Overview
The automobile sector is increasingly acknowledging the vital need for strong cybersecurity solutions to protect vehicles from cyber threats. The growth of vehicle connection and the use of Over-The-Air (OTA) updates have increased the risk of cyber-attacks on embedded systems, Electronic Control Units (ECUs), and other vehicle components. Connectivity in vehicles improves comfort and safety and can also bring risks. Cyber hackers can use connectivity to infiltrate and modify automobile systems. In the worst-case situation, this can compromise the safety of passengers and road users, leading to tragic accidents. In recent years, the automotive industry has faced an increasing number of cyber threats. Cyber hazards are increasing as software-defined vehicles, electro-mobility, autonomous driving, and a connected supply chain become more prevalent. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of having a professional cyber security strategy as a vital hygiene aspect in the automobile industry. However, the quality of design and implementation varies greatly among companies. A high degree of cyber security performance improves resilience to the growing number of cyber threats and allows for prompt identification and response to corresponding issues.
Regulations and Standards
- The UNECE World Harmonization Forum for Vehicle Regulation in Geneva identified the problem and issued the new R155 cybersecurity regulation. In 2024, R155 will apply to car registrations under national law in 56 countries, including the EU, as an extra formal instance. This only affects automobile manufacturers.
UNECE R-155 rule applies to domestic vehicle registration legislation in all countries that have signed the UNECE 1958 Agreement. OEM criteria are more abstract than those in standards. The UNECE provides additional documentation to aid in the interpretation of regulations, given the high degree of discretion involved.
OEMs must establish a CSMS, show its effectiveness, and regularly assess and maintain it as a management system. This must be verified by a technical service (TS) and certified by an authority, such as the Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt (KBA) in Germany. In UNECE countries (1958 Agreement), an electrical/electronic (E/E) architecture with specified CS features cannot be certified for homologation without valid cybersecurity management system (CSMS) certification.
Vehicle manufacturers must successfully audit their organization before homologation, which is a new and demanding process. CSMS certifications should be checked regularly and renewed every three years
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) collaborated with SAE International to create the new ISO/SAE 21434 standard for road vehicles and cybersecurity engineering. This provides a technological and methodological framework for cybersecurity engineering and management. This affects both vehicle makers and the supplier business. This standard applies to CS risk management throughout all sectors of a firm, including R&D, production, procurement, quality management, marketing, aftersales, HR, IT, risk and auditing
- In 2020, the United Nations formally accepted two new vehicle cybersecurity laws known as WP.29. These regulations address the growing cyber risk in connected automobiles. They maintain security from design to operation, detect and respond to issues, and provide secure software updates. The goal is to improve safety and industry-wide cybersecurity
Software Updation
Software upgrades overlap significantly with CS. Hackers often uncover unknown flaws in software and exploit them to launch attacks. Updates are an effective technique to address software vulnerabilities in-vehicle electronic control units (ECUs), as most allow for software reloading. This includes OTA updates transmitted to vehicles over public networks. As a result, equivalent requirements have been created at both the standardization and regulatory levels.
- UNECE R156 outlines guidelines for approving vehicle software updates and management systems
- ISO 24089: Road Vehicle Software Update Engineering
Global automotive software market is witnessing a substantial growth in recent years owing multiple factors such as rising adoption of infotainment system, increasing deployment of ECUs, rapid development of autonomous vehicle and others. According to Data Bridge Market Research analysis, the market for global automotive software market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.70% from 2022- 2029.
To learn more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-automotive-software-market
Current Cybersecurity Threats to the Automotive Industry
Figure 1: Security Vulnerabilities from Vehicle Perspective

Source: DBMR Analysis
Evidently, the automotive industry confronts significant cybersecurity threats, such as compromised safety, privacy breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Attackers use unauthorized remote access mechanisms to disrupt critical systems and obtain sensitive data, creating safety and privacy risks. Addressing these concerns has become critical for automobile stakeholders, motivated by moral and safety considerations.
- Automotive cyber security is critical to protecting vehicle users' safety and privacy in the face of increasing targeted remote-control attacks and data breaches. A significant vulnerability in Hyundai and Genesis vehicles was discovered, allowing attackers to remotely control different automotive functions such as vehicle locks, engine functions, horns, and more. Sam Curry, a security engineer at Yuga Labs, and a team of researchers discovered this issue. This automotive cyber-attack was launched with only an email address and a Python proof-of-concept script, exposing possible security flaws in modern vehicle apps and communication protocols. The problem was reported to Hyundai and later resolved as part of a coordinated vulnerability disclosure initiative
- In March 2023, Synactiv, a French cybersecurity company, accessed a Tesla Model 3's infotainment system in three minutes. Most crucially, they got access to the vehicle's infotainment and gateway systems, including the ability to replace the logo. The crew gained access to the car via an Ethernet network, allowing them to unlock the doors while it was in motion. Tesla's security team acknowledged the hack, and the company intends to provide a patch via an over-the-air update
- In April 2022, General Motors, a U.S. automaker, reported that it had been the victim of a cyber-attack, during which certain customer data was compromised and hackers were able to redeem reward points for gift cards
- In February 2022, Toyota was forced to briefly cease operations at its Japanese facilities after a suspected cyber-attack on a supplier of plastic parts and electronic components, preventing it from building approximately 13,000 cars as planned
- In 2022, cybercriminals also targeted Continental. An examination of the incident discovered that the attackers were able to obtain some data from the compromised IT systems despite existing security measures
Global automotive cyber security market is witnessing substantial growth in recent years owing to increasing technological advancements such as AI, 5g, edge computing and others in autonomous vehicle. Adding to this, the development of software-defined vehicle tends to grow the market in the forecast period. Automotive manufacturers/OEMs use software upgrades to improve functions, add personalization, address issues, increase vehicle performance, and so on. This continuous enhancement in features and performance is an appealing selling point for manufacturers. According to Data Bridge Market Research analysis, the market for global automotive cyber security market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.73% from 2023- 2030.
To learn more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-automotive-cyber-security-market
List of the Security Attacks on Automotive Systems
Figure 2: Cybersecurity Threats

Source: DBMR Analysis
- Ransomware Attacks: Hackers are increasingly utilizing ransomware attacks to extort money from their victims. Unlike other assaults that attempt to steal data, ransomware seizes entire control of computers and demands payment to release them. Meanwhile, another alarming development is the rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service. Here, cybercriminals offer their ransomware services and grab a portion of the proceeds. These attacks have the potential to damage the automotive sector by ransoming entire fleets of vehicles. As a result, it harms vehicle brands' reputations and costs consumers money. Thus, automakers must prioritize modern cybersecurity solutions to reduce these risks and minimize sales objections
- Phishing attack: It uses deceit to deceive people into disclosing login information or unwittingly performing dangerous acts, usually by masquerading legitimate bogus emails or links. They pose a significant threat to the automobile industry, as they have the potential to offer hackers unauthorized access to critical systems such as the manufacturer's infrastructure and autonomous car controls. This could result in accidents or malicious control of self-driving cars via cyber-attacks on critical connected vehicle systems. Phishing is difficult to prevent because it takes advantage of human psychology; user knowledge is still critical in combating phishing attacks. An effective security plan begins with user education on how to recognize and avoid these scams, then progresses to advanced mail filtering techniques and AI-based anomaly detection systems
- Brutal Force Attack: A Brute Force Attack is an unauthorized attempt to access a vehicle's systems by repeatedly trying different passwords or codes. For example, it can be used to unlock or start a car without authorization, resulting in theft or misuse. Automotive cyber-attacks target car network systems, posing dangers to manufacturers, dealers, and owners, and may result in firmware faults, data breaches, or theft. To avoid these possible damages, car firms must implement robust cyber security procedures
- Misuse of EV Charging Stations: Electric vehicle charging stations have long been the foundation of the expanding EV ecosystem. However, the digital infrastructure that includes EVs and charging station equipment could be vulnerable. Hackers can use these flaws to manipulate devices remotely, perpetrate fraud, exploit data, or turn off charging stations. Ensuring the security of EV charging infrastructure is critical for the long-term viability and success of sustainable mobility
Potential Entry points of Cyber risks to the enterprise
To ensure car safety, an enterprise-wide program must integrate cyber defenses across production platforms, internal operations, and supplier chains. Weaknesses in one sector can spread throughout the organization, leading to issues such as car failures and plant slowdowns, intellectual property, and theft or hacking of client data. There are some evident intruders can enter through several points, including
- 3D printing, a popular method for prototyping and additive manufacturing, utilizes digital files that are vulnerable to theft.
Global 3D printing market is witnessing substantial growth in recent years owing to rising demand towards minimization in the weight of the vehicle and development time. 3D printing enables the fabrication of complex shapes and the use of lightweight materials to meet the structural requirements of automobile parts while lowering weight. In addition, 3D printing has several benefits, including cost savings, shorter production times, and the capacity to construct complicated geometries that traditional manufacturing processes may fail to produce. Thus, as the market for electric and self-driving vehicles grows, 3D printing technology is projected to play an increasingly important role in driving innovation and developments in the automotive sector. According to Data Bridge Market Research analysis, the market for global 3D printing market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.50% from 2024-2031.
To learn more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-3d-printing-market
- Auto finance companies acquire significant amounts of client data. Data theft can cause financial loss and damage an organization's brand
- Factory machinery are designed for continuous operation and rarely requires downtime for maintenance or upgrades. Legacy technology with poor control mechanisms poses a risk to company and corporate processes, particularly when connected to the internet
- Smaller vendors, who frequently lack basic security procedures, pose a unique risk to supply chains. As IoT improves transparency and efficiency between OEMs and suppliers, supply chain risk will rise significantly
Innovative techniques to integrate cybersecurity
A Cyber Security Management System (CSMS) includes the processes, artefacts, descriptions, rules, and models to effectively secure a product from cyber threats and maintain security throughout its lifecycle. Processes must be defined, implemented, regulated, and continuously monitored for improvement. Within a certain conceptual and development context, this includes:
- TARA methodologies (ISO/SAE 21434) are used to analyze CS risk at the vehicle level, starting with a basic design of an E/E architecture
- Managing identified CS risks through avoidance, reduction, transfer, and acceptance and implementing iterative adjustments to initial E/E designs as needed
- Define CS goals and associated requirements, including functional safety (FuSa). Close coordination is needed with stakeholders for functional development, FuSa, and CS
- Iteratively assessing and adapting TARA during development
- Determining product-specific CS support requirements, including termination and end-of-life policies
- Sign a cybersecurity interface agreement (CIA) with vendors and service providers, clearly defining and assigning responsibilities using the RASIC project management tool
- Monitor CS-relevant information before and during development to incorporate new findings using change management techniques
- Implemented a verification and validation (V&V) strategy, including CS protections (vulnerability scanning, fuzzing, and penetration testing)
- Conduct final checks on CS activities to ensure effectiveness, completeness, correctness, and consistency before production
Best Practices of Automotive Cybersecurity
As a first step, developing an incident response strategy is critical for planning for any potential security breaches that may affect the automotive ecosystem. It ensures that you have a well-defined plan of action in place, allowing you to respond quickly and effectively to any potential crises. After establishing it, it is advised that you follow the best practices outlined below to safeguard your vehicles against cyber threats.
Figure 3: Automotive Cyber Security Principles for Protecting Vehicles from Hackers

Source: DBMR Analysis
- Regular Risk Assessment and Secure Coding Practices: Regular risk assessments are an important proactive step that includes detecting potential hazards, analyzing the scope and impact of vulnerabilities, and implementing suitable risk mitigation measures. Furthermore, implementing secure coding techniques, such as following industry-standard coding principles, is critical. Using tight review methods to uncover potential vulnerabilities and safe development frameworks might help reduce coding flaws
- Continuous Software Updation and Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Issuing software updates guarantees that potential vulnerabilities are corrected as soon as possible, reduces the danger of hackers exploiting the system, and improves overall security. Furthermore, strong authentication procedures, such as biometric identity and multi-factor authentication, prohibit unauthorized access to vehicle systems, as do other modern encryption techniques that safeguard critical data from cyber-attacks
- Enhancing Industry Expertise and Implementing Best Practices: Automakers should invest in cybersecurity training to continuously monitor and defend connected and autonomous vehicles. It is also suggested to adhere to automotive cybersecurity best practices established by independent bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the International Standardization Organization (ISO), and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). These methods priorities secure design, development, and post-production security measures
- Collaboration between Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Vendors: Collaboration with security vendors enables strong frameworks, knowledge, and platforms, ensuring the security of automotive systems throughout the value chain. Establishing explicit security standards and monitoring compliance contributes to the long-term resilience of vehicle systems. Furthermore, intrusion detection systems help spot suspicious activity or attempted intrusions in real time by proactively monitoring vehicle network traffic, thereby preventing automotive cyberattacks before they cause major damage
- Compliance with Regulations and Utilizing Guidelines and Standards: Automotive companies should follow automotive cybersecurity rules such as the Federal Trade Commission's (FTC) Safeguards Rule. These requirements ensure that car companies maintain safeguards to secure client information. To secure connected vehicles from cyber-attacks throughout their lifecycle, the industry should use cybersecurity engineering standards such as ISO/SAE
Figure 4: Implementation of Cybersecurity: Automotive Industry vs. IT Industry
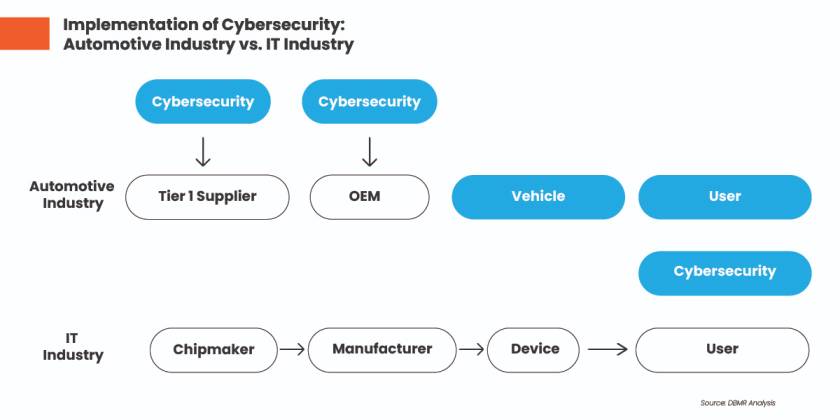
Source: DBMR Analysis
- Prioritizing cybersecurity across the lifecycle: Cybersecurity should be a top priority throughout the automotive systems development process. It should be included in all phases of system design, software development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Integrating cybersecurity across the lifecycle reduces risks, improves resilience, and identifies the optimal security measures for mission-critical scenarios
- Emerging Technologies Utilization and Training of Employees: The sector can use emerging technologies, namely blockchain, to assist protect against cybersecurity threats. For example, blockchain technology enables safe transactions inside the automobile ecosystem, which often includes numerous unique businesses. Employee training can also raise digital security awareness, ensuring that staff and stakeholders understand the importance of automotive cyber security and are well-prepared to avoid cyber threats
Thus, by using these techniques, automotive firms may build systematic and robust cyber defense frameworks that secure both their vehicle offers and passengers in our digital-native ecosystem.
Potential Solutions for Security by Design
Defining many tiers of protection prevents attackers from compromising the system. The vehicle is the topmost level, followed by domains, systems, and components that can be isolated using bus systems, firewalls, and segmented buses. The protective methods are consistent across all tiers, however the implementation method varies.
Figure 5: Levels of Protection or Isolation
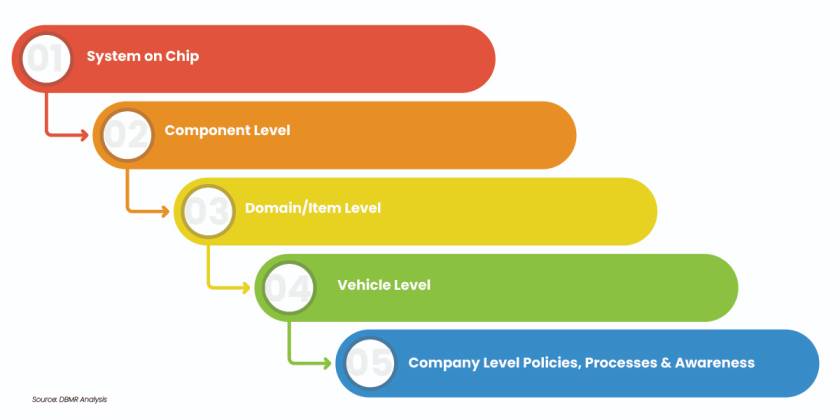
Source: DBMR Analysis
- General Vehicle Security
- Functions are securely released: Activating or releasing car functions based on driving scenarios
- Securing data recording (logging): Ensure accurate and tamper-proof tracking of internal procedures for forensic analysis and documentation reasons
- Intruder detection: Detecting process irregularities resulting from attacks or manipulation
- Encryptions: Protection of confidentiality
- Provides protection against installing compromised or outdated software and unauthorized changes to permissions
- Secure Diagnostics
- Authentication of the on-board diagnostics (OBD) access device through the OEM backend
- Authorization approvals through the OEM backend
- Diagnostic firewall, limiting diagnostic tasks to specific vehicle states
- Public key infrastructure
- Network Security, both on and off board
- Authentication, integrity checks, and real-time message encryption (SecOC or IPse) for CAN, FlexRay, and automotive Ethernet
- End-to-end security: Critical functions adhere to the notion of end-to-end communication. Reciprocal checks are conducted at both transmission and reception points to ensure integrity and authenticity. This comprises both on-board and off-board communication between the vehicle and the OEM backend, such as TLS and VLAN
- ECU Security
- Authenticated Access: Access to external devices for diagnostics or programming requires approval from the OEM backend. Ensure data integrity during transmission.
- Ensure secure booting by utilizing only OEM-released software
- ECU operating modes: ECU must have many modes throughout their life cycle and allow for secure mode switching (via authentication).
- Key and certificate management: Keys and certificates provide a foundation for authentication and encryption, ensuring confidentiality.
- Software integrity tests: Verifies the authenticity of software and configurations
- Enhancements to CS operating systems and crypto/HSMs, including safe key storage, crypto algorithm support, and 'hardened' operating systems.
- Hypervisor protection: Isolated sandboxes for unknown internet apps (such as telematics and entertainment control units)
Conclusion
The automobile business is rapidly evolving as vehicles become more digitally advanced. Carmakers are addressing customer expectations for assistance systems, self-driving vehicles, smartphone integration, and wireless communication (V2X and V2V) in order to maintain or grow market share. Customers value ease and security, but as these functions expand and become more complicated, the industry must devote more time and effort in protecting them.
The automobile industry is facing huge problems as linked cars become the standard and fully autonomous vehicles hit the mainstream later this decade. While these technologies are projected to alter the business, they also pose increased cyber dangers that could harm a company's brand and financial future. To reduce risks, companies must create a cybersecurity culture that identifies and combats threats within their organization and supply chain.
Cloud-based services offer real-time updates that aggregate information to keep up with evolving threat actors and vectors. Investing in cutting-edge tools and technologies can help lessen the impact of an infiltration.