Introduction
The semiconductor industry is a linchpin of modern technological advancement, driving innovation across multiple sectors including electronics, automotive, telecommunications, healthcare, and more. The demand for semiconductors is increasing rapidly due to the proliferation of connected devices, the advancements in artificial intelligence, expansion of 5G networks, and growing significance of the Internet of Things (IoT). In this dynamic environment, semiconductor manufacturers are seeking partners capable of providing robust global supply chain solutions that deliver added value, flexibility, security, and cost-efficiency while maximizing returns on investment (ROI).
The Evolving Semiconductor Landscape
Market Dynamics
The semiconductor market is influenced by several key dynamics:
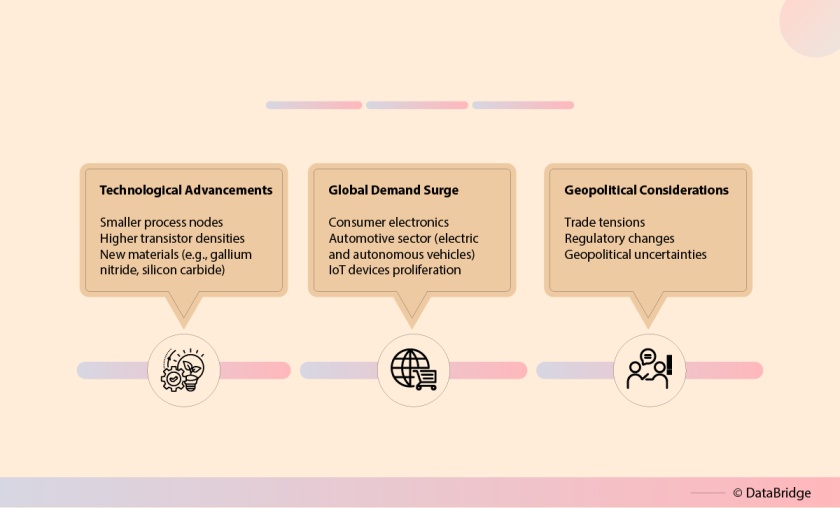
- Technological Innovations: The relentless pace of technological advancements is a hallmark of the semiconductor industry. Innovations such as smaller process nodes, higher transistor densities, and new materials (e.g., gallium nitride and silicon carbide) are pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency.
- Global Demand Surge: The exponential growth of consumer electronics, the automotive sector's shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles, and the widespread adoption of IoT devices have fueled unprecedented demand for semiconductors.
- Geopolitical Considerations: Trade tensions, regulatory changes, and geopolitical uncertainties have profound impacts on the global semiconductor supply chain, necessitating adaptive and resilient strategies.
Fig 1: Key Dynamics Influencing the Semiconductor Market
Challenges
Despite the opportunities, the semiconductor industry faces several challenges:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, pandemics, and other unforeseen events can cause significant disruptions in the supply chain, affecting production and delivery timelines.
- Rising Costs: The increasing costs of raw materials, energy, and labor are putting pressure on manufacturers to find cost-efficient solutions without compromising on quality.
- Complex Supply Networks: The complexity of supply networks, involving multiple tiers of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors across different regions, poses logistical and coordination challenges.
The Need for Comprehensive Supply Chain Solutions
To address these challenges and harness market opportunities, semiconductor manufacturers require comprehensive global supply chain solutions. These solutions must provide:
- Added Value
- Flexibility
- Security
- Cost-Efficiency
- Maximized ROI
Added Value: Enhancing the Customer Experience
Integrated Services
Integrated supply chain services ensure a seamless experience from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Key components include:
- End-to-End Visibility: Real-time tracking and monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain ensure transparency and timely interventions. Technologies such as IoT and blockchain play crucial roles in providing this visibility.
- Collaborative Platforms: Digital platforms that enable collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and customers enhance communication and coordination, leading to more efficient and responsive supply chains.
Customization and Innovation
Providing customized solutions tailored to specific customer needs and fostering innovation significantly enhances value. This involves:
- Tailored Solutions: Developing bespoke supply chain strategies that align with individual customer requirements and market demands ensures that solutions are not only effective but also adaptable to specific contexts.
- Innovation Hubs: Establishing innovation hubs to co-create solutions with customers fosters a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement, driving mutual growth and competitive advantage.
Flexibility: Adapting to Market Changes
Agile Supply Chains
Agility in supply chains is essential for responding to market fluctuations and disruptions. Key strategies include:
- Modular Supply Chains: Designing supply chains that can be quickly reconfigured to address changing market conditions and demands ensures that manufacturers can remain responsive and competitive.
- Flexible Manufacturing: Implementing flexible manufacturing processes that can adapt to different production requirements and volumes allows manufacturers to scale production up or down based on the market needs.
Scalable Solutions
Scalable supply chain solutions enable manufacturers to adjust their operations based on demand. This involves:
- Dynamic Inventory Management: Utilizing advanced analytics to optimize inventory levels and reduce excess stock ensures that resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
- Capacity Planning: Implementing robust capacity planning tools to align production capabilities with market demands helps prevent bottlenecks and ensures the timely delivery of products.
Security: Ensuring Resilience and Reliability
Risk Management
Effective risk management strategies are crucial for maintaining supply chain security. Key components include:
- Risk Assessment: Conducting comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and develop mitigation strategies ensures that risks are managed proactively.
- Contingency Planning: Establishing contingency plans to address potential disruptions, such as alternative sourcing and logistics options, ensures that the supply chain remains resilient and enduring against the challenges..
Cybersecurity
With the increasing digitization of supply chains, cybersecurity has become a critical aspect of supply chain security. This involves:
- Cybersecurity Protocols: Implementing stringent cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and intellectual property from cyber threats is essential for maintaining the integrity of the supply chain.
- Threat Monitoring: Continuous monitoring for cyber threats and implementing proactive measures to mitigate risks ensures that potential vulnerabilities are addressed before they can be exploited and cause hazards.
Cost-Efficiency: Reducing Expenses and Improving Margins
Lean Supply Chains
Lean supply chain practices focus on minimizing waste and optimizing resources. Key strategies include:
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: Implementing JIT inventory practices to reduce carrying costs and minimize excess stock ensures that resources are used efficiently and costs are kept under control.
- Process Optimization: Streamlining processes to eliminate inefficiencies and reduce operational costs helps improve overall cost-efficiency.
Strategic Sourcing
Strategic sourcing involves selecting suppliers based on their ability to deliver value and cost-efficiency. This includes:
- Supplier Collaboration: Building strong relationships with key suppliers to negotiate favorable terms and ensure reliable supply helps reduce costs and improve supply chain reliability.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including acquisition, operation, and disposal costs, ensures that sourcing decisions are made based on a comprehensive understanding of the costs.
Maximized ROI: Delivering Financial Returns
Performance Metrics
Implementing performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure supply chain effectiveness and ROI is essential. Key metrics include:
- Delivery Performance: Measuring on-time delivery rates and order fulfillment accuracy helps ensure that customers receive their products as expected, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost Savings: Tracking cost savings achieved through supply chain optimization efforts helps demonstrate the financial benefits of supply chain improvements.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement initiatives drive long-term value and ROI. This involves:
- Kaizen Practices: Adopting Kaizen practices to foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation ensures that the supply chain remains competitive and responsive to changing market conditions.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing feedback loops with customers and suppliers to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions ensures that the supply chain is constantly evolving and improving.
Case Studies: Successful Supply Chain Solutions
Case Study 1: Company A
Company A, a leading semiconductor manufacturer, partnered with a supply chain solutions provider to enhance its global supply chain. Key outcomes included:
- Increased Visibility: Implementation of a digital supply chain platform provided real-time visibility and improved decision-making.
- Reduced Costs: Lean supply chain practices and strategic sourcing initiatives led to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Security: Robust risk management and cybersecurity measures ensured supply chain resilience and data protection.
Case Study 2: Company B
Company B, another major player in the semiconductor industry, leveraged a comprehensive supply chain solution to achieve the following:
- Agility and Flexibility: Modular supply chains and flexible manufacturing processes enabled rapid response to market changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customized solutions and innovation hubs fostered strong customer relationships and drove growth.
- Maximized ROI: Performance metrics and continuous improvement initiatives delivered substantial financial returns.
Future Trends and Innovations
Digital Transformation
The digital transformation of supply chains is set to revolutionize the semiconductor industry. Key trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered analytics and predictive modeling to optimize supply chain operations and enhance decision-making.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology to ensure transparency, traceability, and security in the supply chain.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices for real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, enhancing visibility and efficiency.
Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a key focus for semiconductor manufacturers. Future supply chain solutions will prioritize:
- Green Supply Chains: Implementing environmentally friendly practices to reduce carbon footprint and promote sustainability.
- Circular Economy: Adopting circular economy principles to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
Comprehensive Supply Chain Solutions in Practice
Building a Resilient Supply Chain Network
A resilient supply chain network is vital for semiconductor manufacturers to withstand disruptions and maintain continuity. This involves:
- Diverse Supplier Base: Developing a diverse supplier base to mitigate risks associated with supplier dependency and ensure continuous supply.
- Geographic Diversification: Diversifying supply chain operations across multiple regions to reduce the impact of localized disruptions.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
Advanced technologies are transforming supply chain operations, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. Key technologies include:
- Automation: Implementing automation in manufacturing and logistics processes to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
- Big Data Analytics: Utilizing big data analytics to gain insights into supply chain performance and identify opportunities for optimization.
Enhancing Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration and communication among supply chain stakeholders are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. This involves:
- Integrated Communication Platforms: Implementing integrated communication platforms to facilitate seamless interaction and information sharing among stakeholders.
- Collaborative Planning: Engaging in collaborative planning with suppliers and customers to align supply chain strategies and achieve mutual goals.
Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Management
Supplier Selection and Evaluation
Selecting the right suppliers and continuously evaluating their performance is critical for maintaining a reliable and cost-efficient supply chain. Key practices include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular supplier audits to assess compliance with quality standards, sustainability practices, and ethical guidelines.
- Performance Metrics: Establishing performance metrics to evaluate supplier reliability, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Long-Term Partnerships
Building long-term partnerships with key suppliers fosters collaboration and drives mutual growth. This involves:
- Strategic Alliances: Forming strategic alliances with suppliers to enhance innovation, share risks, and achieve cost savings.
- Joint Development Programs: Engaging in joint development programs to co-create new technologies and solutions, driving competitive advantage.
Addressing Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical Risk Assessment
Assessing geopolitical risks and developing strategies to mitigate their impact is essential for maintaining supply chain stability. This involves:
- Scenario Planning: Engaging in scenario planning to anticipate potential geopolitical developments and prepare contingency plans.
- Diversification: Diversifying supply chain operations and sourcing strategies to reduce dependency on specific regions or suppliers.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with international regulations and standards is crucial for avoiding legal and operational challenges. This involves:
- Regulatory Monitoring: Continuously monitoring regulatory changes and assessing their impact on supply chain operations.
- Compliance Programs: Implementing comprehensive compliance programs to ensure adherence to relevant laws and standards.
Implementing Sustainability Practices
Sustainable Sourcing
Sustainable sourcing practices are increasingly important for semiconductor manufacturers. This involves:
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that raw materials are sourced ethically,while respecting the human rights and environmental sustainability.
- Green Procurement: Prioritizing suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices and offer sustainable products.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Reducing the carbon footprint of supply chain operations is a key sustainability goal. This involves:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices to reduce energy consumption in manufacturing and logistics.
- Renewable Energy: Increasing the use of renewable energy sources in supply chain operations to minimize environmental impact.
The Role of Innovation in Supply Chain Solutions
Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Creating a culture of innovation within supply chain operations drives continuous improvement and competitive advantage. This involves:
- Innovation Labs: Establishing innovation labs to experiment with new technologies and processes.
- Employee Empowerment: Empowering employees to contribute ideas and engage in innovative projects.
Adopting Emerging Technologies
Adopting emerging technologies is crucial for staying ahead in the competitive semiconductor market. Key technologies include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leveraging AI and machine learning to optimize supply chain operations and enhance decision-making.
- Blockchain Technology: Implementing blockchain technology to ensure transparency, traceability, and security in the supply chain.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Supply Chain Performance Metrics
Implementing KPIs to measure supply chain performance and drive improvement is essential. Key metrics include:
- On-Time Delivery: Tracking the percentage of orders delivered on time to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Turnover: Measuring inventory turnover rates to assess the efficiency of inventory management practices.
Financial Metrics
Financial metrics help measure the ROI of supply chain solutions and demonstrate their value. Key metrics include:
- Cost Savings: Tracking cost savings achieved through supply chain optimization efforts.
- Revenue Growth: Measuring revenue growth resulting from improved supply chain performance and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, the need for comprehensive global supply chain solutions has never been more critical. By offering added value, flexibility, security, and cost-efficiency, these solutions enable semiconductor manufacturers to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and maximize returns on investment. Through strategic partnerships, innovative practices, and continuous improvement, the future of semiconductor supply chains promises to be resilient, efficient, and sustainable.