to ensure user data's confidentiality, integrity, and availability, preventing unauthorized access and mitigating risks. Through robust security protocols, encryption techniques, and continuous monitoring, organizations strive to safeguard user data and maintain the trust of their customers in the digital realm.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity solutions refer to the solutions that assist organizations in detecting, monitoring, reporting and countering cyber threats to maintain data confidentiality. Safeguarding devices connected to the internet are categorized under cyber security, which help protect from various cyberspace threats.
Global Cybersecurity Market was valued at USD 217.90 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 551.18 billion by 2029, registering a CAGR of 12.30% during the forecast period of 2022-2029.
To know more, visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cybersecurity-market

Ensuring the Protection of User Data Online Through-
- Strong security measures protect user data from cybercriminals and identity theft.
- Safeguarding user data builds trust, encourages engagement, and enhances reputation
- Safeguarding user data ensures compliance with data protection regulations worldwide.
- Safeguarding user data mitigates risks and ensures business continuity.
The Intrusive Nature of Online Tracking: Impact of Cookies and ISP Monitoring on Internet Users
Browsing habits and website visits
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) can monitor and potentially compromise users' internet activity. In addition, cookies, small text files stored by browsers, can track the websites users visit. Furthermore, browser plugins can further monitor activity across various websites. This level of tracking, although used for personalization and targeted advertising, can be deemed intrusive and compromise user privacy.
Why does it Matter?
Cookies are used to personalize web browsing, including customized advertising. However, when the distinctive identifiers added to a cookie are used across various services and on different marketing platforms, such tracking can go too far. These actions are frequently regarded as intrusive.
Internet Safety Rules and What Not to Do Online
To ensure internet safety, it is essential for them to be aware of common online practices that may expose them to cyberbullying. Sharing personal information on public platforms like social media can be risky, so it is crucial to be cautious and limit what is shared to maintain professionalism and privacy.
Moreover, educating students about the dangers of downloading files from untrusted sources is essential. Clicking on unknown links can lead to malware infections and other cyberbullying threats. By following internet safety rules and avoiding risky behaviors, students can significantly reduce their vulnerability to online dangers.
Emphasizing these internet safety rules protects students and promotes their overall digital well-being. Raising awareness empowers them to make informed decisions and navigate the online world with caution, fostering safer and more secure internet interactions for themselves and others.
Additionally, network security plays a vital role in safeguarding data privacy and integrity. It provides protection against malicious practices such as data theft and unauthorized access, effectively preventing and detecting potential threats. Implementing network security measures ensures the security of data and sensitive information.
The growth of the growth of the network security market is the surge in the adoption of efficient and effective network security solutions, growing incidences of cyber-crimes and cyber threats, and rise in the number of small and medium scale enterprises, especially in the developing economies. Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the network security market will exhibit a CAGR of 12.0% for the forecast period of 2021-2028
To know more about the study, visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-network-security-market
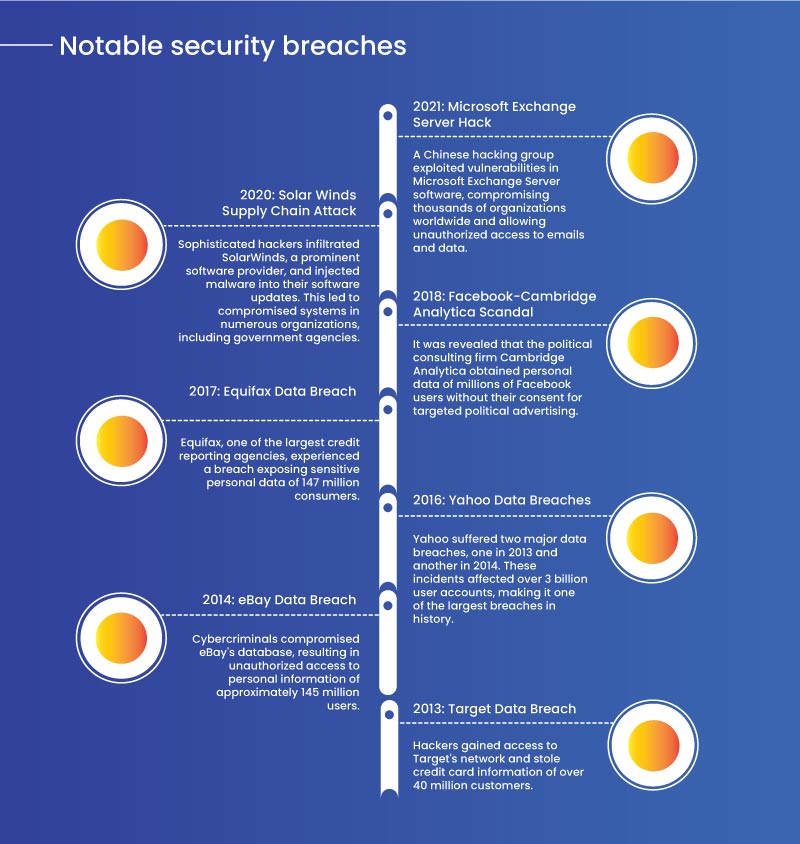
Notable Security Breaches
- 2013: Target Data Breach - Hackers gained access to Target's network and stole the credit card information of over 40 million customers.
- 2014: eBay Data Breach - Cybercriminals compromised eBay's database, resulting in unauthorized access to the personal information of approximately 145 million users.
- 2016: Yahoo Data Breaches - Yahoo suffered two major data breaches, one in 2013 and another in 2014. These incidents affected over 3 billion user accounts, making it one of the largest breaches in history.
- 2017: Equifax Data Breach - Equifax, one of the largest credit reporting agencies, experienced a breach exposing the sensitive personal data of 147 million consumers.
- 2018: Facebook-Cambridge Analytical Scandal - It was revealed that the political consulting firm Cambridge Analytical obtained the personal data of millions of Facebook users without their consent for targeted political advertising.
- 2020: Solar Winds Supply Chain Attack - Sophisticated hackers infiltrated Solar Winds, a prominent software provider, and injected malware into their software updates. This led to compromised systems in numerous organizations, including government agencies.
- 2021: Microsoft Exchange Server Hack - A Chinese hacking group exploited vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server software, compromising thousands of organizations worldwide and allowing unauthorized access to emails and data.
Data Breaches: Common Pathways to Unauthorized Access and Information Compromise
- Hacking: Hackers employ various techniques to gain unauthorized access to systems or networks. This can involve exploiting vulnerabilities in software, using malware to gain control over systems, or employing techniques like brute force attacks to crack passwords.
- Phishing: Phishing is a method where attackers trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card details. They often impersonate trusted entities through fraudulent emails, websites, or phone calls to deceive users into disclosing their data.
- Malware: Malware, including viruses, worms, ransomware, or spyware, can infect systems and compromise data security. Malware can be introduced through malicious email attachments, infected software downloads, or visiting compromised websites.
- Insider Threats: Data breaches can also occur due to insiders with authorized access who misuse or abuse their privileges. This can involve intentionally stealing or leaking sensitive data or accidentally exposing it through negligence or lack of proper security practices.
- Physical Theft or Loss: Data breaches can happen through physical theft or loss of devices such as laptops, smartphones, or storage media. If these devices contain sensitive data without proper encryption or security measures, unauthorized individuals can access the information.
- Third-Party Breaches: Organizations often share data with third-party vendors, partners, or service providers. If these entities experience a data breach, it can indirectly impact the organizations that share the data. This can happen if the third party's systems are compromised or if they mishandle or misuse the data.
- Weak Security Measures: Inadequate security practices, such as weak passwords, lack of encryption, unpatched software, or improper access controls, can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
Best Practices for User Data Protection
Strong Passwords: Creating strong and unique passwords is essential for protecting online accounts from unauthorized access. Strong passwords are complex, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information like names or birthdays. Additionally, ensure that each account has a unique password to prevent a single breach from compromising multiple accounts. Managing multiple strong passwords can be challenging, so using a password manager is highly recommended. Password managers securely store and generate passwords, eliminating the need to remember them all. This enables users to maintain strong passwords without the risk of forgetting or reusing them across multiple accounts.
Two-Factor Authentication: Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an additional layer of security for online accounts. It requires users to provide two different forms of verification to access their accounts, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if the password is compromised. Various 2FA methods exist, such as SMS codes, where a one-time code is sent to the user's registered mobile number. Authenticator apps generate time-based codes or push notifications for verification. Biometrics, like fingerprint or facial recognition, can also be used. Using 2FA, wherever available, significantly enhances account security by adding an extra step only authorized users can complete, mitigating the impact of password theft or phishing attacks.
Two-factor authentication market is expected to gain market growth in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. Data Bridge Market Research analyses the two-factor authentication market to exhibit a CAGR of 18.45% for the forecast period of 2022 to 2029.
To know more about the study, visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-two-factor-authentication-market
Phishing Awareness: Phishing attacks pose significant risks to individuals and organizations. Attackers often impersonate trusted entities through emails, messages, or websites to deceive users into revealing sensitive information such passwords or credit card details. To identify and avoid phishing attacks, be vigilant about suspicious emails, especially those requesting urgent action or containing unexpected attachments or links. Verify the legitimacy of websites by checking the URL and ensuring it uses HTTPS. Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited emails or messages. Instead, manually enter the website address in the browser. Remember, legitimate organizations will never ask for sensitive information via email. Being cautious and practicing skepticism can help mitigate the risks associated with phishing attacks.
Spear phishing market size will be valued at USD 2,416.06 million by 2028. North America leads the spear phishing market due to the presence of advanced technology and high adoption in the countries such as the U.S.
To know more about the study, visit https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-spear-phishing-market
Regular Software Updates: Keeping software, operating systems, and applications up to date is crucial for maintaining robust cybersecurity. Software updates often include critical security patches that address known vulnerabilities. Hackers constantly search for vulnerabilities to exploit, and outdated software becomes an easy target. By installing updates promptly, users ensure that their systems have the latest security measures in place, effectively mitigating the risk of cyberattacks. These updates not only fix software bugs but also patch security flaws that attackers could exploit. Regularly updating software is a proactive measure to enhance the security posture and protect against emerging threats.
Educating Users: User education and awareness are essential for maintaining strong cybersecurity practices. Many security breaches occur due to human error, such as falling victim to phishing emails or using weak passwords. Training programs and guidelines help users understand the risks, recognize common threats, and adopt secure practices. Ongoing awareness campaigns keep users informed about emerging threats and evolving best practices. By promoting user education, organizations can empower individuals to make informed decisions, identify potential security risks, and actively contribute to a secure digital environment. Ultimately, user awareness serves as a critical defense against cyber threats and reinforces the importance of cybersecurity in daily online activities.
Secure Wi-Fi Practices: Securing Wi-Fi networks is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. Start by setting a strong and unique password for your Wi-Fi router. Avoid using default or common passwords. Enable WPA2 or WPA3 encryption protocols to encrypt data transmitted over the network. This prevents eavesdropping and unauthorized interception. Also, disable remote administration, limiting access to your router's settings from outside your network. Regularly update your router's firmware to patch security vulnerabilities. By implementing these measures, you enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network and reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Data Backup and Recovery: Regular data backups and robust recovery mechanisms are crucial to effective cybersecurity. The 3-2-1 backup rule provides a simple yet effective guideline for data protection. By maintaining three copies of important data, using two different storage media (e.g., external hard drives, cloud storage), and keeping one copy off-site, users can minimize the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, ransomware attacks, or natural disasters. This approach ensures redundancy, accessibility, and resilience, allowing for swift data recovery and reducing the impact of potential data breaches or incidents. Implementing the 3-2-1 backup rule is an essential safeguard against permanent data loss and facilitates the restoration of critical information when needed.
Antivirus: Ensuring System Security and Peace of Mind
An antivirus is a software program designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software, commonly known as malware, from computer systems. When a security breach occurs, antivirus software plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact and providing several benefits:
Malware Detection: Antivirus software scans files, programs, and incoming data to identify known malware signatures and suspicious patterns. It helps detect viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and other types of malware that may have breached the system.
- Threat Prevention: Antivirus programs proactively block malware from infecting the system by recognizing and stopping potentially malicious files or activities. They often include real-time scanning, web protection, and email filtering to prevent malware from entering the system.
- Removal and Quarantine: If malware is detected, antivirus software can isolate and quarantine infected files to prevent further damage. It can also remove or neutralize the identified malware from the system, eliminating the threat and reducing potential harm.
- System Performance Optimization: Antivirus software helps optimize system performance by detecting and removing potentially unwanted programs (PUPs) and other non-malicious software that may impact system resources or slow down the system.
- Protection against Exploits: Antivirus programs often include additional security features to protect against vulnerabilities and exploits. They can detect and block exploit attempts that target software vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of an attacker gaining unauthorized access.
- Web Browsing Safety: Many antivirus solutions include web protection features that help safeguard users while browsing the internet. They can block access to malicious websites, warn against phishing attempts, and provide safe search results to prevent users from visiting compromised or harmful websites.
- Regular Updates and Threat Intelligence: Antivirus software relies on regular updates to stay effective against the ever-evolving threat landscape. Updates provide the latest malware definitions, security patches, and new detection techniques to ensure optimal protection.
- Peace of Mind: Antivirus software offers peace of mind to users, knowing that their systems are actively protected against malware threats. It creates a layer of defense that helps prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and potential loss of sensitive information.
The Future of Cybersecurity
Emerging Technologies: The future of cybersecurity will rely on emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) for threat detection and response, Quantum Computing for enhanced encryption, blockchain for secure transactions, and Biometrics for advanced authentication. These technologies will shape a more robust and proactive defense against evolving cyber threats.
Privacy Regulations: Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA have significantly impacted organizations' data protection practices. These regulations have strengthened individuals' rights over their personal data and increased accountability for organizations. Companies are now required to obtain explicit consent for data collection, provide transparent privacy policies, and implement robust security measures. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage.
Cybersecurity Workforce: Highlight the increasing demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals. Discuss the importance of attracting and training individuals to meet this workforce shortage.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability by defending computer systems, networks, and user data against unauthorized access and online threats. Compliance, risk reduction, and business continuity depend on it. Cookies and ISP monitoring that facilitate online tracking can jeopardize user privacy. Due to its intrusive nature, people should be aware of it and take precautions to protect their privacy, such as changing settings, using VPNs, and being careful when disclosing personal information. Adopting best practices improves online safety for college students. It is crucial to protect passwords with strong and unique ones, enable two-factor authentication, use caution with suspicious messages, avoid unknown links and attachments, limit public Wi-Fi usage, exercise discretion when sharing on social media, keep apps and software updated, safeguard personal information, shop securely online, and implement measures like educating users, installing security software, and more in order to improve cyber safety for college students. Utilizing cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain will be essential for cybersecurity in the future in order to automate threat detection and response, enhance anomaly detection, and improve data protection. In order to guarantee user data privacy and security, privacy laws and the need for qualified cybersecurity professionals are essential.









